AT4
| AT4 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Disposable anti-tank launcher |
| Place of origin | Sweden United States |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1987–present |
| Used by | See Operators |
| Wars | See Wars |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Förenade Fabriksverken |
| Manufacturer |
|
| Unit cost | US$1,480[1] |
| No. built | 600,000+[2] |
| Variants | See Variants |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 6.7 kg (14.8 lb) (AT4)[3] 8 kg (18 lb) (AT4-CS) |
| Length | 102 cm (40 in)[3] |
| Caliber | 84 mm |
| Muzzle velocity | 290 m/s (950 ft/s; 1,000 km/h), 220 m/s (720 ft/s; 790 km/h) (CS)[4] |
| Effective firing range | 300 m (point target)[3] |
| Maximum firing range | 500 m (area target) 2,100 m (maximum) |
| Sights | Iron sights, optional AN/PVS-4 night vision unit |
| Filling | Octol |
| Filling weight | 440 g high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) round |
| External images | |
|---|---|
| Prototype AT4 Sweden tested 1981/82 | |
The AT4[a] is a Swedish 84 mm (3.31 in) unguided, man-portable, disposable, shoulder-fired recoilless anti-tank weapon manufactured by Saab Bofors Dynamics (formerly: FFV Ordance, later, Bofors Anti-Armour Systems).[5][unreliable source?] The AT4 is not a rocket launcher strictly speaking, because the explosive warhead is not propelled by a rocket motor. Rather, it is a smooth-bore recoilless gun (as opposed to a recoilless rifle, which has a rifled barrel).[6] Saab has had considerable sales success with the AT4, making it one of the most common light anti-tank weapons in the world.[7][8] The M136 AT4 and M136A1 AT4CS-RS are the variants used by the United States Army.[9]
The name AT4 is a word play on the 84 mm caliber of the weapon, (84) 'eighty four' being a homophone of 'A-T-4'.[10] The name also doubles as an alpha-phonetic word play on the weapon's role, due to "AT" being a common military abbreviation for "anti-tank".[11] The name was created for export purposes as the nickname "eighty-four" was already a common English nickname for the Carl Gustaf 8.4 cm recoilless rifle after its caliber.[10]
The AT4 is intended to give infantry units a means to destroy or disable armoured fighting vehicles and fortifications, although it is generally ineffective against more modern main battle tanks (MBTs), especially those with reactive armour, unless weaker sections of armour are exploited. The launcher and projectile are manufactured prepacked and issued as one unit of ammunition, with the launcher discarded after one use.
Development
[edit]The AT4 is a development of the 74-mm Pansarskott m/68[12] (Miniman) adopted by the Swedish Army in the late 1960s. Like the m/68, the AT4 was designed by Försvarets Fabriksverk (FFV) and manufactured at their facility at Zakrisdal, Karlstad, Sweden.[5] FFV began research on a replacement for the m/68 in 1976, deliberately designing an individual anti-armour weapon that would not be able to defeat the heavy armour protection of MBTs (main battle tanks) in frontal engagements, believing that to be counterproductive. The AT4 was designed as a weapon to engage medium-to-light armoured vehicles from any direction or MBTs from the sides or rear, and as an assault weapon effective against buildings and fortifications. FFV's prime design goal was a weapon that was simple to use, rugged, and far more accurate against moving targets than previous individual antiarmour weapons. Another key requirement was that the AT4 not only be able to penetrate armour, but also exhibit devastating beyond-armour effect after penetration. FFV and the Swedish Army began the first evaluation firings of the prototype AT4s in the spring of 1981, with 100 tested by early 1982.[13]
Even before the AT4 had been adopted by Sweden, it was entered into a United States Army competition for a new anti-tank weapon mandated by Congress in 1982 when the FGR-17 Viper failed as a replacement for the M72 LAW. Six weapons were tested in 1983 by the US Army: the British LAW 80, the German Armbrust, the French APILAS, the Norwegian M72E4 (an upgraded M72 LAW), the US Viper (for baseline comparison purposes) and the Swedish AT4. The US Army reported to Congress in November 1983 that the FFV AT4 came the closest to meeting all the major requirements established to replace the M72 LAW,[14] with the Armbrust coming in second.[15]
Though very impressed with the simplicity and durability of the tested version of the AT4, the US Army saw some room for improvement, specifically the addition of rear and front bumpers on the launch tube and changes to the sights and slings. After these changes, the AT4 was adopted by the US Army as the Lightweight Multipurpose Weapon M136.[16] The Swedish Army also recognized these improvements and subsequently adopted the Americanized version of the AT4 as the Pansarskott m/86 (Pskott m/86), with the addition of a forward folding hand grip to help steady the AT4 when being aimed and fired. The forward folding grip is the only difference between the AT4 adopted by Sweden and the US Army version.

