Convention on the Political Rights of Women
| Convention on the Political Rights of Women | |
|---|---|
| Signed | 31 March 1953 |
| Location | New York City, United States |
| Effective | 7 July 1954 |
| Condition | 6 ratifications |
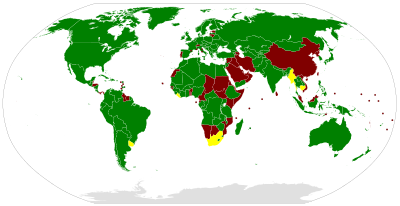
| Signatories | 47 |
| Parties | 123 |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish The Five Official Languages of the UN General Assembly |
| Full text | |
The Convention on the Political Rights of Women was approved by the United Nations General Assembly during the 409th plenary meeting, on 20 December 1952, and adopted on 31 March 1953.
The Convention's purpose is to codify a basic international standard for women's political rights.[1]
Background
[edit]In the aftermath of World War II, many countries had still not granted women full political liberty.[2] In 1952, the year before the Convention was adopted, women's suffrage had been granted in less than 100 countries worldwide.[1]
The main impetus for the legislation, and much of its drafting, came from the United Nations Commission on the Status of Women.[3] The Commission sent a survey about women's political rights to its member states; the resulting replies became the basis for the Convention.[2]
The Convention was adopted on 31 March 1953.[4]
Overview
[edit]Preamble
[edit]The preamble of the Convention reiterates the principles set out in article 21 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which declares that all people have the right to participate in the government of their country, and to access public services. The Convention on the Political Rights of Women specifically protects this right for women.[4]
Articles
[edit]The first three articles of the Convention assert the rights of women to vote (Article I), to be eligible for election (II), and to hold public office (III), with each article ending with the specification: "all on equal terms with men, without any discrimination." The remaining articles cover the mechanics of the legislation itself, specifying how and when it will come into force (Articles IV–XI).[4]
Legacy
[edit]The Convention entered into force on 7 July 1954.[3] As of August 2015, it has 123 state parties, comprising 122 United Nations member states plus the State of Palestine.[5]
The Convention followed the path of the Inter American Convention on the Granting Political Rights to Women that was the first international legislation at the regional level protecting the equal status of women to exercise political rights. The Convention was the first treaty in the context of the United Nations.[3] Moreover, it was the second international treaty to obligate its states to protect citizens' political rights.[2] The Convention was one of the United Nations' several efforts in the postwar period to set standards of nondiscrimination against women; others were the Convention on the Nationality of Married Women and the Convention on Consent to Marriage, Minimum Age for Marriage and Registration of Marriages, brought into force in 1958 and 1964, respectively.[2]
The rights outlined by the Convention were incorporated into the later, more substantial Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women.[3] This later Convention, a wider-reaching and more straightforward legislation for nondiscrimination, was approved by unanimous vote in 1967.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Cherif, Feryal M. (2015), Myths About Women's Rights: How, Where, and Why Rights Advance, Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 271, ISBN 9780190211172
- ^ a b c d e Dustan, Leanne (2008), "Convention on the Political Rights of Women", in Ford, Lynne E. (ed.), Encyclopedia of Women and American Politics, New York: Facts On File, p. 131, ISBN 9781438110325
- ^ a b c d Langley, Winston (1999), Encyclopedia of Human Rights Issues Since 1945, Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, pp. 70–1, ISBN 9780313301636
- ^ a b c Convention on the Political Rights of Women (PDF), New York: United Nations, 1953
- ^ "Convention on the Political Rights of Women", United Nations Treaty Collection, United Nations, archived from the original on 11 April 2011, retrieved 12 August 2015
External links
[edit]- Women's rights instruments
- Women's suffrage
- Treaties entered into force in 1954
- Treaties concluded in 1953
- Treaties adopted by United Nations General Assembly resolutions
- United Nations treaties
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Afghanistan
- Treaties of the People's Socialist Republic of Albania
- Treaties of Algeria
- Treaties of the People's Republic of Angola
- Treaties of Antigua and Barbuda
- Treaties of Argentina
- Treaties of Armenia
- Treaties of Australia
- Treaties of Austria
- Treaties of the Bahamas
- Treaties of Bangladesh
