Kettlebell

In weight training, a kettlebell is a cast-iron or cast-steel ball with a handle attached to the top, resembling a cannonball with a handle.[1] It is used to perform a range of exercises; primarily ballistic exercises that combine cardiovascular, strength and mobility training. Kettlebells are the primary equipment used in the strength sport of kettlebell lifting.
History
[edit]
The Russian girya (ги́ря, plural ги́ри giri) was a type of metal weight, primarily used to weigh crops in the 18th century. The use of such weights by circus strongmen is recorded for the 19th century. They began to be used for recreational and competition strength athletics in Russia and Europe in the late 19th century. The birth of competitive kettlebell lifting or girevoy sport (гиревой спорт) is dated to 1885, with the founding of the "Circle for Amateur Athletics" (Кружок любителей атлетики).[2] Russian girya are traditionally measured in weight by pood, corresponding to 16.38 kilograms (36.1 lb).[3] The English term kettle bell has been in use since the early 20th century.[4]
Similar weights used in Classical Greece were the haltere, comparable to the modern kettlebell in terms of movements.
Shape
[edit]
Unlike traditional dumbbells, a kettlebell's centre of mass is extended beyond the hand, similar to Indian clubs or ishi sashi. This facilitates ballistic and swinging movements.[5] Variants of the kettlebell include bags filled with sand, water, or steel shot.[6] The kettlebell allows for swing movements and release moves with added safety and added grip, wrist, arm and core strengthening. The weight of a kettlebell is not distributed evenly. Thus, the unique shape of a kettlebell provides the "unstable force" for handling,[7] which is important for the effectiveness of the kettlebell exercises.[8]
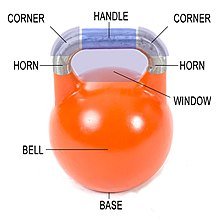
The parts of the kettlebell can be broken down into: handle, corners, horns, window, bell, and base.
Usage
[edit]By their nature, typical kettlebell exercises build strength and endurance, particularly in the lower back, legs, and shoulders, and increase grip strength.[9][5] The basic movements, such as the swing, snatch, and the clean and jerk, engage the entire body at once,[9] and in a way that mimics real world activities such as shoveling or farm work.[3][5]
Unlike the exercises with dumbbells or barbells, kettlebell exercises involve large numbers of repetitions in the sport, and can also involve large reps in normal training. Kettlebell exercises are in their nature holistic; therefore they work several muscles simultaneously and may be repeated continuously for several minutes or with short breaks. This combination makes the exercise partially aerobic and more similar to high-intensity interval training rather than to traditional weight lifting. In a 2010 study, kettlebell enthusiasts performing a 20-minute snatch workout were measured to burn, on average, 13.6 calories/minute aerobically and 6.6 calories/minute anaerobically during the entire workout - "equivalent to running a 6-minute mile pace".[10] When training with high repetitions, kettlebell progression should start out slowly to build muscle endurance, support the joints and prevent injury.
When done without the right instruction and progression, these exercises, like those done with any workout equipment, can be harmful to anyone who have shoulder or back issues or a weak core. But when done correctly, they have a lot of health benefits. They can provide greater strength, mental toughness, cardiovascular endurance, agility, range of motion, and mobility.[11]
Kettlebell swing
[edit]The kettlebell swing (also the Russian swing, double-arm swing or conventional kettlebell swing) is the fundamental ballistic exercise used to train the posterior chain in a manner similar to broad jumping. The kettlebell is swung from just below the groin to somewhere between the upper abdomen and shoulders, with arms straight or slightly bent, the degree of flexion depends on the trajectory of the kettlebell.[12] The key to a good kettlebell swing is effectively thrusting the hips, not bending too much at the knees, and sending the weight forwards, as opposed to squatting the weight up, or lifting up with the arms. Some knee flexion (squat) may occur during the swing, though the force generated originates from the poster chain hinging muscles that control the hip.
This exercise requires an intense contraction of the hand, gluteal, abdominal and latissimus muscles as dynamic force is generated in multiple joints including the; hip, knee, ankle and shoulder.
Variations
[edit]There are many variations of the kettlebell swing, some are, but not limited to: the release and catch swing (two hands switching from pronated to supinated grip), the one-arm swing (a significant anti-rotation challenge), the one-arm alternating catch swing, the walking swing, the suitcase swing, the lateral swing, two kettlebells double arm swing, swing squat style and high swing.
