China Pharmaceutical University
中国药科大学 | |||||||
 | |||||||
Former names | National Pharmaceutical School | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motto | 精业济群[1] | ||||||
Motto in English | Be proficient and benefit others[2] | ||||||
| Type | Public university | ||||||
| Established | 1936 (as National College of Pharmacy)
1986 (as China Pharmaceutical University) | ||||||
Total staff | 1,868 | ||||||
| Students | 19,730 | ||||||
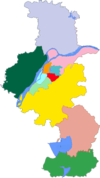
| Location | , , | ||||||
| Campus | Urban | ||||||
| Affiliations | ASRMU | ||||||
| Website | http://www.cpu.edu.cn/ | ||||||
 | |||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 中国药科大学 | ||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 中國藥科大學 | ||||||
| |||||||
China Pharmaceutical University (CPU; 中国药科大学)[3] is a public university in Nanjing, Jiangsu, China. It is affiliated with the Ministry of Education, and co-sponsored by the Ministry of Education and the Province of Jiangsu. It was founded in 1968 through mergers between the National College of Pharmacy and other smaller universities.[4] The university is part of Project 211 and the Double First-Class Construction.[5][6]
History
[edit]In September 1936, the National Pharmacy College (four-year system) was founded. During the Second Sino-Japanese War, the school moved to Hankou, Wuhan, and then to Chongqing, and in June 1950, the school was renamed East China Pharmacy College (Chinese: 华东药学专科学校).[7] In November 1952, the Department of Pharmacy of Qilu University and the Department of Pharmacy of Soochow University were merged into the East China Pharmacy College, and the pharmacy class of Wuhan Central and South China College of Hygiene was merged into the school in 1953, and the school began to enroll postgraduates in 1955. In 1956, the school was renamed Nanjing Pharmacy College, and in October 1986, the school was merged with Nanjing College of Chinese Medicine to establish China Pharmaceutical University. In 1996, university entered the ranks of the national "Project 211", in February 2000, turned into the Ministry of Education directly management. In 2001, Jiangsu Pharmaceutical School was merged into it.[8]
| National College of Pharmacy (1936) Nanjing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| East China School of Pharmacy (1950) Nanjing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmacy Dept., Cheeloo University | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| East China College of Pharmacy 1952 Nanjing | School of Pharmacy, Soochow University | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nanjing College of Pharmacy (1956) Nanjing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nanjing College of Pharmacy (1983) Nanjing | Nanjing College of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy (preparatory phase) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China Pharmaceutical University 1986 Nanjing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Campus
[edit]CPU is located in the ancient capital of Nanjing and comprises two campuses including Xuanwumen campus located in downtown Nanjing and Jiangning campus in the southeast outskirts of Nanjing.






Schools and departments
[edit]CPU consists of six schools (School of Pharmacy, School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy, School of life science and Technology, School of International Pharmaceutical Business, School of Continuing Education, and School of Higher Vocational Education), four independent departments (Dept. of Basic Sciences, Dept. of Foreign Languages, Dept. of Social Sciences, and Dept. of Physical Education), and five key labs and centers at state or provincial levels.
Programs
[edit]The university has 3 first-level disciplinary doctoral degree authorization points (pharmacy, traditional Chinese medicine, biology), 1 doctoral professional degree authorization point (biology and medicine), 8 first-level disciplinary master's degree authorization points (pharmacy, traditional Chinese medicine, biology, chemistry, biomedical engineering, basic medical science, public administration, public health and preventive medicine), 5 master's professional degree authorization points (pharmacy, traditional Chinese medicine, biology and medicine, applied statistics, public administration), with two postdoctoral mobile stations in Pharmacy and Traditional Chinese Medicine. The first-level discipline of Pharmacy is a key discipline at the national level.[9]
Faculty
[edit]Among the 530 faculty members, 2 are academicians (members of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Engineering), and more than 40% have advanced academic titles. So far, the university has undertaken more than 70 research projects financed by the State Key Programs Foundation, and more than 300 research projects financed by the State Natural Sciences Foundation and the State New Drug Research Foundation. There are also funding from other national, provincial and municipal departments. Many projects have reached the international level and filled the gaps in the country's pharmaceutical field.
Students
[edit]As of 2024[update], CPU has 19,730 full-time students, including 448 international students.[10] CPU is the only institution that is authorized by the Ministry of Education to admit full-time pharmacy students, continuing education students and senior visiting scholars from overseas. It is also one of the higher educational institutions in the mainland for students from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan.
International
[edit]The university is also active in international academic exchanges. It has made academic exchange agreements with more than 30 higher education institutions in different countries and regions of the world, including Japan, the United States, UK, Australia, Italy and Hong Kong. In addition, it maintains academic relationships with research institutions and universities in more than 40 countries and regions.
See also
[edit]- Pharmacy in China
- Pharmaceutical industry in China
- List of medical schools in the People's Republic of China
References
[edit]- ^ "学校简介 (in Chinese)". CPU. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ^ "Overview". CPU. Archived from the original on 2013-06-26. Retrieved 2015-11-04.
- ^ "China Pharmaceutical University". SICAS. 4 Mar 2013 – 22 Feb 2021. Archived from the original on 2018-05-22.
- ^ Chiu, Patrick (2023), "Pharmaceutical Education and Manpower Development", A History of Western Pharmacy in China, Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, pp. 113–133, doi:10.1007/978-981-99-8635-4_6, ISBN 978-981-99-8634-7, retrieved 2024-07-22
- ^ 中国著名大学概览 (in Chinese). 山东人民出版社. 1991. p. 499. ISBN 978-7-209-00687-3. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ 中国大学指南/2006版/1/"211工程"国家重点建设大学. 中囯大学指南 (in Chinese). China Statistics Press. 2006. ISBN 978-7-5037-4869-1. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ 中国著名大学概览 (in Chinese). 山东人民出版社. 1991. p. 495. ISBN 978-7-209-00687-3. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ 《中国敎育年鉴》编辑部 (2003). 中国敎育年鉴 (in Chinese). 中国大百科全书出版社. p. 208. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ "学校简介". China Pharmaceutical University (in Chinese). Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ^ "CPU at a Glance". China Pharmaceutical University. Retrieved 2024-07-22.