LGBTQ rights by country or territory

| Same-sex intercourse illegal. Penalties: | |
Prison; death not enforced | |
Death under militias | Prison, with arrests or detention |
Prison, not enforced1 | |
| Same-sex intercourse legal. Recognition of unions: | |
Extraterritorial marriage2 | |
Limited foreign | Optional certification |
None | Restrictions of expression, not enforced |
Restrictions of association with arrests or detention | |
1No imprisonment in the past three years[timeframe?] or moratorium on law.
2Marriage not available locally. Some jurisdictions may perform other types of partnerships.

| | Neither | States which did not support either declaration |
| | Non-member states | States that are not voting members of the United Nations |
| | Oppose | States which supported an opposing declaration in 2008 and continued their opposition in 2011 |
| | Subsequent member | South Sudan, did not exist in 2008 |
| | Support | States which supported the LGBT rights declaration in the General Assembly or on the Human Rights Council in 2008 or 2011 |
| Part of a series on |
| LGBTQ rights |
|---|
 |
| Lesbian ∙ Gay ∙ Bisexual ∙ Transgender ∙ Queer |
|
|
| Rights |
|---|
 |
| Theoretical distinctions |
| Human rights |
| Rights by beneficiary |
| Other groups of rights |
|
| Part of a series on |
| LGBTQ topics |
|---|
|
|
| Part of a series on |
| Discrimination |
|---|
 |
Rights affecting lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people vary greatly by country or jurisdiction—encompassing everything from the legal recognition of same-sex marriage to the death penalty for homosexuality.

Notably, as of May 2024[update], 37 countries recognize same-sex marriage.[1][2] By contrast, not counting non-state actors and extrajudicial killings, only two countries are believed to impose the death penalty on consensual same-sex sexual acts: Iran and Afghanistan.[3][4][5][6] The death penalty is officially law, but generally not practiced, in Mauritania, Saudi Arabia, Somalia (in the autonomous state of Jubaland) and the United Arab Emirates.[7][8] LGBT people also face extrajudicial killings in the Russian region of Chechnya.[9] Sudan rescinded its unenforced death penalty for anal sex (hetero- or homosexual) in 2020. Fifteen countries have stoning on the books as a penalty for adultery, which (in light of the illegality of gay marriage in those countries) would by default include gay sex, but this is enforced by the legal authorities in Iran and Nigeria (in the northern third of the country).[10][11][12][13][14]
In 2011, the United Nations Human Rights Council passed its first resolution recognizing LGBT rights, following which the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights issued a report documenting violations of the rights of LGBT people, including hate crimes, criminalization of homosexual activity, and discrimination. Following the issuance of the report, the United Nations urged all countries which had not yet done so to enact laws protecting basic LGBT rights.[15][16] A 2022 study found that LGBT rights (as measured by ILGA-Europe's Rainbow Index) were correlated with less HIV/AIDS incidence among gay and bisexual men independently of risky sexual behavior.[17]
The 2023 Equaldex Equality Index ranks the Nordic countries, Chile, Uruguay, Canada, the Benelux countries, Spain, Andorra, and Malta among the best for LGBT rights. The index ranks Nigeria, Yemen, Brunei, Afghanistan, Somalia, Mauritania, Palestine, and Iran among the worst.[18][better source needed] Asher & Lyric ranked Canada, Sweden, and the Netherlands as the three safest nations for LGBT people in its 2023 index.[19]
Scope of laws
Laws that affect LGBT people include, but are not limited to, the following:
- laws concerning the recognition of same-sex relationships, including same-sex marriage, civil unions, and domestic partnerships
- laws concerning same-sex parenting, including same-sex adoption
- anti-discrimination laws in employment, housing, education, public accommodations
- anti-bullying legislation to protect LGBT children at school
- hate crime laws imposing enhanced criminal penalties for prejudice-motivated violence against LGBT people
- bathroom bills affecting access to sex-segregated facilities by transgender people
- laws related to sexual orientation and military service
- laws concerning access to assisted reproductive technology
- sodomy laws that penalize consensual same-sex sexual activity. These may or may not target homosexuals, males or males and females, or leave some homosexual acts legal.
- adultery laws that same-sex couples are subject to
- age of consent laws that may impose higher ages for same-sex sexual activity
- laws regarding donation of blood, corneas, and other tissues by men who have sex with men
- laws concerning access to gender-affirming surgery and gender-affirming hormone replacement therapy
- legal recognition and accommodation of the affirmed gender.
History of LGBT-related laws
Ancient India
Ayoni or non-vaginal sex of all types is punishable in the Arthashastra. Homosexual acts are, however, treated as a smaller offence punishable by a fine, while unlawful heterosexual sex carries much harsher punishment. The Dharmsastras, especially the later ones, prescribe against non-vaginal sex like the Vashistha Dharmasutra. The Yājñavalkya Smṛti prescribes fines for such acts including those with other men. Manusmriti prescribes light punishments for such acts.[20][21] Vanita states that the verses about punishment for a sex between female and a maiden is due to its strong emphasis on a maiden's sexual purity.[22]
Ancient Israel
The ancient Law of Moses (the Torah) forbids people from lying with people of the same sex (i.e., from having intercourse) in Leviticus 18 and gives a story of attempted homosexual rape in Genesis 19, in the story of Sodom and Gomorrah, after which the cities were soon destroyed with "brimstone and fire, from the Lord"[23][24] and the death penalty was prescribed to its inhabitants – and to Lot's wife, who was turned into a pillar of salt because she turned back to watch the cities' destruction.[25][26] In Deuteronomy 22:5, cross-dressing is condemned as "abominable".[27][28]
Assyria
In Assyrian society, sex crimes were punished identically whether they were homosexual or heterosexual.[29] An individual faced no punishment for penetrating someone of equal social class, a cult prostitute, or with someone whose gender roles were not considered solidly masculine.[29] Such sexual relations were even seen as good fortune, with an Akkadian tablet, the Šumma ālu, reading, "If a man copulates with his equal from the rear, he becomes the leader among his peers and brothers".[30][31] However, homosexual relationships with fellow soldiers, slaves, royal attendants, or those where a social better was submissive or penetrated, were treated as bad omens.[32][33]
Middle Assyrian Law Codes dating 1075 BC has a particularly harsh law for homosexuality in the military, which reads: "If a man have intercourse with his brother-in-arms, they shall turn him into a eunuch."[34][35] A similar law code reads, "If a seignior lay with his neighbor, when they have prosecuted him (and) convicted him, they shall lie with him (and) turn him into a eunuch". This law code condemns a situation that involves homosexual rape. Any Assyrian male could visit a prostitute or lie with another male, just as long as false rumors or forced sex were not involved with another male.[36]
Ancient Rome
In ancient Rome, the bodies of citizen youths were strictly off-limits, and the Lex Scantinia imposed penalties on those who committed a sex crime (stuprum) against a freeborn male minor.[37] Acceptable same-sex partners were males excluded from legal protections as citizens: slaves, male prostitutes, and the infames, entertainers or others who might be technically free but whose lifestyles set them outside the law.