- Treaties of Barbados
- Treaties of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic
- Treaties of Belgium
- Treaties of Bolivia
- Treaties of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Treaties of the Second Brazilian Republic
- Treaties of the People's Republic of Bulgaria
- Treaties of Burkina Faso
- Treaties of Burundi
- Treaties of Canada
- Treaties of the Central African Republic
- Treaties of Chile
- Treaties of Colombia
- Treaties of the Republic of the Congo
- Treaties of Costa Rica
- Treaties of Ivory Coast
- Treaties of Croatia
- Treaties of Cuba
- Treaties of Cyprus
- Treaties of Czechoslovakia
- Treaties of the Czech Republic
- Treaties of Zaire
- Treaties of Denmark
- Treaties of the Dominican Republic
- Treaties of Ecuador
- Treaties of Egypt
- Treaties of El Salvador
- Treaties of the Ethiopian Empire
- Treaties of Fiji
- Treaties of Finland
- Treaties of the French Fourth Republic
- Treaties of Gabon
- Treaties of Georgia (country)
- Treaties of East Germany
- Treaties of West Germany
- Treaties of Ghana
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Greece
- Treaties of Guatemala
- Treaties of Guinea
- Treaties of the Hungarian People's Republic
- Treaties of Haiti
- Treaties of Iceland
- Treaties of India
- Treaties of Indonesia
- Treaties of Ireland
- Treaties of Israel
- Treaties of Italy
- Treaties of Jamaica
- Treaties of Jordan
- Treaties of Kazakhstan
- Treaties of Kyrgyzstan
- Treaties of the Kingdom of Laos
- Treaties of Latvia
- Treaties of Lebanon
- Treaties of Lesotho
- Treaties of the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Treaties of Luxembourg
- Treaties of Madagascar
- Treaties of Malawi
- Treaties of Mali
- Treaties of Malta
- Treaties of Mauritania
- Treaties of Mauritius
- Treaties of Mexico
- Treaties of the Mongolian People's Republic
- Treaties of Montenegro
- Treaties of Morocco
- Treaties of Nepal
- Treaties of the Netherlands
- Treaties of New Zealand
- Treaties of Nicaragua
- Treaties of Niger
- Treaties of Nigeria
- Treaties of Norway
- Treaties of the Dominion of Pakistan
- Treaties of the State of Palestine
- Treaties of Papua New Guinea
- Treaties of Paraguay
- Treaties of Peru
- Treaties of the Philippines
- Treaties of the Polish People's Republic
- Treaties of South Korea
- Treaties of Moldova
- Treaties of the Socialist Republic of Romania
- Treaties of the Soviet Union
- Treaties of Rwanda
- Treaties of Senegal
- Treaties of Serbia and Montenegro
- Treaties of Yugoslavia
- Treaties of Sierra Leone
- Treaties of Slovakia
- Treaties of Slovenia
- Treaties of the Solomon Islands
- Treaties of Spain
- Treaties of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Treaties of Eswatini
- Treaties of Sweden
- Treaties of Tajikistan
- Treaties of Thailand
- Treaties of North Macedonia
- Treaties of Trinidad and Tobago
- Treaties of Tunisia
- Treaties of Turkey
- Treaties of Turkmenistan
- Treaties of Uganda
- Treaties of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
- Treaties of the United Kingdom
- Treaties of Tanzania
- Treaties of the United States
- Treaties of Uzbekistan
- Treaties of Venezuela
- Treaties of South Yemen
- Treaties of Zambia
- Treaties of Zimbabwe
- 1953 in New York City
- Treaties extended to Akrotiri and Dhekelia
- Treaties extended to Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla
- Treaties extended to Bermuda
- Treaties extended to the British Antarctic Territory
- Treaties extended to the British Indian Ocean Territory
- Treaties extended to the British Virgin Islands
- Treaties extended to the Cayman Islands
- Treaties extended to the Falkland Islands
- Treaties extended to Gibraltar
- Treaties extended to Guernsey
- Treaties extended to the Isle of Man
- Treaties extended to Jersey
- Treaties extended to Montserrat
- Treaties extended to the Pitcairn Islands
- Treaties extended to Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Treaties extended to South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Treaties extended to the Turks and Caicos Islands
- Treaties extended to Greenland
- Treaties extended to the Faroe Islands
- Treaties extended to Surinam (Dutch colony)
- Treaties extended to the British Solomon Islands
- Treaties extended to Brunei (protectorate)
- Treaties extended to Swaziland (protectorate)
- Treaties extended to the Kingdom of Tonga (1900–1970)
- Treaties extended to British Hong Kong
- Treaties extended to British Antigua and Barbuda
- Treaties extended to British Dominica
- Treaties extended to British Saint Lucia
- Treaties extended to British Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Treaties extended to British Grenada
- Treaties extended to British Honduras
- Treaties extended to the Colony of the Bahamas
- Treaties extended to West Berlin
- 1953 in women's history