Due to the urban combat conditions that US military forces faced regularly during the Iraq War, the US Army Close Combat Systems manager in charge of purchases of the AT4 suspended orders for the standard version of the AT4; US military forces instead only ordered the AT4 CS (Confined Space) version.[17]
Operation
[edit]
The AT4 may be considered a disposable, low-cost alternative to a Carl Gustaf 8.4 cm recoilless rifle. The AT4 took many of its design features from the Carl Gustaf, which operates on the principle of a recoilless weapon, where the forward inertia of the projectile is balanced by the inertia of propellant gases ejecting from the rear of the barrel. But unlike the Carl Gustaf, which uses a heavier and more expensive steel tube with rifling,[18] the disposable AT4 design greatly reduces manufacturing costs by using a reinforced smoothbore fiberglass outer tube. Being a disposable gun also allows for lighter and cheaper construction. In a single-use disposable gun, the barrel only needs to be able to contain a single pressure spike when firing, when it can be disposed of, even if it is ruined, burnt-out and strained, unlike traditional guns which are required to survive many pressure spikes without failure and thus need to be strongly overbuilt and made of heat-proof materials. Pressures are also kept quite low compared to many traditional guns. This lightweight and thin barrel and low pressure, combined with the almost complete lack of recoil, means that relatively large projectiles (comparable to those found in mortars and artillery systems) can be utilised, which would otherwise be impossible in a man-portable weapon.
In the system originally developed by FFV for the Carl Gustaf, a plastic blowout plug is placed at the centre rear of the shell casing containing the projectile and propellant, which itself is enclosed in the AT4 outer tube. When the gases build up to the correct pressure level, the blowout plug disintegrates, allowing the proper amount of gases to be vented to the rear, balancing the propellant gases pushing the projectile forward.
The AT4 adopted a unique method developed earlier by FFV: the spring-loaded firing rod is located down the side of the outer tube, with the firing pin at the rear of the tube. When released, the firing pin strikes a primer located in the side of the casing's rim.
The disadvantage of the recoilless design is that it creates a large back blast area behind the weapon, which can cause severe burns and overpressure injuries to friendly personnel in the vicinity of the user and sometimes even to the users themselves, especially in confined spaces. The back blast may also reveal the user's position to the enemy. The problem of back blast was solved with the AT4-CS (Confined Space) version, specially designed for urban warfare. This version uses a saltwater countermass in the rear of the launcher to absorb the back blast; the resulting spray captures and dramatically slows down the pressure wave, allowing troops to fire from enclosed areas. The AT4-CS version also reduced its muzzle velocity from the original 290 m/s to 220 m/s as part of its effort to be user-safe in a confined space, making the AT4-CS version more difficult to use as the drop is more pronounced. The effectiveness of the HEAT warhead is not dependent on speed.[19]
-
M136 AT4
-
M136A1 AT4CS-RS
To fire, the gunner first removes the safety pin located at the rear of the tube, which unblocks the firing rod. They then take a firing position, ensuring that no one is present in the back blast area. If firing from the prone position, they must also place their legs well to the side to avoid burning himself. Then, the gunner moves back the front and rear sight covers, allowing the sights to pop up into their firing positions. The AT4 has iron sights that were originally developed for the cancelled Viper, and are similar in concept and use to those on assault rifles.[20] They then remove the first of two safeties by moving the firing rod cocking lever (located on the left side) forward and then over the top to the right side. The gunner takes aim, while at the same time holding down the red safety lever located in front of the cocking lever, and then fires by pressing forward the red firing button with his right thumb. Both the red safety lever and the firing button must be pressed down at the same time to fire the AT4. The red firing button has a similar resistance to the trigger pull of a rifle, so the gunner does not have to jab at the firing button, which could throw their aim off.