A male citizen who willingly performed oral sex or received anal sex was disparaged, but there is only limited evidence of legal penalties against these men.[38] In courtroom and political rhetoric, charges of effeminacy and passive sexual behaviors were directed particularly at "democratic" politicians (populares) such as Julius Caesar and Mark Antony.[39]
Roman law addressed the rape of a male citizen as early as the 2nd century BC when it was ruled that even a man who was "disreputable and questionable" had the same right as other citizens not to have his body subjected to forced sex.[40] A law probably dating to the dictatorship of Julius Caesar defined rape as forced sex against "boy, woman, or anyone"; the rapist was subject to execution, a rare penalty in Roman law.[41] A male classified as infamis, such as a prostitute or actor, could not as a matter of law be raped, nor could a slave, who was legally classified as property; the slave's owner, however, could prosecute the rapist for property damage.[42]
In the Roman army of the Republic, sex among fellow soldiers violated the decorum against intercourse with citizens and was subject to harsh penalties, including death,[43] as a violation of military discipline.[44] The Greek historian Polybius (2nd century BC) lists deserters, thieves, perjurers, and "...on young men who have abused their persons" as subject to the fustuarium, clubbing to death.[45] Ancient sources are most concerned with the effects of sexual harassment by officers, but the young soldier who brought an accusation against his superior needed to show that he had not willingly taken the passive role or prostituted himself.[46] Soldiers were free to have relations with their male slaves;[47] the use of a fellow citizen-soldier's body was prohibited, not homosexual behaviors per se.[48] By the late Republic and throughout the Imperial period, there is increasing evidence that men whose lifestyle marked them as "homosexual" in the modern sense served openly.[49]
Although Roman law did not recognize marriage between men, and in general Romans regarded marriage as a heterosexual union with the primary purpose of producing children, in the early Imperial period some male couples were celebrating traditional marriage rites. Juvenal remarks with disapproval that his friends often attended such ceremonies.[50] The emperor Nero had two marriages to men, once as the bride (with a freedman Pythagoras) and once as the groom. His consort Sporus appeared in public as Nero's wife wearing the regalia that was customary for the Roman empress.[51]
Apart from measures to protect the prerogatives of citizens, the prosecution of homosexuality as a general crime began in the 3rd century of the Christian era when male prostitution was banned by Philip the Arab. By the end of the 4th century, after the Roman Empire had come under Christian rule, passive homosexuality was punishable by burning.[52] "Death by sword" was the punishment for a "man coupling like a woman" under the Theodosian Code.[53] Under Justinian, all same-sex acts, passive or active, no matter who the partners are, were declared contrary to nature and punishable by death.[54]
British Empire
The United Kingdom introduced anti-homosexuality laws throughout its colonies, particularly in the 19th century when the British Empire was at its peak.[55] As of 2018, more than half of the 71 countries that criminalised homosexuality were former British colonies or protectorates.[56]
Netherlands
In 2001, the Netherlands was the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage.[57]
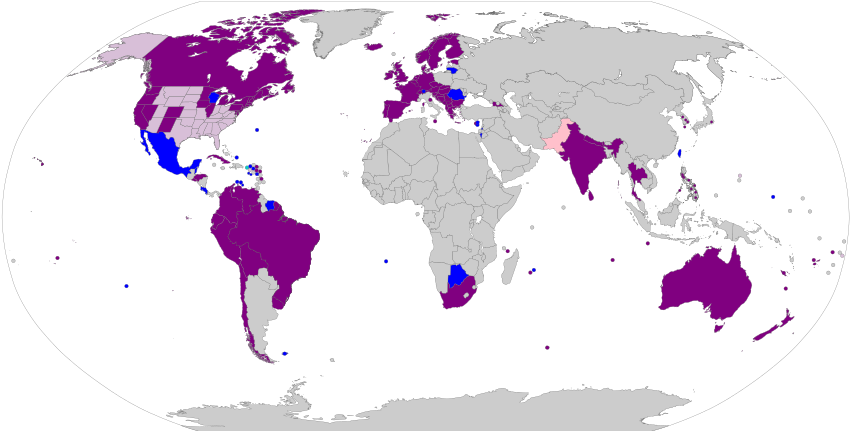
Global LGBT rights maps
Note that for simplicity the table below does not distinguish between 'legal' and 'lawful'. An action can only be legal or illegal where a specific law has been passed.
| Laws regarding same-sex sexuality by country or territory | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Worldwide laws regarding same-sex intercourse, unions and expression
1No imprisonment in the past three years[timeframe?] or moratorium on law. 2Marriage not available locally. Some jurisdictions may perform other types of partnerships. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LGBT rights at the United Nations |
|---|
 Support Countries which have signed a General Assembly declaration of LGBT rights or sponsored the Human Rights Council's 2011 resolution on LGBT rights (96 members) Oppose Countries which signed a 2008 statement opposing LGBT rights (initially 57 members, now 54 members after withdrawal of Fiji, Rwanda and Sierra Leone) Neither Countries which, as regards the UN, have expressed neither official support nor opposition to LGBT rights (44 members) |
| Homosexual "propaganda" and "morality" laws by country or territory |
|---|
 Countries or territories that do not have homosexual "propaganda" or "morality" laws Fine[58] Imprisonment |
| Decriminalization of same-sex sexual intercourse by country or territory |
|---|
| Equalization of age of consent laws for same-sex couples by country or territory |
|---|
 1790–1829 1830–1839 1840–1859 1860–1869 1870–1879 1880–1889 1890–1929 1930–1939 1940–19491 1950–1959 1960–1969 1970–1979 1980–1989 1990–1999 2000–2009 2010–2019 2020–present Unknown date for equal age of consent laws for opposite and same-sex couples No consent laws/equal age of consent laws always equal for opposite and same-sex couples Unequal age of consent laws for same-sex couples Same-sex sexual intercourse illegal 1During World War II, Nazi Germany annexed or occupied territory, extending Germany's laws against same-sex sexual intercourse. Age of consent was previously equalized for same-sex couples in the following countries or territories before the war: Belluno (legal in 1890), Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol (legal in 1890), Friuli-Venezia Giulia (legal in 1890),[59][60] and Poland (decriminalized in 1932).[61][62] During World War II Germany did not consistently enforce anti-homosexual laws in all occupied countries.[63][64] All countries and territories listed that were annexed or established into reichskommissariats by Nazi Germany during World War II were restored as independent countries or reincorporated into their previous countries during or after the war and thus re-legalized equal age of consent laws for same-sex couples in those areas.[citation needed] |
| Legal status of same-sex marriage |
|---|
 Marriage open to same-sex couples Mixed jurisdiction: marriage recognized by the state but not by tribal government for residents who are members of the tribe Legislation or binding domestic court ruling establishing same-sex marriage, but marriage is not yet provided for Same-sex marriage recognized with full rights when performed in certain other jurisdictions Civil unions or domestic partnerships Limited legal recognition Local certification without legal force Limited recognition of marriage performed in certain other jurisdictions (residency rights for spouses) Other countries where same-sex unions are not legally recognized |
| Legal status of adoption by same-sex couples by country or territory |
|---|
| LGBT service in national militaries by country or territory |
|---|
| Employment discrimination laws by sexual orientation or gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
 Sexual orientation and gender identity: all employment Sexual orientation with anti–employment discrimination ordinance and gender identity solely in public employment Sexual orientation: all employment Gender identity: all employment Sexual orientation and gender identity: federal public employment and federal contractors Sexual orientation and gender identity: public employment Sexual orientation: public employment No national-level employment laws covering sexual orientation or gender identity |
| Anti-discrimination laws covering goods and services by sexual orientation and/or gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
 Sexual orientation and gender identity covered Sexual orientation covered Gender identity covered No national or local level anti-discrimination laws covering sexual orientation and/or gender identity in goods and services |
| Constitutional discrimination laws by sexual orientation and/or gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
| LGBT hate crime laws by country or territory |
|---|
| Incitement to hatred based on sexual orientation and gender identity prohibited by country or territory |
|---|
| Legal status on conversion therapy for minors on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity by country or territory |
|---|
 Ban on conversion therapy on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity De facto ban on conversion therapy No ban on conversion therapy |
| Immigration equality by country or territory[citation needed] |
|---|
| Bans on same-sex unions by country or territory |
|---|
 No specific prohibition of same-sex marriages or unions Same-sex marriage banned by secular constitution Same-sex marriage banned by constitutionally mandated religious law |
| Blood donation policies for men who have sex with men by country or territory |
|---|
 Men who have sex with men may donate blood; No deferral Men who have sex with men may donate blood; Temporary deferral Men who have sex with men may not donate blood; Permanent deferral No Data |
| Blood donation policies for female sex partners of men who have sex with men by country or territory |
|---|
 Female sex partners of men who have sex with men may donate blood; No deferral Female sex partners of men who have sex with men may donate blood; Temporary deferral Female sex partners of men who have sex with men may not donate blood; Permanent deferral No Data |
| Laws concerning gender identity-expression by country or territory |
|---|
| Legal recognition of non-binary genders and third gender |
|---|
Timeline
LGBT-related laws by country or territory
Note: A country in this list is to be presumed to have equalized the age of consent at the same time as it decriminalized homosexual acts, unless otherwise noted.
