Battle of the Jabara Valley
| Battle of the Jabara Valley | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Operation Victory from God | |||||||
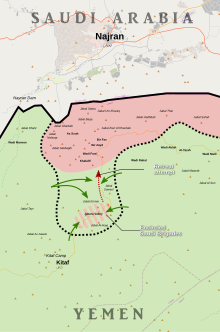 Map of the battle Houthi forces Saudi-led forces | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Unknown |
Radad al-Hashemi[2] (al-Fateh Brigade) | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Around 500 | 1,100-2,000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Unknown but less than 250 |
1,000–1,900 killed or captured, 100 escaped 200+ vehicles destroyed or captured[3][4] | ||||||
The Battle of the Jabara Valley occurred between 26 and 29 August 2019, during the Second Yemeni Civil War. It was part of Operation Victory from God, a major Houthi-led offensive along the Saudi Arabian-Yemeni border.
The battle
[edit]A Saudi Arabian auxiliary force of around 1,100 men from the al-Fateh Brigade launched an offensive into the Jabara Valley in Yemen's Saada Governorate against Houthi forces.[4] When the al-Fateh Brigade entered the valley, it was initially met with no resistance. A Houthi force then enveloped the Saudi-aligned force and besieged it for four days. Saudi air support was ineffective at breaking the envelopment, with Houthi sources reporting that the Saudis accidentally struck their own positions with airstrikes.[4][2] On 29 August 2019, a small breakout occurred with about 100 men from the pro-Saudi force escaping. The remaining thousand pro-Saudi troops capitulated, with approximately 1,000 to 2,000 killed or captured.[4] The battle was part of the initial phase of Operation Victory from God.[5]
Aftermath
[edit]Houthi sources reported that a Saudi airstrike killed several Yemeni prisoners of war captured during the battle.[3]
The Houthis continued their offensive in course of September 2019.[6]
Use of foreign weaponry by Saudis
[edit]NGOs from the EU have discovered Arms Exports to Saudi Arabia that had been used in Yemen, notably in the Jabara Valley.[7]
References
[edit]- ^ Orkaby, Asher (25 March 2015). "Houthi Who?". Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ^ a b Hassan Mohammed (3 October 2019). "روايات من قلب الانتكاسة .. كيف وقع لواء الفتح فريسة سهلة للحوثيين" [Novels from the heart of the setback .. How the brigade of conquest fell prey easy to the Houthis]. Balqees TV (in Arabic). Archived from the original on 14 October 2019. Retrieved 14 October 2019.
- ^ a b "منهم الأسرى الذين قصف طيران التحالف مركز احتجازهم في مدينة ذمار..؟" [Who were the prisoners killed in the Coalition bombing of detention center in Dhamar?]. Yemenat.net (in Arabic). 1 September 2019. Retrieved 4 September 2019.
- ^ a b c d "'I curse myself': Yemeni mercenaries say their Saudi fighting days are over". Middle East Eye. 3 September 2019. Retrieved 4 September 2019.
- ^ Weiss, Caleb (29 September 2019). "Houthis claim major operation inside Saudi Arabia". Long War Journal. Retrieved 8 October 2019.
- ^ Cole, Juan. "Yemen's Houthis Claim Invasion of Saudi Arabia, Capture of Thousands of Troops in Najran". Common Dreams. Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ^ Lammerant, Hans (17 October 2020). "BELGIAN ARMS IN YEMEN". Istopthearmstrade.eu.