Other exercises
[edit]The following is a list of common exercises that are uniquely suited to the kettlebell. Some of these exercises may be performed with one or two kettlebells.[13]

- Around-the-world/slingshot
- The kettlebell is held in one arm and moved in a circular motion around the body, switching hands in front and behind. Variations can include passing through the legs in a figure-8.
- Bent press
- A press utilizing a bent-leg windmill position to lift heavier weight than is otherwise possible.
- Clean
- The bell is swung between the legs and brought back up to the racked position (resting on the forearm in the crook of the elbow, with the elbow against the chest). Variations can include lateral movement to the sides, alternating cleans with two bells, static cleans with no swing component.[14]
- Deadlift
- Can be performed different styles, sumo, squat or hip hinge, with one or more kettlebells between the legs, it can also be performed with the kettlebells on the outside (suitcase).
- Halo
- The kettlebell is held by the horns in front of the shoulders, usually upside-down, and moved in a circle around the head while keeping the head straight in place. This movement is done to improve upper body mobility.
- High pull
- A movement which begins with a swing and ends with the arm parallel to the floor instead of completing the arc of the arm to a full snatch.[15]
- Overhead press
- The kettlebell is held in the rack position and pushed overhead with one arm, keeping the body rigid. Variations include using two bells, the push press, the Sots press (named after Viktor Sots) and the alternating press amongst others.
- Snatch
- The kettlebell is held in one hand, lowered to behind the knees via hip hinge, swung to an overhead position and held stable, before repeating the movement. Variations may include movements begun from a static position or a swing.[16][17]
- Squat
- The basic squat is performed holding one or more kettlebells in the racked position, or a single bell in the goblet position. Variations include Cossack squat with movement to the side and overhead squats where the bell is held above the head, amongst others.

- Swing
- The traditional Russian swing is swung from just below the groin to somewhere between the upper abdomen and shoulders, with arms straight or slightly bent. Variations can include going higher than shoulder height (American) or using one hand and alternating hands if required.[12]
- Turkish get-up
- A kettlebell exercise that combines the lunge, bridge and side plank in a slow, controlled movement. Keeping the arm holding the bell extended vertically, the athlete transitions from lying supine on the floor to standing, and back again.[18]
- Windmill
- Start in a standing position with one arm fully extended and holding up a kettlebell overhead. Keeping the bell arm vertical, hinge at your hips so the upper body is lowered to the opposite side and rotated until the other hand is touching the floor. Then reverse the movement to return to the starting position, and repeat for the desired number of reps. This improves mobility and stability in both the hips and shoulders. Alternatively the bell may be held in the other hand, or with one in each hand. An easier version is the bent-leg windmill where the off-side leg is bent, or the supported windmill where the free hand rests against the off leg.


Grips
[edit]More than 25 grips are available on the kettlebell, which can be used to add variation, test various muscles, improve proprioception, and increase or decrease complexity. Pressing grips, racking grips, lifting grips, ballistic grips, juggling grips, and isometric hold grips are a few of the different types of grips.
Lifting styles
[edit]
Contemporary kettlebell training is represented basically by five styles.
Hardstyle has its roots in powerlifting and Gōjū-ryū karate training, particularly hojo undō concepts. With emphasis on the "hard" component and borrowing the concept of kime, the Hardstyle focuses on strength and power and duality of relaxation and tension.
Girevoy, sometimes referred to as the fluid style in comparison to the Hardstyle, represents the training regimen for the competitive sport of kettlebell lifting, focusing on strength endurance.
Crossfit kettlebell refers to implementation of kettlebell training as in CrossFit curricula, often with significant modifications to preceding styles (e.g. American Swing vs. conventional swing, placing the kettlebell down between snatches).
Juggling is a training style where the practitioner releases and catches the kettlebell with all manner of spins and flips around the body.
Kettlebell training is all that is done with a kettlebell outside of the above 4 categories. Kettlebell training is extremely broad and caters to many different goals, some being, but not limited to: mobility, flexibility, cardiovascular endurance, strength, speed and power. If an athlete is training in the gym, on the beach, or in the park, and not performing any of the above disciplines, they are participating in kettlebell training.