Africa
| List of countries or territories by LGBT rights in Africa | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This table:
Northern Africa
Western Africa
Central Africa
Eastern Africa
Indian Ocean states
Southern Africa
|
Americas
| List of countries or territories by LGBT rights in the Americas | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tables:
North America
Central America
Caribbean
South America
|
Antarctica
Asia
| List of countries or territories by LGBT rights in Asia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This table:
North Asia
Central Asia
West Asia
South Asia
East Asia
Southeast Asia
|
Europe
| List of countries or territories by LGBT rights in Europe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tables:
European Union
Central Europe
Eastern Europe
Northern Europe
Southern Europe
Western Europe
|
Oceania
| List of countries or territories by LGBT rights in Oceania | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tables:
Australasia
Melanesia
Micronesia
Polynesia
|
See also
- Capital punishment for non-violent offenses
- Criminalization of homosexuality
- Decriminalization of homosexuality
- Discrimination against LGBTQ people
- Human rights
- Legal status of transgender people
- Legality of conversion therapy
- LGBTQ people in prison
- Minority rights
- Societal attitudes toward homosexuality
Notes
- ^ Legal nationwide, except in the province of Aceh
- ^ De facto illegal in Chechnya
- ^ In Taiwan, gender change is not explicitly stated in any law; instead it is permitted by an executive order published by the Ministry of the Interior, which dictates that sex reassignment surgeries are required before gender change. In 2021 a judgement by the Taipei High Administrative Court[435] ruled that the executive order above was unconstitutional and therefore the defendant (district household registration office) must allow the plaintiff to change their gender. The judgement was finalized since the defendant did not appeal. However, since rulings in Taiwan are generally not precedential, said judgement only applies to the plaintiff and does not bind other cases nor the executive branch.
- ^ Except for the settlements Marawi and M'lang.
- ^ In January 2019, a lower administrative court in Warsaw ruled that the language in Article 18 of the Constitution does not explicitly ban same-sex marriage.[506]
References
- ^ "Countries that allow same-sex marriage". timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 15 June 2023.
- ^ "Same-Sex Marriage Around the World". Pew Research Center. 9 June 2023. Retrieved 26 October 2023.
- ^ "LGBT People in Afghanistan After the Taliban Takeover". Human Rights Watch. 26 January 2022. Retrieved 15 November 2022.
- ^ Ahmady, Kameel Et al 2020: Forbidden Tale (A comprehensive study on lesbian, gay, bisexuals (LGB) in Iran). AP Lambert Academic Publishing, Germany.
- ^ Kumar, Ruchi (26 January 2022). "Lives of LGBTQ+ Afghans 'dramatically worse' under Taliban rule, finds survey". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 10 February 2024.
- ^ 'They Torture And Kill Us': Gay Afghan Men Fear For Lives Under The Taliban, 7 November 2022, retrieved 10 February 2024
- ^ "United Arab Emirates". Human Dignity Trust. 13 February 2019. Retrieved 10 February 2024.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia: Man sentenced for homosexuality. Amnesty" (PDF).
- ^ "He Was Targeted in Chechnya for Being Gay. Now, He's Being Hunted in Europe". Time. Retrieved 10 February 2024.
- ^ Hazzad, Ardo (2 July 2022). "Nigerian Islamic court orders death by stoning for men convicted of homosexuality". Reuters. Retrieved 13 July 2022.
- ^ Milton, Josh (5 July 2022). "Three men sentenced to death by stoning for being gay". PinkNews. Retrieved 13 July 2022.
- ^ "Ahmady, Kameel, LGBT In Iran: The Homophobic Laws and Social System in Islamic Republic of Iran, PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt / Egyptology, Volume 18, Pages 1446- 1464, Issue, No. 18 (2021)". PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt / Egyptology.
- ^ Mendos, Lucas Ramón (2019). State-Sponsored Homophobia 2019 (PDF) (13th ed.). Geneva: ILGA. p. 15. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 December 2019. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
- ^ Dick, Samantha (4 April 2019). "Brunei not the only place LGBTQI can be killed for who they love". The New Daily. Archived from the original on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ^ Dougherty, Jill (17 June 2011). "U.N. council passes gay rights resolution". CNN. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ "UN issues first report on human rights of gay and lesbian people". United Nations. 15 December 2011. Archived from the original on 7 January 2018. Retrieved 20 September 2018.
- ^ Stojanovski, Kristefer; King, Elizabeth J.; Amico, K. Rivet; Eisenberg, Marisa C.; Geronimus, Arline T.; Baros, Sladjana; Schmidt, Axel J. (2022). "Stigmatizing Policies Interact with Mental Health and Sexual Behaviours to Structurally Induce HIV Diagnoses Among European Men Who Have Sex with Men". AIDS and Behavior. 26 (10): 3400–3410. doi:10.1007/s10461-022-03683-9. PMC 9556380. PMID 35434774. S2CID 248220063.
- ^ Staff (1 January 2023). "LGBT Equality Index: The Most LGBT-Friendly Countries in the World". Equaldex. Retrieved 5 March 2023.
- ^ "The 203 Worst (& Safest) Countries for LGBTQ+ Travel in 2023". Asher & Lyric. 5 June 2023. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ Ali, Daud (2012). "Censured sexual acts and early medieval society in India". In Reyes, Raquel A. G.; Clarence-Smith, William G. (eds.). Sexual Diversity in Asia, c. 600–1950. Routledge. pp. 50–51. ISBN 978-0415600590. LCCN 2011049072. Archived from the original on 14 June 2020. Retrieved 16 August 2019.
- ^ Vanita, Ruth (20 October 2008). Same-Sex Love in India. Penguin Books Limited. ISBN 978-81-8475-969-3. Archived from the original on 4 August 2020. Retrieved 12 May 2024.
- ^ Vanita, Ruth (2005). "Introduction". Love's Rite: Same-Sex Marriage in India and the West. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 32. ISBN 978-1403970381. LCCN 2005047571. Archived from the original on 4 August 2020. Retrieved 16 August 2019.
- ^ Fields, Weston W. (1997). Sodom and Gomorrah: History and Motif in Biblical Narrative. A&C Black. ISBN 978-0567062611. Archived from the original on 17 February 2022. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ Loader, J. A. (1990). A Tale of Two Cities: Sodom and Gomorrah in the Old Testament, Early Jewish and Early Christian Traditions. Peeters Publishers. ISBN 9789024253333. LCCN 91207650. Archived from the original on 7 May 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ STRAUSS, Gerhard Friedrich Abraham; SLEE, Jane Mary (1837). On Restitution; Lot and his Wife; The Rich Man; Christian Composure; [sermons] by ... F. S. ... translated from the German, by Miss Slee. Archived from the original on 1 April 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ R. W (1607). Lot's Wife. A sermon at Paule's Crosse [on Luke xvii. 32. By R. W., i.e. R. Wilkinson.]. Archived from the original on 1 April 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ Upson-Saia, Kristi; Daniel-Hughes, Carly; Batten, Alicia J., eds. (2016) [2014]. "Cross-dressing, Masculinity, and the Social Body in Late Antiquity". Dressing Judeans and Christians in Antiquity. Routledge. p. 39. ISBN 978-1317147978. LCCN 2014000554. Archived from the original on 1 April 2021. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ Bullough, Vern L.; Bullough, Bonnie (1993). "Introduction". Cross Dressing, Sex, and Gender. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. x. ISBN 9780812214314. LCCN 92032030. Archived from the original on 1 April 2021. Retrieved 18 October 2020.
- ^ a b Nissinen, Martti (2004). Homoeroticism in the Biblical World: A Historical Perspective. Fortress Press. pp. 24–28. ISBN 978-1-4514-1433-2. Archived from the original on 14 April 2020. Retrieved 12 May 2024.
- ^ Greenberg, David F. (15 August 1990). The Construction of Homosexuality. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 9780226306285. Archived from the original on 28 June 2014. Retrieved 31 July 2018.
- ^ "Homosexuality in the Ancient Near East, beyond Egypt by Bruce Gerig in the Ancient Near East, beyond Egypt". epistle.us. Archived from the original on 2 October 2018. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- ^ Pritchard, p. 181.
- ^ Gay Rights Or Wrongs: A Christian's Guide to Homosexual Issues and Ministry, by Mike Mazzalonga, 1996, p.11
- ^ Halsall, Paul. "The Code of the Assura". Internet History Sourcebooks Project. Fordham University. Archived from the original on 11 September 2015. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ^ Wilhelm, Amara Das (18 May 2010). Tritiya-Prakriti: People of the Third Sex. Xlibris Corporation. ISBN 9781453503164. Archived from the original on 17 February 2022. Retrieved 22 March 2017.
- ^ G. R. Driver and J. C. Miles, The Assyrian Laws (Oxford, Clarendon Press [1935]), 71.
- ^ Plutarch, Moralia 288a; Thomas Habinek, "The Invention of Sexuality in the World-City of Rome," in The Roman Cultural Revolution (Cambridge University Press, 1997), p. 39; Richlin, "Not before Homosexuality," pp. 545–546. Scholars disagree as to whether the Lex Scantinia imposed the death penalty or a hefty fine.