After firing, the AT4 is discarded. Gunners are often trained to break off the sights after use, in order to prevent other soldiers from mistaking used launchers for unused ones. Unlike the heavier Carl Gustaf, the AT4 outer tube is built to take the stress of just one firing; it is not reusable and cannot be reloaded.
The AT4 can mount an optical night sight on a removable fixture. In US military use, the launcher can be fitted with the AN/PAQ-4C, AN/PEQ-2, or the AN/PAS-13 night sights.
The AT4 requires little training and is quite simple to use, making it suitable for general issue. However, as the cost of each launcher makes regular live-fire training very expensive, practice versions exist that are identical in operation but fire reloadable 9×19mm or 20mm tracer ammunition. Both practice cartridges are unique to their respective weapons, with their trajectory matched to that of the live round. The 20mm version also has a recoilless weapon effect with the same high noise and back blast as the AT4 firing and is favoured by the Swedish army because of the added realism of the back blast as compared to the "plonk" sound of the 9mm round (similar to the sound of a finger tapping on an empty can).
Specifications
[edit]- Time of flight (to 250 metres (820 ft)): less than 1 second[citation needed]
- Operating temperature: −40–60 °C (−40–140 °F)[citation needed]
- Ammunition: fin-stabilized projectile with HEAT warhead[citation needed]
Projectiles
[edit]There are several different projectiles for the AT4. Because it is a one-shot weapon, projectiles are preloaded into the launcher tubes.[5]
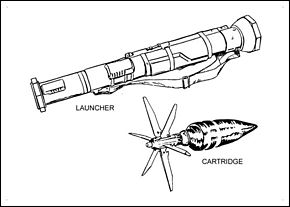
High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) – Can penetrate up to 45 centimetres (18 in) of rolled homogeneous armour (RHA) with beyond-armour effect.[21]
High-explosive dual purpose (HEDP) 502[5][22] – For use against bunkers, buildings, enemy personnel in the open, and light armour. It can be set to detonate on impact or with a brief detonation delay. The heavier nose cap allows either to penetrate light walls or windows before exploding, or to be "skipped" off the ground for an air burst. For use against light armour, there is a smaller-cone HEAT warhead with 15 centimetres (5.9 in) penetration of RHA.
High penetration (HP) – Extra high penetration ability, up to 42–60 centimetres (17–24 in) of RHA.[23]
Anti-structure tandem-warheads (AST) – Designed for urban warfare where a projectile heavier than the HEDP AT4 is needed. This combines a shallow-coned HEAT warhead (resulting in low penetration but producing a wide hole) with a tandem-charge and a follow-through high-blast warhead. It has two settings: either to destroy bunkers or to mouse-hole a building wall for combat entry.[24]
Extended range (ER) – Anti-armor version with HEAT warhead. Range is extended from 300 to 600 metres (980 to 1,970 ft), with increased penetration up to 46 centimetres (18 in) of RHA. These major improvements add only about 2 kilograms of mass, despite being CS models.[25][23]
High explosive (HE) – High explosive anti-personnel weapon that can be set for impact or air-burst detonation, with an effective range up to 1,000 metres (3,300 ft).[25]
Variants
[edit]M136 AT4 – American version with modified launch tube bumpers, sights, and slings.[26]
M136A1 AT4CS-RS – American variant with a unique bi-metal warhead design, specially developed to maximize behind-armor effects for higher kill probability. The weapon is capable of firing from confined spaces (CS) and features a reduced sensitivity (RS) explosive, with an armor penetration of over 350 mm. Its effective range is 20–300 m.[27][28][9]
