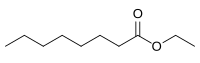
Ethyl octanoate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethyl octanoate | |
| Other names
Ethyl caprylate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.078 |
| EC Number | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H20O2 | |
| Molar mass | 172.268 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.86215 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −48 °C (−54 °F; 225 K)[4] |
| Boiling point | 208 °C (406 °F; 481 K)[4] |
| 70.1 mg/L [2][3] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.2 mbar at 20 °C; 3.18 mbar at 60 °C[4] |
| Viscosity | 1.411 mPa·s[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 79 °C (174 °F; 352 K)[4] |
| 325 °C (617 °F; 598 K)[4] | |
| Explosive limits | 0.7 - Vol.%[4] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
25.96 g/kg (rat, oral)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ethyl octanoate, also known as ethyl caprylate, is a fatty acid ester formed from caprylic acid and ethanol. A colorless liquid at room temperature, it has the semi-developed formula of CH3(CH2)6COOCH2CH3, and is used in food industries as a flavoring and in the perfume industry as a scent additive. It is present in many fruits and alcoholic beverages, and has a strong odor of fruit and flowers. It is used in the creation of synthetic fruity scents.[5]
Synthesis
[edit]Ethyl octanoate can be synthesized from caprylic acid and ethanol via a classic Fischer–Speier esterification.
- CH3(CH2)6COOH + CH3CH2OH ⇌ CH3(CH2)6COOCH2CH3 + H2O
Equilibrium can be shifted towards the right side of the equation through removal of water.
Uses
[edit]Ethyl octanoate does not see widespread use due to the greater availability of reasonably similar esters such as ethyl acetate. However, there are certain applications where it fills a niche. Ethyl octanoate has a strong odor of fruit and flowers and a taste of apricot, and as such it can be used as a flavoring or to create scents. It sees some use as a cleaning agent.[6]
Ethyl octanoate also sees incidental use. It is found in some wines, where overall ester concentration and composition is considered important to the flavor and aroma profile.[7]
Safety
[edit]Like many esters, ethyl octanoate is not considered to be toxic. LD50 in rats is 25.96 g/kg. Though it has a low explosive limit of only 0.67 vol%, it is also weakly volatile, with a vapor pressure of only 0.2 mbar at room temperature. Ethyl octanoate is combustible.
References
[edit]- ^ a b Sheu, Yaw-Wen; Tu, Chein-Hsiun (2006). "Densities and Viscosities of Binary Mixtures of Isoamyl Acetate, Ethyl Caproate, Ethyl Benzoate, Isoamyl Butyrate, Ethyl Phenylacetate, and Ethyl Caprylate with Ethanol at T = (288.15, 298.15, 308.15, and 318.15) K". Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data. 51 (2): 496–503. doi:10.1021/je050389b.
- ^ a b Ethyl octanoate from PubChem, accessed 30 December 2023
- ^ Mark, James E. (2007). Physical Properties of Polymer Handbook (2nd ed.). Springer. p. 294. ISBN 978-0387690025. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f Record of Ethyl octanoate in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 10 August 2010.
- ^ Fahlbusch, Karl-Georg; Hammerschmidt, Franz-Josef; Panten, Johannes; Pickenhagen, Wilhelm; Schatkowski, Dietmar; Bauer, Kurt; Garbe, Dorothea; Surburg, Horst (15 January 2003). "Flavors and Fragrances". Flavors and Flagrances. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ "Ethyl octanoate - Substance Information - ECHA". echa.europa.eu. Retrieved 2021-07-12.
- ^ Marais, J. et al. (2003) http://www.sawislibrary.co.za/dbtextimages/MaraisJ10.pdf "Effect of Different Wine-Making Techniques on the Composition and Quality of Pinotage Wine. I. Low-Temperature Skin Contact Prior to Fermentation"