- ^ Williams, Roman Homosexuality, pp. 214–215; Richlin, "Not before Homosexuality," passim.
- ^ Catharine Edwards, The Politics of Immorality in Ancient Rome (Cambridge University Press, 1993), pp. 63–64.
- ^ As recorded in a fragment of the speech De Re Floria by Cato the Elder (frg. 57 Jordan = Aulus Gellius 9.12.7), noted and discussed by Richlin, "Not before Homosexuality," p. 561.
- ^ Richlin, "Not before Homosexuality," pp. 562–563. See also Digest 48.5.35 [34] on legal definitions of rape that included boys.
- ^ Under the Lex Aquilia. See McGinn, Prostitution, Sexuality, and the Law in Ancient Rome, p. 314.
- ^ McGinn, Prostitution, Sexuality and the Law in Ancient Rome, p. 40.
- ^ Sara Elise Phang, Roman Military Service: Ideologies of Discipline in the Late Republic and Early Principate (Cambridge University Press, 2008), p. 93.
- ^ Polybius. "The Histories Fragments of Book VI". Retrieved 12 May 2024.
- ^ Phang, The Marriage of Roman Soldiers, pp. 280–285.
- ^ Phang, The Marriage of Roman Soldiers, p. 3.
- ^ Williams, Roman Homosexuality, p. 112 et passim.
- ^ Phang, Sara Elise (13 May 2024). The Marriage of Roman Soldiers. BRILL. pp. 285–292. ISBN 978-90-04-12155-3. Archived from the original on 5 August 2020.
- ^ Juvenal, Satire 2; Williams, Roman Homosexuality, p. 28.
- ^ Suetonius Life of Nero 28–29; Williams, Roman Homosexuality, p. 279ff.
- ^ Michael Groneberg, "Reasons for Homophobia: Three Types of Explanation," in Combatting Homophobia: Experiences and Analyses Pertinent to Education (LIT Verlag, 2011), p. 193.
- ^ Codex Theodosianus 9.7.3 (4 December 342), introduced by the sons of Constantine in 342.
- ^ Groneberg, "Reasons for Homophobia," p. 193.
- ^ Kirby, Michael (2013). "The sodomy offence: England's least lovely criminal law export?" (PDF). Human Rights, Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity in the Commonwealth: Struggles for Decriminalisation and Change. London: School of Advanced Study, University of London. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- ^ Ben Westcott (12 September 2018). "The homophobic legacy of the British Empire". CNN. Archived from the original on 8 October 2020. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- ^ Homosexuality and the Law: A Dictionary. Abc-Clio. 2001. ISBN 9781576072677.
- ^ In the Russian law "for the Purpose of Protecting Children from Information Advocating for a Denial of Traditional Family Values", foreigners may be arrested and detained for up to 15 days then deported, or fined up to 5,000 rubles and deported.
- ^ Dama, Francesco (July 2022). "A brief history of homosexuality in Italy from ancient Rome to today". Italy Segreta. Archived from the original on 16 July 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Same sex marriage in Italy: an overview and current status". Wanted in Rome. 16 February 2024. Archived from the original on 16 February 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Ash, Lucy (20 September 2020). "Inside Poland's 'LGBT-free zones'". BBC. Archived from the original on 20 September 2020. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Kottasova, Ivana (1 July 2021). "Eastern Europe was once a world leader on gay rights. Then it ran out of scapegoats". CNN. Archived from the original on 1 July 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Regis Schlagdenhauffen, ed. (August 2018). "Queer in Europe during the second World War". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2024.
- ^ Robertson, Stephen. "Age of Consent Laws". Children & Youth in History. Archived from the original on 20 June 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Carroll, Aengus; Mendos, Lucas Ramón (May 2017). "State Sponsored Homophobia 2017: A world survey of sexual orientation laws: criminalisation, protection and recognition" (PDF). ILGA.
- ^ "Algeria". Human Dignity Trust. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- ^ "Algeria: Treatment of homosexuals by society and government authorities; protection available including recourse to the law for homosexuals who have been subject to ill-treatment (2005-2007)". Refworld. Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada. 30 July 2007. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi bj bk bl bm bn bo bp bq br bs bt bu bv bw bx by bz ca cb cc cd ce cf cg ch ci cj ck cl cm cn co cp cq cr cs ct cu cv cw cx cy cz da db dc dd de df dg dh di dj dk dl dm dn do dp dq dr ds dt du dv dw dx dy dz ea eb ec ed ee ef eg eh ei ej ek el em en eo ep eq er es et eu ev ew ex ey ez fa fb fc fd fe ff fg fh fi fj fk fl fm fn fo fp fq fr fs ft fu fv fw fx fy fz ga gb gc gd ge gf gg gh gi gj gk gl gm gn go gp gq gr gs gt gu gv gw gx gy gz ha hb hc hd he hf hg hh hi hj hk hl hm hn ho hp hq hr hs ht hu hv hw hx hy hz ia "State Sponsored Homophobia 2016: A world survey of sexual orientation laws: criminalisation, protection and recognition" (PDF). International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association. 17 May 2016. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
- ^ Galán, José Ignacio Pichardo. "Same-sex couples in Spain. Historical, contextual and symbolic factors" (PDF). Institut national d'études démographiques. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- ^ a b c "Spain approves liberal gay marriage law". St. Petersburg Times. 1 July 2005. Archived from the original on 28 December 2007. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- ^ a b c "Spain Intercountry Adoption Information". U. S. Department of State — Bureau of Consular Affairs. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Ley 14/2006, de 26 de mayo, sobre técnicas de reproducción humana asistida". Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado (in Spanish). 27 May 2006. Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- ^ a b "Rainbow Europe: legal situation for lesbian, gay and bisexual people in Europe" (PDF). ILGA-Europe. May 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2014.
- ^ a b c "Ley 3/2007, de 15 de marzo, reguladora de la rectificación registral de la mención relativa al sexo de las personas". Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado (in Spanish). 16 March 2007.
- ^ "Reglamento regulador del Registro de Uniones de Hecho, de 11 de septiembre de 1998". Ciudad Autónoma de Ceuta (in Spanish). 11 September 1998.
- ^ "Egypt (Law)". ILGA. Archived from the original on 11 July 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Libyan 'Gay' Men Face Torture, Death By Militia: Report (GRAPHIC)". HuffPost. 26 November 2012.
- ^ Fhelboom, Reda (22 June 2015). "Less than human". Development and Cooperation.
- ^ "Lei n.ᵒ 7/2001" (PDF). Diário da República Eletrónico (in Portuguese). 11 May 2001. Article 1, no. 1.
- ^ "AR altera lei das uniões de facto". TVI 24 (in Portuguese). 3 July 2009. Archived from the original on 15 July 2009. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Law no. 9/2010" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Diario da Republica. 31 May 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 February 2011. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Lei 17/2016 de 20 de junho".
- ^ "Lei que alarga a procriação medicamente assistida publicada em Diário da República". tvi24. 20 June 2016.
- ^ "Todas as mulheres com acesso à PMA a 1 de Agosto". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). 20 June 2016. Archived from the original on 10 March 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "MEPs welcome new gender change law in Portugal; concerned about Lithuania". The European Parliament Intergroup on LGBTI Rights. 21 March 2011. Archived from the original on 6 February 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "REGLAMENTO REGULADOR DEL REGISTRO DE PAREJAS DE HECHO DE LA CIUDAD AUTÓNOMA DE MELILLA" [REGULATORY REGULATION OF THE REGISTER OF COUPLES IN FACT OF THE CIUDAD AUTÓNOMA DE MELILLA] (PDF) (in Spanish). 1 February 2008. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g "LGBT Rights in Melilla". Equaldex. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Morocco (Law)". ilga.org. ILGA. Archived from the original on 24 July 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Lesbian and Gay Histories and Cultures: An Encyclopedia. Gay histories and cultures. Vol. 2. Taylor & Francis. 8 November 2017. ISBN 9780815333548 – via Google Books.
- ^ "La junta de protección a la infancia de Barcelona: Aproximación histórica y guía de su archivo" (PDF). Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ^ "Reforms In Sudan Result In Removal Of Death Penalty And Flogging For Same-Sex Relations". curvemag.com. 16 July 2020.
- ^ "Tunisia (Law)". International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association. Archived from the original on 4 July 2014. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Tunisian presidential committee recommends decriminalizing homosexuality". NBC News. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ^ "Benin (Law)". ilga.org. ILGA. Archived from the original on 3 July 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cd1jx8zxexmo
- ^ "The Gambia passes bill imposing life sentences for some homosexual acts | World news". The Guardian. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Where is it illegal to be gay? - BBC News". Bbc.com. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Gambia outlaws cross-dressing". news.com.au. Retrieved 21 March 2021.