XM919 Individual Assault Weapon (also known as AT4CS TW) – American future variant, to enter service in 2025, and be delivered by 2029 for USD $500 million.[29]
Bunker-busting (AT8) – An AT4 version where the standard HEAT projectile is replaced with the bunker-busting warhead developed for the Mk 153 Shoulder-Launched Multipurpose Assault Weapon (SMAW). No orders were ever placed.[30]
AT12-T – In the early 1990s, there were tests of a tandem charge 120 mm version (Bofors AT 12-T). The 14 kg weapon had a claimed penetration of 90 centimetres (35 in) RHA,[31] and in 1994 was demonstrated to defeat two NATO Single Heavy targets inclined at 68 degrees from vertical with ERA,[32] for a line-of-sight penetration of 600 mm. However, the project was cancelled due to the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the subsequent cuts in Western defence budgets.[citation needed]
Operators
[edit]

 Argentina: Argentine Army[33] and Argentine Marines[34]
Argentina: Argentine Army[33] and Argentine Marines[34] Bosnia and Herzegovina[5]
Bosnia and Herzegovina[5] Brazil[35]
Brazil[35] Canada: JTF2[5]
Canada: JTF2[5] Chile: Chilean Marine Corps, Chilean Army[5]
Chile: Chilean Marine Corps, Chilean Army[5] Colombia[5]
Colombia[5] Croatia[35]
Croatia[35] Denmark: Designated PVV M/95 (Panserværnsvåben Model 1995).[36]: 93
Denmark: Designated PVV M/95 (Panserværnsvåben Model 1995).[36]: 93  Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Finland
Finland France: Designated ABL (Anti Blindé Lourd) by the French Army.[37]
France: Designated ABL (Anti Blindé Lourd) by the French Army.[37] Georgia[35]
Georgia[35] Greece: Used by Hellenic Navy Seals[5]
Greece: Used by Hellenic Navy Seals[5] India[38]
India[38] Indonesia[39]
Indonesia[39] Iraq: The Iraqi Army was supplied with the AT4.[40][41]
Iraq: The Iraqi Army was supplied with the AT4.[40][41] Israel: Locally produced licensed AT4 CS AST
Israel: Locally produced licensed AT4 CS AST Kurdistan: The Peshmerga Have Between 1,000-15,000 AT-4s.[42]
Kurdistan: The Peshmerga Have Between 1,000-15,000 AT-4s.[42] Ireland: Called the SRAAW (Short Range Anti Armour Weapon) by the Irish Defence Forces.[36]: 139
Ireland: Called the SRAAW (Short Range Anti Armour Weapon) by the Irish Defence Forces.[36]: 139  Jaysh al-Islam (Captured from the Syrian Democratic Forces)[43]
Jaysh al-Islam (Captured from the Syrian Democratic Forces)[43] Kurdistan Workers' Party[44][45]
Kurdistan Workers' Party[44][45] Latvia[46]
Latvia[46] Lebanon: Roughly 1,000 pieces purchased.[47]
Lebanon: Roughly 1,000 pieces purchased.[47] Lithuania: Lithuanian Armed Forces[48]
Lithuania: Lithuanian Armed Forces[48] Malaysia: In service with the Grup Gerak Khas[5]
Malaysia: In service with the Grup Gerak Khas[5] Mexico
Mexico
 Netherlands[50] (Replaced by Pzf-3)
Netherlands[50] (Replaced by Pzf-3) Poland (limited use in Special Operations Forces and Air Mobile Forces)[51]
Poland (limited use in Special Operations Forces and Air Mobile Forces)[51] Sweden: Designated Pansarskott m/86.[35]
Sweden: Designated Pansarskott m/86.[35] Syrian Democratic Forces
Syrian Democratic Forces Taiwan (Republic of China)[5]
Taiwan (Republic of China)[5] United Kingdom: Small quantities of AT4 and HP projectiles purchased.[2][5]
United Kingdom: Small quantities of AT4 and HP projectiles purchased.[2][5] Ukraine: 15,000 supplied by Sweden,[52][53] 6,000 supplied by the United States,[54] both in 2022.