Kettlebell sport
[edit]The kettlebell sport having originated in Russia now has competitions across the world, it consists of three main lifts: the snatch, jerk and the long cycle.[19][20]
Competition colours
[edit]Competition grade kettlebells used in kettlebell sport and lesuire lifting are colour coded by bell or horn to allow quick and easy recognition.
| Colour | Weight (kg) | Weight (lb) |
|---|---|---|
| pink | 8 | 17.64 |
| blue | 12 | 26.46 |
| yellow | 16 | 35.27 |
| purple | 20 | 44.09 |
| green | 24 | 52.91 |
| orange | 28 | 61.73 |
| red | 32 | 70.55 |
| grey | 36 | 79.37 |
| white | 40 | 88.18 |
| silver | 44 | 97.00 |
| gold | 48 | 105.82 |
Weights that increment at 2kg such as; 10, 14, 18, 22, 26, 30, 34 are the same colour as the weight 2 kilograms below them but are notated by black bands on the handle in competitive lifting. For example, a 10 Kg bell is pink with black bands on the handle, and an 18 Kg bell is yellow with black bands on the handle.
Kettlebell toss
[edit]Strongmen events include the competitive tossing of kettlebells. For example, in the 2023 World's Strongest Man, the format was to toss seven kettlebells, weighing 45–68 pounds, over a 15-foot bar as quickly as possible. The best performance was by Mateusz Kieliszkowski who successfully tossed all seven kettlebells over the bar in 32.44 seconds.[21]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Kettlebell Workouts: What to Know Before You Start". WebMD. Retrieved 2018-08-24.
- ^ Мария Соколова, Два «бульдога» на грудь. Как доктор Краевский стал «отцом русской атлетики» "Аргументы и Факты", 22 August 2016 (with period photographs).
- ^ a b Jonsson, Patrik (2004-05-02). "The strongman 'kettlebell' makes a comeback at the gym". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ Advertised by A.P. Schmidt in Physical Culture vol. 21 (1908), p. 505: "PEOPLE ALL OVER THE WORLD ARE USING SCHMIDT'S Celebrated 'MONARCH' DUMB-BELL, BAR BELL AND KETTLE BELL SYSTEM"; also spelled KETTLE-BELLS (with hyphen) in a 1910 advertisement for the "Automatic Exerciser")
- ^ a b c Rathbun, Andy (2009-01-04). "The kettlebell way: Focused workouts mimic the movements of everyday activities". HeraldNet. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016.
- ^ Wallack, Roy (2010-04-26). "A Vat of Kettlebells". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ "What Is A Kettlebell? Blast Fat & Build Strength With Innovative Equipment!". Bodybuilding.com. 2008-11-18. Retrieved 2018-08-24.
- ^ Liebenson, Craig "Functional Training with the Kettlebell." Journal of Bodywork & Movement Therapies 15 (2011): 542-544
- ^ a b Ivill, Laura (2008-11-22). "The kettlebell workout Can the kettlebell give you a Hollywood body?". The Times. Archived from the original on June 15, 2011.
- ^ Porcari et al. (2010), University of Wisconsin."Exclusive ACE research examines the fitness benefits of kettlebells" (PDF).
- ^ "Kettlebells vs. Free Weights: The Smackdown". Men's Health. 2012-02-29. Retrieved 2018-08-24.
- ^ a b Martin, C.J. (14 August 2012). "The Great Kettlebell Swing Debate". Crossfit Invictus.
- ^ Greg Brookes (29 January 2015). "33 Kettlebell Exercises from Beginner to Advanced". Retrieved 14 May 2015.
- ^ "The Kettlebell Clean, Stop Banging Your Wrists | The Complete Guide". Kettlebell Workouts for Men and Women. 2018-11-09. Retrieved 2019-08-07.
- ^ "Kettlebell Swing Vs. High Pull". livehealthy.chron.com. Retrieved 2019-08-07.
- ^ "Kettlebell Foundations: Hardstyle Kettlebell Snatch". Kettlebell Kings. Retrieved 2018-08-24.
- ^ "Intro To Kettlebell Sport Part 3: The Kettlebell Sport Snatch". Kettlebell Kings. Retrieved 2018-08-24.
- ^ Liebenson, Craig and Shaughness, Gabrielle "The Turkish Get-up." Journal of Bodywork & Movement Therapies 15 (2011): 125-127
- ^ International Kettlebell lifting Federation website
- ^ "International Union of Kettlebell Lifting". Международный Союз Гиревого Спорта (in Russian). Retrieved 2024-02-08.
- ^ Blechman, Phil (2023-04-20). "2023 World's Strongest Man Event Five "Kettlebell Toss" Results". BarBend. Retrieved 2023-04-28.