- ^ Darkwa, Jacqueline. "Ghana's anti-LGBTIQ bill: Activists are preparing to fight". openDemocracy. Retrieved 10 January 2023.
- ^ Zane, Damian. "Ghana Cardinal Peter Turkson: It's time to understand homosexuality". BBC News. Retrieved 27 November 2023.
- ^
- Naadi, Thomas (29 February 2024). "Ghana passes bill making identifying as LGBTQ+ illegal". BBC News. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
The bill ... will come into effect only if President Nana Akufo-Addo signs it into law.
- Maxwell Akalaare Adombila (9 May 2024). "Ghana's top court postpones hearing on challenge to anti-LGBTQ bill". Reuters. Additional reporting: Karin Strohecker.
Chief Justice Gertrude Torkornoo ... adjourn[ing the] first ... hearing on the challenges without setting a new date further delays any resolution on a bill that, if signed into law ...
- Naadi, Thomas (29 February 2024). "Ghana passes bill making identifying as LGBTQ+ illegal". BBC News. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ "Ghana (Law)". ilga.org. ILGA. Archived from the original on 3 July 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Sexual Minorities: Their Treatment Across the World". Xpats.io. 11 January 2010.
- ^ "LGBT Rights in Liberia". Equaldex. Archived from the original on 18 January 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Milton, Bridgett (19 July 2024). "Liberia: House to Review Anti-Homosexuality Law". The New Dawn. Retrieved 28 July 2024.
- ^ [1]
- ^ [2]
- ^ "Malians approve amendments to constitution in referendum". Aljazeera. 23 June 2023. Archived from the original on 23 June 2023. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Hoppe, Sascha (8 March 2023). "Spartacus Gay Travel Index 2023". Spartacus Gay Travel Blog. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "LGBT Rights in Mauritania". Equaldex. Archived from the original on 13 February 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Nigeria (Law)". ilga.org. ILGA. Archived from the original on 3 July 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Marriage (Ascension) Ordinance, 2016" (PDF).
- ^ Jackman, Josh (20 December 2017). "This tiny island just passed same-sex marriage". PinkNews.
- ^ "LGBT Rights in Senegal". Equaldex.
- ^ Salerno, Rob. "2022 in worldwide LGBT rights progress – Part 6: Global Trends". Erasing 76 Crimes. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ "Cameroonian LGBTI activist found tortured to death in home". glaad.org. 17 July 2013.
- ^ Kojoué, Larissa (18 July 2024). "Cameroon First Daughter Calls for Decriminalization of Same-Sex Conduct". www.hrw.org.
- ^ "Décret n° 160218 du 30 mars 2016 portant promulgation de la Constitution de la République centrafricaine" (PDF). ilo.org.
- ^ "Code Pénal du 8 mai 2017" (PDF). droit-afrique.com.
- ^ "Gabon lawmakers vote to decriminalise homosexuality". Reuters. Reuters. 24 June 2020. Retrieved 1 July 2020.
- ^ a b c Mendos, Lucas Ramon (1 December 2020). "State-Sponsored Homophobia" (PDF). Cite error: The named reference ":0" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Everything you need to know about human rights". Amnesty International. 25 September 2015. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "DJIBOUTI 2015 HUMAN RIGHTS REPORT" (PDF).
- ^ "LGBT Rights in Eritrea". Equaldex. Archived from the original on 4 February 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Asokan, Ishan (16 November 2012). "A bludgeoned horn: Eritrea's abuses and 'guilt by association' policy.'". Consultancy Africa Intelligence. Retrieved 3 November 2013.
- ^ "UN Investigator: Eritreans experienced torture, sexual violence during national service". VOA News. 8 August 2023. Archived from the original on 9 August 2023. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Human rights: Eritrean refugees in Sinai, anti-homosexual bill in Uganda and caning in Malaysia". Novice. 16 December 2010. Archived from the original on 14 May 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Why it is good that Ethiopians are debating homosexuality?". genderit.org. Retrieved 14 June 2019.
- ^ "Ethiopia: Religious Marriage" (PDF). Library of Congress. Retrieved 21 April 2024.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (4 January 2024). "2023 World Same-Sex Marriage and LGBT Rights Progress – Part 6: Global Trends".
- ^ "Laws of Kenya ; The Constitution of Kenya" (PDF). Kenyaembassy.com. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (4 January 2024). "2023 World Same-Sex Marriage and LGBT Rights Progress – Part 4: Africa and Oceania".
- ^ "OutRight Action International: Kenya".
- ^ "Rwanda's Constitution of 2003 with Amendments through 2015" (PDF). 20 June 2023.
- ^ "'Don't come back, they'll kill you for being gay'". BBC NEWS. 2020.
- ^ "2013 HUMAN RIGHTS REPORT" (PDF). Country Reports on Human Rights Practices. 2013. p. 33.
- ^ "Tanzania: Mixed Messages on Anti-Gay Persecution". hrw.org. 6 November 2018.
- ^ Gettleman, Jeffrey (8 November 2017). "David Kato, Gay Rights Activist, Is Killed in Uganda" – via www.nytimes.com.
- ^ "Uganda anti-homosexuality bill sets death penalty as punishment". The Times. 21 March 2023.
- ^ "LGBT Rights in Comoros". Equaldex. Archived from the original on 18 January 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "Mauritius Supreme Court rules law targeting LGBT people is unconstitutional". Human Dignity Trust. Retrieved 4 October 2023.
- ^ a b "Africa: Outspoken activists defend continent's sexual diversity - Norwegian Council for Africa". Afrika.no. 6 August 2009. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Equal Opportunities Act 2008" (PDF). Ilo.org. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Tiny African victory: Seychelles repeals ban on gay sex". 18 May 2016.
- ^ "Diario da Republica" (PDF) (in Portuguese).
- ^ "Employment & labour law in Angola". Lexology. 15 September 2015.
- ^ "Transgender Rights in Angola" (PDF). Southern Africa litigation Centre. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 August 2018. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Fox, Kara. "Botswana scraps gay sex laws in big victory for LGBTQ rights in Africa". CNN.
- ^ "NEWS RELEASE: BOTSWANA HIGH COURT RULES IN LANDMARK GENDER IDENTITY CASE – SALC".
- ^ Stewart, Colin (10 April 2024). "Eswatini LGBTIQ activists challenge ultra-conservative attitudes". Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Labour Act 2024" (PDF). Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ "Children's Protection and Welfare Act, 2011" (PDF). Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ "Transgender Rights in Lesotho" (PDF). Southern Africa Litigation Centre. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2018. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Malawi suspends anti-gay laws as MPs debate repeal | World news". The Guardian. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Could the historic case of a trans sex worker end Malawi's anti-LGBTIQ law?". openDemocracy. 11 December 2023.
- ^ Itai, Daniel (23 July 2023). "Malawi Constitutional Court considers LGBTQ, intersex rights cases". Washington Blade.
- ^ "Mozambique Gay Rights Group Wants Explicit Constitutional Protections | Care2 Causes". Care2.com. 3 March 2011. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Homosexuality Decriminalised in Mozambique". Kuchu Times. 1 June 2015. Retrieved 29 September 2015.
- ^ "Namibian court strikes down law criminalising same-sex relationships". The Guardian. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (21 October 2021). "Namibia court bans anti-gay discrimination in child citizenship case". 76 Crimes. Archived from the original on 22 October 2021. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Transgender Rights in Namibia" (PDF). Southern Africa Litigation Centre. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 August 2018. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Activist asks ConCourt to clarify "the order of nature" in sexual practices". Zambia: News Diggers!. 4 June 2024. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ Chironda, Melody (30 July 2024). "Zimbabwe: Despite Hostility, LGBTQI+ Activists in Zimbabwe Push for Equality". allAfrica.com. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Constitution of Zimbabwe Amendment, (No. 20) Act. 2013" (PDF). 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 May 2017. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ Simpson, Lisa (28 February 2018). "House: Three more months of same-sex marriage". The Royal Gazette. Archived from the original on 28 February 2018. Retrieved 28 February 2018.
- ^ "2014: No. 308" (PDF). Supreme Court of Bermuda. 3 February 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 January 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Johnson, Ayo (15 June 2013). "MPs approve historic Human Rights Act changes". The Royal Gazette. Retrieved 15 June 2013.