Ukraine: 15,000 supplied by Sweden,[52][53] 6,000 supplied by the United States,[54] both in 2022. United States: Designated M136 AT4 in USMC and United States Army service, beginning in early 1987.[55] The AT4 was used in the US invasion of Panama, the War in Afghanistan, the Persian Gulf War, and the Iraq War.[56] Over 300,000 have been built locally, under license by ATK.[2][5]
United States: Designated M136 AT4 in USMC and United States Army service, beginning in early 1987.[55] The AT4 was used in the US invasion of Panama, the War in Afghanistan, the Persian Gulf War, and the Iraq War.[56] Over 300,000 have been built locally, under license by ATK.[2][5] Venezuela: The AT4 has been in the Venezuelan arsenal since the 1980s.[35][57] In 2009, it was reported that AT4s sold to Venezuela had been captured from FARC insurgents in Colombia, leading Colombia to accuse Venezuela of selling the weapons to the insurgents, and Venezuela reporting that they were stolen by a rebel attack on a Venezuelan position in 1995,[58] thus heightening tensions between the two countries.[57][59]
Venezuela: The AT4 has been in the Venezuelan arsenal since the 1980s.[35][57] In 2009, it was reported that AT4s sold to Venezuela had been captured from FARC insurgents in Colombia, leading Colombia to accuse Venezuela of selling the weapons to the insurgents, and Venezuela reporting that they were stolen by a rebel attack on a Venezuelan position in 1995,[58] thus heightening tensions between the two countries.[57][59]
Wars
[edit]- US invasion of Panama[56]
- Kurdish–Turkish conflict (1978–present)
- Soviet–Afghan War
- Gulf War
- War in Afghanistan (2001–2021)[56]
- Iraq War[56]
- Second Ivorian Civil War[60]
- Mali War[61]
- 2013 Lahad Datu standoff
- War in Iraq (2013–2017)
- Syrian Civil War
- Russian invasion of Ukraine
See also
[edit]- List of rocket launchers
- List of anti-tank missiles
- ALAC (Arma Leve Anticarro)
- Alcotan-100 – (Spain)
- APILAS – (France)
- B-300 – (Israel)
- DZJ-08 – (China)
- LAW 80 – (United Kingdom)
- MARA (anti-tank weapon) – (Argentina)
- MATADOR – (Israel, Singapore)
- NLAW – (Sweden, United Kingdom)
- Panzerfaust 3 – (West Germany)
- RPG-76 Komar – (Polish People's Republic, Poland)
- RPG-75 – (Czechoslovakia)
- Urban Assault Weapon – (United States)
- M141 Bunker Defeat Munition – (United States)
- Kestrel (rocket launcher) – (Taiwan)
References and notes
[edit]Explanatory footnotes
[edit]- ^ Sometimes also spelled AT-4 or AT 4.
Citations
[edit]- ^ M136 AT4, FAS, archived from the original on 3 April 2007, retrieved 3 April 2007
- ^ a b c Kemp, Ian (April–May 2006), "The law gets tougher: the shoulder-launched light anti-armour weapon has evolved to become a multipurpose assault weapon much in demand for asymmetric warfare", Armada International, ISSN 0252-9793
- ^ a b c McManners, Hugh (2003). Ultimate Special Forces. DK Publishing. ISBN 0-7894-9973-8.
- ^ Owen, William F. (2007). "Light Anti-Armour Weapons: Anti-Everything?" (PDF). Asian Military Review. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "AT4 Light Anti-Armour Weapon". Army Technology. 30 April 2018. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016.
- ^ "84mm M136 (AT-4) Projected Grenade". Collective Awareness to UXO. Archived from the original on 3 August 2022. Retrieved 3 August 2022.
- ^ Atlamazoglou, Stavros (20 February 2024). "AT4: NATO Orders Proven Anti-Tank Weapon Used in Ukraine". The National Interest. Retrieved 15 April 2024.
Made in Sweden by SAAB, the AT-4 is one of the most successful weapons in its category, with over a million sales.
- ^ "France buys AT4 man-portable anti-tank weapon". mil.in.ua. 28 January 2023. Retrieved 15 April 2024.
Currently, the AT4 is one of the most popular and successful man-portable, disposable anti-tank weapon in the world.
- ^ a b Defense and Aerospace Competitive Intelligence Service (DACIS) (March 2019). "Shoulder Launched Munitions, All Types" (PDF).
- ^ a b Åkerström, Linda (2018). Den svenska vapenexporten. Sweden: Leopard Förlag. p. 72. ISBN 9789173438384.
