Double bell euphonium
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2017) |
 | |
| Brass instrument | |
|---|---|
| Classification | |
| Hornbostel–Sachs classification | 423.232 & 423.233 (Valved aerophone sounded by lip vibration) |
| Developed | Until 1960 |
| Playing range | |
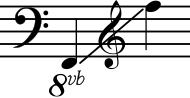 | |
| Related instruments | |

The double bell euphonium is a duplex instrument based on the euphonium. The larger bell produces the mellow tone of a standard euphonium; the second smaller bell has a brighter tone, similar to a baritone horn or valve trombone. The instrument is sometimes dismissed as a novelty, but has had some enthusiastic adherents, including few professional musicians using it as their sole or primary instrument. The smaller bell can give more appropriate tone in the higher range of the instrument. The two bells can also be used for special effects, such as echoes, and using the distinctly different tone of the two bells for a single musician to give the effect of call and response.
Construction
[edit]The last valve on the horn (either the fourth or the fifth, depending upon the model) is used to switch the sound from the main bell to the secondary bell. Both bells cannot play at the same time because each bell usually has its own tuning slide loop, such that they can be matched adequately for consistent performance. Unlike the double horn, there is only one set of valve slides with a double bell euphonium, so only the basic pitch of the two bells can be matched.
History
[edit]The double bell euphonium was mass-produced starting in the 1880s, first produced by the C.G. Conn company in the United States[1] Other major U.S. brass-instrument manufacturers soon began production of similar instruments. The instrument was first popularized by Italian-born euphonium virtuoso Miguel Raffayolo, soloist with the Patrick Gilmore band, documented in American newspapers by 1880.[2] Harry Whittier, also of Gilmore's band, took up the instrument by 1888; the John Philip Sousa band added the instrument the following year [Bone Paull and Morris, p. 12], with other US brass bands following the example. Peak production of the instrument was from about the 1890s into the 1920s, although it was never one of the more popular brass instruments. In the 19th century press, Raffayolo is described as inventor the instrument, known then as the "Euphonium Trombone."[3]
Decline
[edit]The last double bell euphoniums were made around 1960. In practice, most double bell models ended up being used with the large bell only, effectively a very heavy single bell euphonium. About the second bell, famous euphonium soloist Arthur W. Lehman once said during a Marine Band concert, "We use it to hold our white gloves when we are not wearing them."[4]
Soloists
[edit]Simone Mantia used to play a double-bell euphonium as a virtuoso. While part of the Sousa and Pryor Bands, Simone at times favored the double-belled euphonium and he even composed "Priscilla" (in tribute to Jane Priscilla Sousa), a double-bell euphonium solo.
References
[edit]- ^ "Conn Selmer Homepage". November 14, 2011. Archived from the original on November 14, 2011.
- ^ "News and Gossip." Danville (NY) Adviser, 27 May 1880.
- ^ "Music Loved by the Masses." New York Press, 29 December 1889. ("The...instrument was invented by the versatile Signor Raffayolo and is a euphonium with a trombone bell attached so that by pressing a piston the trombone bell may be used.")
- ^ Long, Joshua E. (8 November 2012). "Double Bell Euphonium, I Beg Your Pardon?" (PDF). University of Hartford, Hartt School. p. 11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2016. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
Bibliography
[edit]- Bone, Lloyd E.; Paull, Eric; Morris, R. Winston. Guide to the Euphonium Repertoire: the Euphonium Source Book.