- ^ "Criminal Code (R.S., 1985, c. C-46), Section 159, Subsection (1)". Department of Justice Canada \access-date=May 15, 2024. Archived from the original on 8 June 2011.
- ^ Anonymous (27 November 2017). "Law Reform (2000) Act".
- ^ "An Act instituting civil unions and establishing new rules of filiation" (PDF). National Assembly. 2002. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 March 2009. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Alberta: Adult Interdependent Relationships". Legal Resource Center of Alberta. 2006. Retrieved 28 July 2007.
- ^ Justice, Manitoba. "Manitoba Laws". web2.gov.mb.ca.
- ^ "LOI CONCERNANT CERTAINES CONDITIONS DE FOND DU MARIAGE CIVIL" (PDF).
- ^ Status differs in provinces and territories:
- Mary C. Hurley (31 May 2007). "Sexual Orientation and Legal Rights". Parliament of Canada. Retrieved 21 January 2010.
- Jennifer A. Cooper (31 December 2001). "Opinion on Common-Law Relationships". Government of Manitoba. Retrieved 21 January 2010.
- "Gay couple leaps 'walls' to adopt son". Edmonton Journal. 19 February 2007.
- "Legal Information for Same Sex Couples" (PDF). Legal Information for Same Sex Couples. Retrieved 3 September 2010.
- "Yukon Adoption: Important Adoption Issues". Adoptiveparents.ca. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ "Canadian Armed Forces". The Canadian Lesbian & Gay Archives. Retrieved 30 September 2010.
- ^ a b Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Northwest Territories Human Rights Act, S.N.W.T. 2002, c.18. Section 5".
- ^ "Ontario passes law to protect transgender people". CBC News. 13 June 2012. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- ^ Services, Ministry of Citizens. "Change Your Personal Information - Province of British Columbia". www2.gov.bc.ca.
- ^ "Manitoba Vital Statistics Agency | Province of Manitoba". Province of Manitoba - Manitoba Vital Statistics Agency.
- ^ "1995-96 - L 162 (oversigt): Forslag til lov om ændring af kriminalloven og arveloven for Grønland. (Ændringer som følge af indførelse af registreret partnerskab)" (in Danish). Webarkiv.dk. Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- ^ "Anordning om ikrafttræden for Grønland af lov om ændring af lov om registreret partnerskab m.v." (PDF).
- ^ "Folketinget - L 122 - 2014-15 (1. samling)Om forældreansvarslovgivningen og lovgivningen om ægteskab mellem to personer af samme køn". Folketingstidende (in Danish). Archived from the original on 2 July 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "§2, Imm. 3, Qitiusumik Inunnik Nalunaarsuiffik pillugu inatsisip (CPR pillugu inatsit) allanngortinneqarneranik inatsisit Kalaallit Nunaannut atuutilersinneqarnerannik peqqussut (Greenlandic)" (PDF). Retrieved 1 September 2020.
- ^ "§2, Stk 3., Anordning om ikrafttræden for Grønland af love om ændring af lov om Det Centrale Personregister (Danish)". Retrieved 1 September 2020.
- ^ (in Spanish) Leopoldo Ramos (11 January 2007). "Aprueba Coahuila la figura del pacto civil de solidaridad". La Jornada. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- ^ (in Spanish) Pedro Zamora Briseño (29 July 2013). "Aprueba Colima "enlace conyugal" entre parejas del mismo sexo". Proceso. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- ^ "Legalizan bodas gays en Campeche". SDPnoticias (in Spanish). 23 December 2013. Archived from the original on 9 February 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ (in Spanish) "Jalisco avala Ley de Libre Convivencia para regular parejas del mismo sexo". CNN México. 31 October 2013. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- ^ "Mexico City's gay marriage law takes effect". MSNBC. Associated Press. 4 March 2010. Retrieved 6 March 2010.
- ^ (in Spanish) Jesús Castro (12 February 2014). "Ya pueden parejas gay adoptar en Coahuila; PAN vota en contra". Vanguardia. Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ "Intercountry Adoption: Mexico". Office of Children Issues, U.S. Dept. of State. November 2009.
- ^ International Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission (IGLHRC) (23 April 2003). "Mexico protects its gay and lesbian citizens with new law". Retrieved 27 November 2009.
- ^ International Lesbian and Gay Association (ILGA) Trans (29 August 2008). "Mexico City extends official rights to transgender individuals". Retrieved 27 November 2009.
- ^ Ulises, Edgar (9 March 2022). "¿Qué es la ley de identidad de género y qué estados la aprobaron?". Homosensual.
- ^ a b c d e f "Loi n° 99-944 du 15 novembre 1999 relative au pacte civil de solidarité". Legifrance (in French). Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f Vignal, Francois (15 April 2013). "Mariage pour tous : le détail du vote au Sénat" (in French). Public Senat. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f "France". travel.state.gov.
- ^ a b c d e f "France: Transsexualism will no longer be classified as a mental illness in France / News / Welcome to the ILGA Trans Secretariat / Trans / ilga - ILGA". Trans.ilga.org. 16 May 2009. Retrieved 21 November 2013.
- ^ "Biden overturns Trump transgender military ban". BBC News. 25 January 2021.
- ^ a b "Medical Conditions That Can Keep You From Joining the Military". Military.com. 7 May 2012. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ "US citizens can now select a gender neutral 'X' on their passport". Sky News. 11 April 2022. Archived from the original on 11 April 2022. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Belize Supreme Court Overturns Anti-Gay Law". NBC News. 10 August 2016.
- ^ "Chapter 4 of the Laws of Belize - THE CONSTITUTION OF BELIZE PART II: Protection of Fundamental Rights and Freedoms". Belmopan, Belize: The Government of Belize. 1981. Archived from the original on 21 August 2013. Retrieved 10 August 2016.
- ^ Littauer, Dan (10 August 2016). "Love wins! Belize anti-gay law struck down". Scotland: KaleidoScot. Retrieved 10 August 2016.
- ^ "Supreme Court declares Section 53 unconstitutional". Port of Spain, Trinidad: Daily Express. Cana News. 10 August 2016. Retrieved 10 August 2016.
- ^ "Transgender Culture in Belize". United Belize Advocacy Movement (UNIBAM). Retrieved 16 October 2016.
- ^ "CCSS aprobó extender seguro de salud a parejas gais". La Nación, Grupo Nación. 23 May 2014.
- ^ Dyer, Zach (19 March 2015). "Costa Rica Government To Prioritize Bill Legalizing Gay Civil Unions". The Tico Times. Archived from the original on 19 March 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Costa Rica". Bureau of Consular Affairs U.S. Department of State. Archived from the original on 3 February 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Transgender Population in Costa Rica Will be Able to Choose the Name Shown in Their ID". Costa Rica Star News. 14 May 2018. Retrieved 15 May 2018.
- ^ Quesada, Armando (23 May 2018). "Omisión de sexo en las cédulas: Un cambio simbólico" [Omission of sex on ID cards: A symbolic change]. La República (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ Cambronero, Julieta (24 May 2021). "Primer aniversario del matrimonio igualitario llama a resolver pendientes con la población diversa" [First anniversary of same-sex marriage calls for resolving pending issues with sexually diverse citizens]. Costa Rica Medios (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ Solano, Glenda (11 March 2022). "Personas trans obtendrán pasaporte con identidad de género autopercibida sin trámites engorrosos" [Trans people will obtain passports with self-perceived gender identity without cumbersome procedures]. Teletica.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 12 March 2022.
- ^ a b HUMAN RIGHTS SITUATION OF LESBIAN, GAY, BISEXUAL AND TRANSGENDER PERSONS IN EL SALVADOR: Shadow Report submitted to the United Nations Human Rights Committee (PDF). San Salvador: Asociación Salvadoreña de Derechos Humanos “Entre Amigos”. 2010.
- ^ "Consulta Nacional sobre realidades LGBTI en El Salvador". Dirección de Diversidad Sexual (in Spanish). 2012.
- ^ "El Salvador: la Corte Suprema reconoce la identidad de género de una persona trans". NODAL (in European Spanish). 10 May 2017. Retrieved 16 May 2017.
- ^ Perez, Sonia (31 July 2016). "In socially conservative Guatemala, transgender people sees gains". LGBTQ Nation. Associated Press.
- ^ "Honduras: Constitución de 1982". pdba.georgetown.edu.
- ^ "Honduras Bans Gay Marriage & Adoption". Global Gayz. 30 March 2005. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ^ ""DECRETO 144-83" CÓDIGO PENAL" (PDF).
- ^ "Ley No. 16 Que regula el derecho de admisión en los establecimientos públicos y Dicta medidas para evitar la discriminación" (PDF) (in Spanish). Defensoria del Pueblo. 10 April 2002. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 June 2012. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Buscan que orientación sexual e identidad género sean reconocidos en Panamá". El Nuevo Diario (in Spanish). 20 August 2015. Archived from the original on 24 August 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Transexuales panameños tramitan cédulas de mujer". La Prensa. 5 November 2012.
- ^ "Por primera vez, una transexual logra en Panamá cambiar su nombre en la cédula". El Espectador (in Spanish). Retrieved 1 August 2016.
- ^ "LANDSBESLUIT van 2 juni 2021 no. 1, houdende inwerkingtreding van de Aanpassingsverordening aanvulling Burgerlijk Wetboek van Aruba (AB 2021 no. 43) en de Landsverordening van 23 september 2016 tot wijziging van het Burgerlijk Wetboek van Aruba (AB 1989 no. GT 100) in verband met een aantal onderwerpen die nog een regeling of aanpassing in het Burgerlijk Wetboek van Aruba behoeven (AB 2016 no. 51)". 9 March 2023.
- ^ "Supreme Court rules that same-sex marriage is now permitted in Aruba and Curaçao | NL Times". NL Times. Retrieved 12 July 2024.
- ^ "Wetboek van Strafrecht van Aruba". overheid.aw (in Dutch). 3 July 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ Smith, Reiss (22 July 2020). "Barbados invites same-sex couples to live on the island for a year as it begins unpicking colonial-era homophobia". PinkNews. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ "Government to recognise 'a form of civil unions' for same sex couples". Barbados Today. 15 September 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ "Employment (Prevention of Discrimination) Bill, 2020". Barbados Parliament Bills Archive. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ^ a b c Waaldijk, Kees. "Major legal consequences of marriage, cohabitation and registered partnership for different-sex and same-sex partners in the Netherlands" (PDF). INED. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- ^ a b c "Gay Marriage Goes Dutch". CBS News. Associated Press. 1 April 2001. Retrieved 21 January 2010.
- ^ a b c "Burgerlijk Wetboek, Boek 1 (Civil Code, Book 1)". Government of the Netherlands. Retrieved 19 April 2013.
- ^ a b c "Wetboek van Strafrecht BSE". Overheid.nl (in Dutch). 1 May 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ "The Virgin Islands Constitution Order 2007". UK Legislation. 2007. Archived from the original on 5 April 2011. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Civil partnerships now legal in the Cayman Islands". Cayman News Service. 4 September 2020.
- ^ "LGBT MILITARY PERSONNEL A STRATEGIC VISION FOR INCLUSION" (PDF). The Hague Center for Strategic Studies.
- ^ "Gaceta Oficial No. 29 Extraordinaria de 17 de junio de 2014" (PDF).
- ^ "Entra en vigor nuevo Código del Trabajo". cubaencuentro.com (in Spanish).
- ^ "Constitución de la República de Cuba" (PDF). Cuba (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 19 January 2024. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Cuba approves sex change operations". Reuters. 6 June 2008. Archived from the original on 22 January 2010. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Supreme Court rules that same-sex marriage is now permitted in Aruba and Curaçao | NL Times". NL Times. Retrieved 12 July 2024.
- ^ "LANDSVERORDENING van de 2de november 2011 houdende vaststelling van een nieuw Wetboek van Strafrecht" (PDF). gobiernu.cw (in Dutch). 2 November 2011.
- ^ Stewart, Colin (22 April 2024). "Dominica court overturns anti-sodomy law". Erasing 76 Crimes. Retrieved 23 April 2024.
- ^ Potts, Andrew (13 June 2024). "Dominican Republic reiterates ban on gay cops and soldiers". Gaystarnews. Archived from the original on 16 June 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Taylor, Jeff (23 April 2018). "Homosexuality Is Still Illegal In These 9 Caribbean Countries". newnownext.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (9 January 2023). "2022 in worldwide LGBT rights progress – Part 6: Global Trends". Erasing 76 Crimes. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (9 January 2023). "2022 in worldwide LGBT rights progress – Part 6: Global Trends". Erasing 76 Crimes. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ "Constitution of Montserrat Part I: Fundamental Rights & Freedoms". Government of Montserrat. Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^ "Puerto Rico to amend laws after US ruling on gay marriage".
- ^ a b "In 60 days, gays will be allowed to serve openly in the military". CNN. 23 July 2011.
- ^ a b "Beginning today, transgender individuals can join the US military". ABC News. 1 January 2018.
- ^ Chiam, Zhan; Duffy, Sandra; González Gil, Matilda; Goodwin, Lara; Timothy Mpemba Patel, Nigel. "Trans Legal Mapping Report 2019: Recognition before the law" (PDF). ILGA World. Retrieved 5 March 2022.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (9 January 2023). "2022 in worldwide LGBT rights progress – Part 6: Global Trends". Erasing 76 Crimes. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (9 January 2023). "2022 in worldwide LGBT rights progress – Part 6: Global Trends". Erasing 76 Crimes. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ "LANDSVERORDENING van de 13e december 2012 houdende vaststelling van een nieuw Wetboek van Strafrecht". Overheid.nl (in Dutch). 13 December 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ Loutoo, Jada (12 April 2018). "Historic ruling on Sexual Offences Act". Trinidad and Tobago Newsday. Port of Spain, Trinidad. Archived from the original on 12 April 2018. Retrieved 12 April 2018.
- ^ a b c Liptak, Adam (26 June 2015). "Gay Marriage Backers Win Supreme Court Victory". The New York Times. Retrieved 26 June 2015.
- ^ a b "Governor Bryan Takes Action on 26 Bills from Final Session of 34th Legislature". Government of the Virgin Island. 2 February 2023. Archived from the original on 16 February 2023. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Ley 1.004". Buenos Aires Ciudad (in Spanish).
- ^ "Ley 3.736". Legislatura de la Provincia de Río Negro (in Spanish).
- ^ "Ley 26.994 Código Civil y Comercial de la Nación". InfoLEG (in Spanish).
- ^ "Ley 26.618". InfoLEG (in Spanish).
- ^ Smink, Veronica (28 February 2009). "Argentina: abren paso a gays en FF.AA". BBC Mundo (in Spanish). Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ^ "Ley 26.791". InfoLEG (in Spanish).
- ^ Ruchansky, Emilio (10 May 2012). "Una norma de vanguardia". Página/12 (in Spanish).
- ^ "New law in Argentina could change lives in the transgender community".
- ^ "SENTENCIA CONSTITUCIONAL PLURINACIONAL 0577/2022-S2" (PDF). Tribunal Constitucional Plurinacional. 20 March 2023. Retrieved 23 June 2023.
- ^ "Constitución Política del Estado (CPE) (7-Febrero-2009)" (in Spanish). Infoleyes. Retrieved 15 September 2012.
- ^ "CÓDIGO NIÑA, NIÑO Y ADOLESCENTE LEY Nº 548" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 January 2017. Retrieved 6 March 2017.
- ^ Maria Eugenia Duran (28 August 2014). "Militares y homosexualidad: los avances y tabus en los otros paises de latinoamerica". Nacion (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 2 September 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Fuerzas Armadas de Bolivia abren sus puertas a los gays". confluenciafm.com.ar.
- ^ "Militares gay, entre la discriminación y la clandestinidad en FFAA de Bolivia" (in Spanish). 25 August 2014. Retrieved 2 September 2016.
- ^ "Constitucion Politica de Estado vingente Bolivia" (PDF) (in Spanish). Corte Nacional Electoral. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 October 2009. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Perez, Wilma (9 February 2012). "'Soy el primero en Latinoamérica en cambiar de nombre y sexo'". La Razón (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 5 August 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "En Bolivia, seis transexuales lograron cambiar de identidad". Pagina Siete (in Spanish). 10 August 2014. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Brazilian go-ahead for gay unions". 5 March 2004 – via news.bbc.co.uk.
- ^ "Notícias STF". Supremo Tribunal Federal (in Portuguese). 5 May 2011. Archived from the original on 2 August 2011. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Seligman, Felipe (14 May 2013). "CNJ obriga cartórios de todo o país a celebrar casamento entre gays". Folha de S.Paulo (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 9 June 2013. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Recondo, Felipe (14 May 2013). "CNJ obriga cartórios a celebrar casamento entre homossexuais". Estadão (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 16 May 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Seligman, Felipe (27 April 2010). "Casal homossexual pode adotar criança, decide STJ". Athosgls (in Portuguese). Archived from the original on 15 July 2010. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ (in Portuguese).Patricia Silva Gadelha (March 2006). "A prática da pederastia é crime militar". Jus Navigandi. Archived from the original on 11 August 2013. Retrieved 10 September 2013.