- ^ Hewish, Mark, "FFV's Lightweight AT4, first of a new family of Swedish anti-armour weapons" International Defense Review, May 1980, p. 70.
- ^ Pansarskott is a Swedish term that roughly translates to "armour shot".
- ^ International Defense Review, May 1980, p. 71.
- ^ The French APILAS was the only tested weapon that had the maximum penetration to defeat the frontal armour of the new Russian T-72 MBT, but it was rejected due to its weight and size.
- ^ The Armbrust, while an impressive weapon with its almost total lack of launch signature, which enabled it to be fired from enclosed spaces, was rejected due to higher cost and lack of effective range against moving targets.
- ^ The U.S. Army had so much grief in the early 1980s from various committee members of the U.S. Congress over the M72 LAW being officially referred to in manuals as a Light Antitank Weapon that they named the AT4 to make sure no member of Congress could question that again.
- ^ John Antal. "Packing a Punch: America's Man-Portable Antitank Weapons". page 90. Military Technology. March 2010. ISSN 0722-3226.
- ^ Until the 1980s the Carl Gustaf was constructed of high-alloy steel, but later versions used a thin steel liner containing the rifling, strengthened by a carbon fibre outer sleeve.
- ^ "ODIN - OE Data Integration Network". odin.tradoc.army.mil. Retrieved 23 December 2024.
- ^ FFV and the Swedish Army were so impressed by these sights that they adopted them for their AT4s; while adequate during the day, the original plastic sights were difficult to see at night or under low light conditions.
- ^ "An Infantryman's Guide to Combat in Built-Up Areas" (PDF). bits.de. 3 October 1995. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- ^ the complete disposable launcher and HEDP projectile is referred to by the manufacture in brochures as the LMAW (light multipurpose-assault weapon) see external links for link on early photos and press releases for further information on brochure
- ^ a b "AT4 Family | Saab".
- ^ "2008 SAAB video on AT4 versions including new multipurpose warhead for urban combat". YouTube. 14 August 2008. Archived from the original on 18 October 2014. Retrieved 11 October 2014.
- ^ a b Saab to integrate new projectile variants for disposable shoulder-launched rocket system Archived 24 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine - Janes.com, 11 June 2014
- ^ "AT4 Light Anti-Armour Weapon - Army Technology". Archived from the original on 31 July 2018.
- ^ "AT4 Family | Saab". Start. Retrieved 14 December 2024.
- ^ "The New 84mm AT4 – Small Arms Defense Journal". Retrieved 14 December 2024.
- ^ "AT4CS TW wird die zukünftige Individual Assault Munition der U.S. Army" (in German). 28 August 2024. Retrieved 29 August 2024.
- ^ Jane's Infantry Weapons 1995–96, page 220. The reference refers to Allaint Techsystems as the manufacture, but they soon after were acquired by Honeywell. The SMAW-D offered by Talley was chosen for the U.S. Army program that the AT4 entered. See external images at the SMAW-D link for an arms brochure on the FFV AT8
- ^ "Small Arms Archive Detail Page for S00437".
- ^ "Bofors demo 92 2-4". YouTube. 13 December 2011.
- ^ "Carl Gustaf, AT-4CS y fusiles Steyr HS.50 M1 para el Ejército Argentino". 27 October 2017. Archived from the original on 29 October 2017. Retrieved 29 October 2017.
- ^ "La Infantería de Marina adquirió armamento antitanque descartable". Archived from the original on 2 November 2010. Retrieved 25 October 2010.
- ^ a b c d e Jones, Richard D (27 January 2009), Infantry Weapons 2009/2010 (35 ed.), Jane's Information, ISBN 978-0-7106-2869-5
- ^ a b "The World Defence Almanac", World Defence Almanac: The Balance of Military Power, 2000, ISSN 0722-3226
- ^ Replaced the APILAS: AT 4 CS – L'arme anti blindé lourd AT 4 CS – The anti-heavy armor weapon, France: Ministry of Defense, archived from the original on 8 January 2014, retrieved 29 June 2013
- ^ "Saab Awarded Indian Contract for AT4 Support Weapon". Saab. Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 27 January 2022.
