Portal:Energy
| Main page | New articles & Tasks |
 The Energy Portal Welcome to Wikipedia's Energy portal, your gateway to energy. This portal is aimed at giving you access to all energy related topics in all of its forms.
|
Page contents: Selected article • Selected image • Selected biography • Did you know? • General images • Quotations • Related portals • Wikiprojects • Major topics • Categories • Help • Associated Wikimedia |
Introduction
Energy (from Ancient Greek ἐνέργεια (enérgeia) 'activity') is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).
Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass. These are not mutually exclusive.
All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primarily by radiant energy from the sun. The energy industry provides the energy required for human civilization to function, which it obtains from energy resources such as fossil fuels, nuclear fuel, and renewable energy. (Full article...)
Selected article
Iceland's location on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge makes it one of the most tectonically active places in the world, with over 200 volcanoes and over 20 high-temperature steam fields. Geothermal energy for heating was first used in 1907 when a farmer piped steam from a hot spring into his house. In 1930, the first pipeline was constructed in Reykjavík, heating two schools, 60 homes, and the main hospital. In 1943, the first geothermal district heating company started. Geothermal power now heats 89% of the nation's houses, provides around 19% of electricity generation and over 54% of primary energy. The first hydroelectric plant was built in 1904 and produced 9 kW of power. Hydropower now provides 81% of Iceland's electricity supply.
Imported oil provides most of Iceland's remaining energy. Replacing this with hydrogen was first suggested after the 1970s energy crisis, but the idea was not adopted until 1998. Iceland's small size makes it ideal for testing the viability of hydrogen as a fuel source for the future, while the plentiful renewable energy sources can be harnessed for its production. Iceland participates in international hydrogen fuel research and development programs, and many countries are following the nation's progress.
As a result of its transition to renewable energy, Iceland is ranked 53rd in the list of countries by carbon dioxide emissions per capita in 2003, emitting 62% less than the United States despite using more primary energy per capita.
Selected image
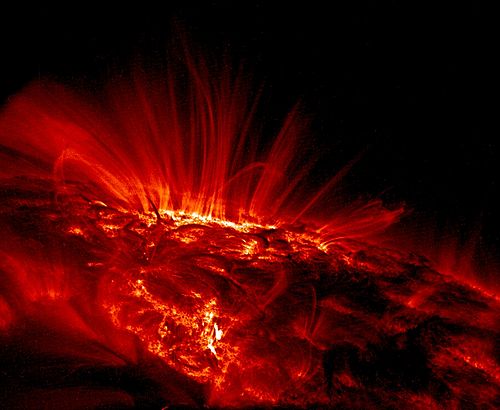

Photo credit: NASA/TRACE
Plasma being channeled by the magnetic field loops of a sunspot.
Did you know?

- Buildings constructed to the German Passivhaus standard use 75% to 95% less energy for space heating and cooling than current new buildings in the United States?
- Crossing 4,000 km (2,500 miles), the Druzhba pipeline is the world's longest oil pipeline?
- Coal is ground to a powder before being burnt in fossil fuel power plants?
- Compact fluorescent lamps (pictured) use about 1/4 of the energy of normal incandescent light bulbs, and pay for themselves after about 500 hours of use?
- Nuclear power in France produces 78% of all the country's electricity - more than in any other nation?
- Positive lightning bolts are typically six to ten times more powerful than normal lightning — and aircraft are not designed to withstand them?
- Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy which permeates all of space?
Selected biography
Between 1992 and 1995, after Soviet president Mikhail Gorbachev's 'perestroika' economic reforms permitted the opening of small private businesses, Abramovich founded five companies that eventually evolved to specialize in the trading of oil and oil products. With the approved by Boris Yeltsin, in 1995 Roman Abramovich and partner Boris Berezovsky paid $100m for a controlling interest in the major Russian Sibneft oil company, then valued at $150 million. Berezovsky subsequently sold his stake to Abramovich after fleeing to London. In September 2005 Abramovich sold his interest in Sibneft to state energy giant Gazprom for $13 billion.
Despite maintaining that his primary residence is Moscow, in 2006 Abramovich was named as the second-wealthiest person in the United Kingdom. His property investments and other assets were estimated at £10.8 billion. In June 2003, Abramovich became the owner of the companies that control Chelsea Football Club (soccer club). He also became the world's greatest spender on luxury yachts, with four boats in what the media have called the 'Abramovich Navy'.
Although he rarely visits the area, in October 2005 Abramovich was reappointed governor of the impoverished Chukotka Autonomous Okrug in the Russian Far East where he has made significant financial contributions. He was originally elected to the governorship in 1999.
In the news
- 2 July 2025 –
- Iranian president Masoud Pezeshkian orders the suspension of cooperation with the International Atomic Energy Agency following the Iran–Israel war and the United States strikes on Iranian nuclear sites. (AP)
- 22 June 2025 – Middle Eastern crisis
- The International Atomic Energy Agency says no increase in off-site radiation levels was detected at the three targeted nuclear sites. (Al Jazeera)
- 13 June 2025 – Middle Eastern crisis
- Israeli decapitation strikes kill commander-in-chief of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Hossein Salami, senior nuclear scientist and former head of the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran Fereydoon Abbasi, and chief of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Islamic Republic of Iran Mohammad Bagheri and Quds Force commander Esmail Qaani. (The Times of Israel) (BBC News)
- 12 June 2025 – Nuclear program of Iran
- The International Atomic Energy Agency finds Iran in breach of its obligations to limit uranium enrichment and provision of information on its nuclear materials. (BBC News) (The Guardian)
General images
Quotations
- "Our children will enjoy in their homes electrical energy too cheap to meter." – Lewis Lichtenstein Strauss, 1954
- "There is every possibility that you will soon be able to tax it." – Michael Faraday, talking to William Gladstone on the future purpose of electricity.
- "Higher energy prices act like a tax. They reduce the disposable income people have available for other things after they've paid their energy bills." – John W. Snow, 2005
- "Our dependence on foreign energy is like a foreign tax on the American people." – George W. Bush, 2005
Related portals
WikiProjects
WikiProjects connected with energy:
Other WikiProjects that may be of interest:
Major topics
Major categories
National energy supply, use & conservation
National electricity sector
Politics, economics, environment
- Climate change
- Energy conservation
- Energy economics
- Energy crises
- Energy development
- Energy policy
- Peak oil
Energy sources
- Fuels
- Biofuels
- Fossil fuels
- Fusion power
- Nuclear technology
- Renewable energy
- Energy conversion
- Electric power
- Energy storage
Energy-related design
Scientific usage
Help

Puzzled by energy?
Can't answer your question?
Don't understand the answer?
- Ask at the reference desk
- Read the Wikipedia help pages
For further ideas, to leave a comment, or to learn how you can help improve and update this portal, see the talk page.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus