Portal:Internet
The Internet PortalThe Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, internet telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the internetwork. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, the subsequent commercialization of the Internet in the 1990s and beyond incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Selected articleA Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), formerly Universal Resource Identifier, is a unique sequence of characters that identifies an abstract or physical resource, such as resources on a webpage, mail address, phone number, books, real-world objects such as people and places, concepts. URIs are used to identify anything described using the Resource Description Framework (RDF), for example, concepts that are part of an ontology defined using the Web Ontology Language (OWL), and people who are described using the Friend of a Friend vocabulary would each have an individual URI. URIs which provide a means of locating and retrieving information resources on a network (either on the Internet or on another private network, such as a computer filesystem or an Intranet) are Uniform Resource Locators (URLs). Therefore, URLs are a subset of URIs, i.e. every URL is a URI (and not necessarily the other way around). Other URIs provide only a unique name, without a means of locating or retrieving the resource or information about it; these are Uniform Resource Names (URNs). The web technologies that use URIs are not limited to web browsers. (Full article...) Selected picture Wardriving is the act of searching for Wi-Fi wireless networks by a person in a moving vehicle using a Wi-Fi-equipped computer, such as a laptop or a PDA. It is similar to using a radio scanner, or to the amateur radio practice of DXing. Fucking Machines (also known as fuckingmachines.com and fuckingmachines) is a pornographic website founded in 2000 that features video and photographs of women engaged in autoerotic sexual stimulation with penetrative sex-machines and sex toys. Based in San Francisco, California, the site is operated by Kink.com. Web entrepreneur Peter Acworth launched Fucking Machines on September 25, 2000, as his company's second website after Kink.com. Devices shown on the site were created with the intent to bring women authentic orgasms. Performers were instructed to allow themselves to be recorded experiencing pleasure. After the site applied in 2005 to trademark the phrase "fuckingmachines", the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) denied the application and ruled that the mark was obscene. Free speech lawyer Marc Randazza represented the site and appealed the decision. Orlando Weekly called his legal brief "one of the most entertaining legal documents you're likely to come across." The appeal was denied in April 2008 and the case was terminated. Randazza's argument in the case became known as The Fuck Brief. The website has been the subject of attention from journalists and academics studying sexuality. Writer Regina Lynn highlighted the site's emphasis on communication, and Annalee Newitz of AlterNet classed it as part of Porn 2.0. Violet Blue wrote in The Adventurous Couple's Guide to Sex Toys that it helped popularize the idea of machines aiding in sex acts. The 2008 edition of The Oxford Encyclopedia of Women in World History described the aesthetic of the devices as disturbing. Jessica Roy wrote for The New York Observer that Fucking Machines' examples of orgasms were a form of transhumanism. Sarah Schaschek devoted a chapter to the phenomenon in Screening the Dark Side of Love: From Euro-Horror to American Cinema, titled "Fucking Machines: High-Tech Bodies in Pornography". She observed, "Strictly speaking, the women in these videos are both the controllers and the controlled." (Full article...) WikiProjects
Did you know (auto-generated) -
Selected biography
Steve Paul Jobs (born February 24, 1955) was the American co-founder, Chairman and CEO of Apple Inc, and was the CEO of Pixar Animation Studios until it was acquired by the Walt Disney Company in 2006. Jobs is currently the Walt Disney Company's largest individual shareholder and a member of its Board of Directors. He is considered a leading figure in both the computer and entertainment industries. He is also widely credited as the inventor of the Macintosh, the iPod, the iTunes Store, and the iPhone. Jobs's history in business has contributed greatly to the myths of the quirky, individualistic Silicon Valley entrepreneur, emphasizing the importance of design while understanding the crucial role aesthetics play in public appeal. Together with Apple co-founder Steve Wozniak, Jobs helped popularize the personal computer in the late '70s. In the early '80s, still at Apple, Jobs was among the first to see the commercial potential of the mouse-driven GUI. After losing a power struggle with the board of directors in 1985, Jobs resigned from Apple and founded NeXT, a computer platform development company specializing in the higher education and business markets. Next's subsequent 1997 buyout by Apple brought Jobs back to the company he co-founded, and he has served as its chief executive officer since shortly after his return.
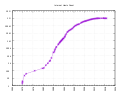
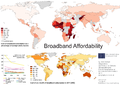
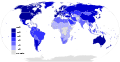
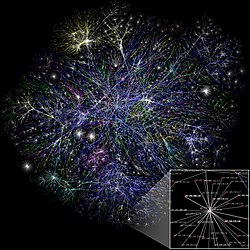
General images -The following are images from various internet-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected quoteMain topics
Featured contentCategoriesRelated portalsThings you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia's portals |