- ^ "AT-4 Senjata Andalan Unit Infanteri". Radarmiliter.com (in Indonesian). Retrieved 16 May 2022.
- ^ "Swedish weapons in the Iraqi military?", Radio Sweden, 18 November 2010, archived from the original on 19 February 2011, retrieved 18 November 2010
- ^ Vining, Miles (19 June 2018). "ISOF Arms & Equipment Part 4 – Grenade Launchers & Anti-Armour Weapons". armamentresearch.com. Archived from the original on 28 July 2018. Retrieved 31 July 2018.
- ^ International Institute for Strategic Studies (February 2016). The Military Balance 2016. Vol. 116. Routledge. p. 491. ISBN 9781857438352.
- ^ "Archived copy". pbs.twimg.com. Archived from the original on 8 November 2019. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Northern Iraq PKK-Weapon Caches of Operation 'Claw Tiger'". Silah Report. 27 August 2020. Retrieved 27 May 2021.
- ^ sabah, daily (16 August 2017). "2 Swedish-made antitank missiles found in PKK hideout in Turkey's southeast". Daily Sabah. Retrieved 27 May 2021.
- ^ "The World Defence Almanac", World Defence Almanac: The Balance of Military Power: 172, 2010, ISSN 0722-3226
- ^ Kahwaji, Riad (13 November 2007). "Lebanon: Foreign Arms Vital to Hizbollah Fight" (JPEG). Defense News. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 25 January 2009.
- ^ "Lietuvos kariuomenė :: Ginkluotė ir karinė technika » Granatsvaidžiai ir prieštankiniai ginklai » Prieštankinis granatsvaidis AT-4". Archived from the original on 9 October 2014. Retrieved 11 October 2014.
- ^ "Rusia alerta a México: lanzacohetes de cárteles es de los enviados por EU a Ucrania". 31 May 2023. Retrieved 31 May 2023.
- ^ "The World Defence Almanac", World Defence Almanac: The Balance of Military Power: 105, 2005, ISSN 0722-3226
- ^ "Polish Army Photogallery". Polish Ministry of Defence. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 26 April 2010.
- ^ "Mer svenska vapen till Ukraina". Sydsvenskan (in Swedish). 23 March 2022. Retrieved 23 March 2022.
- ^ Nilsson, Maja (2 June 2022). "Sverige bistår Ukraina med sjömålsroboten Robot 17". SVT Nyheter (in Swedish). Retrieved 2 June 2022.
- ^ Collins, Kaitlan; Liptak, Kevin; Mattingly, Phil; LeBlanc, Paul; Vazquez, Maegan (17 March 2022). "Biden announces hundreds of millions in new security aid for Ukraine following Zelensky's speech". CNN. Retrieved 25 April 2022.
- ^ "Modernizing and Equipping the Army". Department of the Army Historical Summary, FY. United States Army Center of Military History. 1987. p. 43. CMH Pub 101-19. Archived from the original on 21 September 2010. Retrieved 13 August 2010.
- ^ a b c d Vapenexport (PDF), SE: Svenskafreds[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b "Global Security - News and Defence Headlines - IHS Jane's 360". IHS Jane's 360. Archived from the original on 10 March 2011. Retrieved 11 October 2014.
- ^ "Presentan video del ELN con armas de Cararabo - Internacional - EL UNIVERSAL". www.eluniversal.com. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2015.
- ^ "Colombia and Venezuela face off". GlobalPost. Archived from the original on 18 October 2014. Retrieved 11 October 2014.
- ^ Richard, Christophe (2014). "Battle of Abidjan: accurate and timely fires" (PDF). Fantassins. No. 32. p. 28. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ Capdeville, Thibault (Spring 2014). "Infantry units fires during OP Serval" (PDF). Fantassins. No. 32. pp. 55–58. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
External links
[edit]- Official website, covers the different versions
- Saab AT4 PDF Archived 19 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- AT4 – Saab Bofors Dynamics video of various AT4 versions
- AT4 Information Page – Modern Firearms
- Swedish article on AT4 translated to English
- U.S. Army field manual 3–23.25
- Brazilian newspaper recorded a AT-4 at Rocinha slum (translated to English)




