Portal:History of science
The History of Science Portal
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal. Protoscience, early sciences, and natural philosophies such as alchemy and astrology that existed during the Bronze Age, Iron Age, classical antiquity and the Middle Ages, declined during the early modern period after the establishment of formal disciplines of science in the Age of Enlightenment.
The earliest roots of scientific thinking and practice can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia during the 3rd and 2nd millennia BCE. These civilizations' contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine influenced later Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, wherein formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Latin-speaking Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but continued to thrive in the Greek-speaking Byzantine Empire. Aided by translations of Greek texts, the Hellenistic worldview was preserved and absorbed into the Arabic-speaking Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. The recovery and assimilation of Greek works and Islamic inquiries into Western Europe from the 10th to 13th century revived the learning of natural philosophy in the West. Traditions of early science were also developed in ancient India and separately in ancient China, the Chinese model having influenced Vietnam, Korea and Japan before Western exploration. Among the Pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica, the Zapotec civilization established their first known traditions of astronomy and mathematics for producing calendars, followed by other civilizations such as the Maya.
Natural philosophy was transformed by the Scientific Revolution that transpired during the 16th and 17th centuries in Europe, as new ideas and discoveries departed from previous Greek conceptions and traditions. The New Science that emerged was more mechanistic in its worldview, more integrated with mathematics, and more reliable and open as its knowledge was based on a newly defined scientific method. More "revolutions" in subsequent centuries soon followed. The chemical revolution of the 18th century, for instance, introduced new quantitative methods and measurements for chemistry. In the 19th century, new perspectives regarding the conservation of energy, age of Earth, and evolution came into focus. And in the 20th century, new discoveries in genetics and physics laid the foundations for new sub disciplines such as molecular biology and particle physics. Moreover, industrial and military concerns as well as the increasing complexity of new research endeavors ushered in the era of "big science," particularly after World War II. (Full article...)
Selected article -

The great chain of being is a hierarchical structure of all matter and life, thought by medieval Christianity to have been decreed by God. The chain begins with God and descends through angels, humans, animals and plants to minerals.
The great chain of being (from Latin scala naturae 'ladder of being') is a concept derived from Plato, Aristotle (in his Historia Animalium), Plotinus and Proclus. Further developed during the Middle Ages, it reached full expression in early modern Neoplatonism. (Full article...)
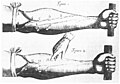
Selected image

Craniometry, the technique of measuring the bones of the skull, was once intensively practiced in anthropology/ethnology. Through the 20th century, craniometry—especially measurements of brain volume—was a matter of considerable; among other misuses, the apparent scientific support of craniometric theories for racism was used to the support the racist ideologies, and ultimately genocidal policies, of the Nazi party.
Did you know
...that the history of biochemistry spans approximately 400 years, but the word "biochemistry" in the modern sense was first proposed only in 1903, by German chemist Carl Neuberg?
...that the Great Comet of 1577 was viewed by people all over Europe, including famous Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe and the six year old Johannes Kepler?
...that the Society for Social Studies of Science (often abbreviated as 4S) is, as its website claims, "the oldest and largest scholarly association devoted to understanding science and technology"?
Selected Biography -

Luther Burbank (March 7, 1849 – April 11, 1926) was an American botanist, horticulturist, and pioneer in agricultural science who developed more than 800 strains and varieties of plants over his 55-year career. Burbank primarily worked with fruits, flowers, grains, grasses, and vegetables. He developed (but did not create) a spineless cactus (useful for cattle-feed) and the plumcot.
Burbank's most successful strains and varieties included the Shasta daisy, the fire poppy (note possible confusion with the California wildflower, Papaver californicum, which is also called a "fire poppy"), the "July Elberta" peach, the "Santa Rosa" plum, the "Flaming Gold" nectarine, the "Wickson" plum (named after the agronomist Edward J. Wickson), the freestone peach, and the white blackberry. (Full article...)
Selected anniversaries
- 1429 - death of Ghiyath al-Kashi, Persian astronomer and mathematician (b. 1380)
- 1633 - The Holy Office in Rome forces Galileo Galilei to recant his view that the Sun, not the Earth, is the center of the Universe.
- 1744 - birth of Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben, German naturalist (d. 1777)
- 1864 - birth of Hermann Minkowski, German mathematician (d. 1909)
- 1887 - birth of Julian Huxley, British biologist (d. 1975)
- 1892 - death of Pierre Ossian Bonnet, French mathematician (b. 1819)
- 1925 - death of Felix Klein, German mathematician (b. 1849)
- 1990 - death of Ilya Frank, Soviet physicist and Nobel laureate (b. 1908)
- 2004 - death of Bob Bemer, American computer scientist (b. 1920)
- 2006 - The newly discovered moons of Pluto are officially named Hydra and Nix by the International Astronomical Union.
Related portals
Topics
General images
Subcategories
Things you can do
Help out by participating in the History of Science Wikiproject (which also coordinates the histories of medicine, technology and philosophy of science) or join the discussion.
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus