Barkers Creek
| Barkers Creek | |
|---|---|
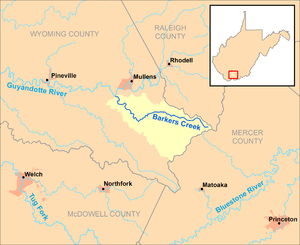 Barkers Creek and its watershed in Wyoming County, West Virginia. | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | West Virginia |
| County | Wyoming |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | eastern Wyoming County |
| • coordinates | 37°30′52″N 81°13′40″W / 37.5145603°N 81.2278771°W[1] |
| • elevation | 3,477 ft (1,060 m)[2] |
| Mouth | Guyandotte River |
• location | northwest of Tralee |
• coordinates | 37°33′40″N 81°24′30″W / 37.5612252°N 81.4084362°W[1] |
• elevation | 1,381 ft (421 m)[1] |
| Length | 8.0 mi (12.9 km) |
| Basin size | 36.85 sq mi (95.4 km2) |
Barkers Creek is a tributary of the Guyandotte River, 8 miles (13 km) long,[3] in southern West Virginia in the United States. Via the Guyandotte and Ohio rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of 36.85 square miles (95.4 km2) in a rural area on the unglaciated portion of the Allegheny Plateau.[4]
Barkers Creek's entire course and drainage area are in southeastern Wyoming County. It rises in the eastern extremity of Wyoming County, near the common boundary of Wyoming, Raleigh, and Mercer counties, approximately 3 miles (4.8 km) northeast of Arista, and flows initially westward, then turns northwestward through the unincorporated communities of Bud, Alpoca, and Tralee. It flows into the Guyandotte River from the south, approximately 0.5 miles (0.80 km) northwest of Tralee and 1 mile (1.6 km) southeast of Itmann. In its lower course the creek is paralleled by West Virginia Route 10.[5]
According to 1992 data from the United States Geological Survey, approximately 94% of the Barkers Creek watershed was forested; approximately 2% was used for agriculture; and approximately 2% was used for commercial or mining purposes.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Geographic Names Information System. "Geographic Names Information System entry for Barkers Creek (Feature ID #1535239)". Retrieved 2011-10-20.
- ^ Google Earth elevation for GNIS source coordinates. Retrieved on 2011-10-20.
- ^ United States Environmental Protection Agency. "Watershed Assessment, Tracking & Environmental Results: Assessment Summary for Reporting Year 2008, West Virginia, Upper Guyandotte Watershed". Archived from the original on 2012-12-12. Retrieved 2011-10-20.
- ^ a b Upper Guyandotte Watershed Association (February 2006). "Upper Guyandotte River" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-27. Retrieved 2011-10-20.
- ^ West Virginia Atlas & Gazetteer. Yarmouth, Me.: DeLorme. 1997. pp. 58–59. ISBN 0-89933-246-3.