- ^ "STF permite criminalização da homofobia e da transfobia". G1 (in Portuguese). 13 June 2019.
- ^ "Homosexuality is not deviant - Federal Council of Psychologists of Brazil".
- ^ "Psychiatrist Jairo Bouer talks about the "collateral effects" of "gay cure" bill".
- ^ Expresso da Notícia (13 January 2006). "Justiça autoriza alteração no registro de transexual que trocou de sexo" (in Portuguese). Jus Brasil. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ Expresso da Notícia (25 December 2005). "Justica autoriza mudança de sexo em documentos" (in Portuguese). Jus Brasil. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ "Mudar o nome e o sexo nos documentos".
- ^ "LEY-20830 21-ABR-2015 MINISTERIO SECRETARIA GENERAL DE GOBIERNO - Ley Chile - Biblioteca del Congreso Nacional". 21 April 2015.
- ^ a b Bonnefoy, Pascale; Londoño, Ernesto (7 December 2021). "Chile Legalizes Same-Sex Marriage at Fraught Political Moment". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ (in Spanish) Claudio Ortiz Lazo. "Reflexiones en torno a la homosexualidad y fuerzas armadas". Revista Fuerzas Armadas y Sociedad. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ^ Chile, C. N. N. "Histórico: Ejército admite por primera vez en sus filas a un hombre trans". CNN Chile (in Spanish). Retrieved 2 February 2021.
- ^ "Chile Congress passes anti-discrimination law". Jurist.org. 5 April 2012. Retrieved 29 June 2012.
- ^ "Chilean President Signs Transgender Rights Law". On Top Magazine.
- ^ "Consulta de la Norma". Alcaldiabogota (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 3 October 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Colombia legalises gay marriage". BBC. 29 April 2016. Archived from the original on 2 May 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Colombia: constitutional court upholds same-sex marriage". Human Rights Watch. 28 April 2016. Archived from the original on 4 June 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Histórico fallo de Corte Constitucional sobre adopción de menores por parte de parejas del mismo sexo". RCN Radio. 28 August 2014.
- ^ "Colombia High Court Rules for Adoptions by Same-Sex Couples". The New York Times.
- ^ "Este miércoles el presidente Santos sanciona ley antidiscriminación". ElTiempo.com. 29 November 2011. Retrieved 29 November 2011.(in Spanish)
- ^ ""Cambio de género en la cédula será ágil y simple": Minjusticia - ELESPECTADOR.COM". 6 June 2015.
- ^ "Constitution of Ecuador" (PDF). ecuadorencifras.gob.ec.
- ^ "LEY REFORMATORIA AL CÓDIGO CIVIL" (PDF).
- ^ "Ecuador's highest court votes to legalise same-sex marriage". France 24. 13 June 2019.
- ^ "Ecuador". travel.state.gov.
- ^ "LACHR takes case concerning Ecuador to the Inter-American court". Organization of American States. 30 April 2015. Archived from the original on 13 September 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Ecuador: 2008 Constitution in English". pdba.georgetown.edu.
- ^ "Registro Oficial Segundo Suplemento" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Organo del Gobierno del Ecuador. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 February 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "Bay Area Reporter :: Article.php". The Bay Area Reporter / B.A.R. Inc.
- ^ a b "Family law review 2015". Falkland Islands. 13 May 2015. Archived from the original on 30 October 2015. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "The Falkland Islands Constitution Order 2008" (PDF). South Atlantic Territories. 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 November 2013. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ Salerno, Rob (9 January 2023). "2022 in worldwide LGBT rights progress – Part 6: Global Trends". Erasing 76 Crimes. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ^ "Homosexuals can adopt, be foster parents, guardians – CPA Director". 16 December 2015.
- ^ "HOME". thedailyherald.sx.
- ^ "Constitución del Paraguay, 1992". www.oas.org.
- ^ "Paraguay – Constitution". Retrieved 15 October 2010.
- ^ "Diputados rechazan ley que prohíbe ingreso de homosexuales a FFAA". Paraguay (in Spanish). 17 June 2010. Archived from the original on 19 June 2010. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- ^ "El Tribunal Constitucional de Perú considera que no se puede excluir de la Polícia o el Ejército a las personas homosexuales". Dos Manzanas. 13 December 2009. Retrieved 30 September 2010.
- ^ "Código Penal peruano 2018 actualizado". Legis.pe (in European Spanish). 3 June 2018. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ^ "Peruvian Congress Votes to Remove LGBT from Hate Crime Legislation". The Perchy Bird. 6 May 2017. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- ^ (in Spanish)"Peruvian Penal Code" (PDF). Retrieved 8 October 2015.
- ^ "Peru lags behind other Latin American countries on LGBT rights". 18 September 2014.
- ^ "Finalmente se aprobó la ley contra crímenes de odio y discriminación por orientación sexual". Útero.Pe (in Spanish). Retrieved 7 January 2017.
- ^ "TC reconoce derecho de transexuales a pedir cambio de nombre y sexo en DNI". larepublica.pe (in Spanish). 8 November 2016.
- ^ "Sex reassignment surgery in Peru". Streets of Lima. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ a b "Local laws and customs - South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands (British Overseas Territory) travel advice - GOV.UK". www.gov.uk.
- ^ "Wetboek van Strafrecht 2015" (PDF) (in Dutch). Retrieved 1 January 2017.
- ^ "Grote stap in erkennen mensenrechten transgenders | Suriname Nieuws Centrale". surinamenieuwscentrale.com (in Dutch). Retrieved 2 December 2022.
- ^ "Transgender wins case for sex change recognition". thedailyherald.sx. Retrieved 13 January 2017.
- ^ "Suriname appeals transgender verdict". www.thedailyherald.sx. Archived from the original on 16 February 2017.
- ^ "Ley Nº 18.246 UNIÓN CONCUBINARIA".
- ^ "Document" (PDF). archivo.presidencia.gub.uy.
- ^ "Lawmakers in Uruguay Vote to Allow Gay Couples to Adopt". New York Times. Reuters. 9 September 2009. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ Rachel Weiner (15 May 2009). "Uruguay Lifts Ban On Gays In The Military". Huffington Post. Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ (in Spanish) Congress of Uruguay (18 August 2004). "Ley N° 17.817". Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ Free Speech Radio News (11 December 2009). "Uruguay passes bill to allow citizens to choose gender identity". Retrieved 1 January 2010.
- ^ Supreme Court of Justice Venezuela (16 March 2023). "SUPREME COURT OF JUSTICE DECLARES NULLITY OF THE PRE-CONSTITUTIONAL NORM OF THE ORGANIC CODE OF MILITARY JUSTICE". Retrieved 16 March 2023.
- ^ a b "Russian Gay History". community.middlebury.edu. Archived from the original on 26 July 2023. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ a b "Russian parliament begins legalising ban on same-sex marriage". Reuters. 15 July 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ ""Держите язык за зубами!" Правда о гомосексуалистах в российской армии". Rambler. 8 August 2017. Retrieved 26 November 2022.
- ^ "Putin Signs Gender Reassignment Ban Into Law". The Moscow Times. 24 July 2023. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- ^ "В Минобороны ответили на вопрос о сексуальных меньшинствах в армии". Tengrinews. 25 February 2022. Retrieved 5 May 2022.
- ^ a b c Masci, David (11 February 2014). "Gay rights in Russia and the former Soviet republics". Pew Research Center. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ^ "Kyrgyz Voters Back Amendments On Same-Sex Marriage, Presidential Power". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 11 December 2016. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ^ Bennett, Dalton (5 July 2010). "Kyrgyzstan's Transgender Advocates Call for Right to Change Gender in Passports". Eurasianet. Archived from the original on 13 January 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ Isamova, Lidia (12 May 2014). "Transgender in Tajikistan". Institute for War and Peace Reporting. Archived from the original on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ a b "The lives of LGBT people in Turkmenistan, the most closed-off country in Eastern Europe and Central Asia". TGEU. 20 March 2024. Archived from the original on 4 April 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ "Employment (Equality) Ordinance 2013" (PDF). Gazette No 1678. 8 February 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ "Referendum in Armenia brings constitutional reforms". ILGA-Europe. 16 December 2015. Archived from the original on 12 January 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ "Armenia Central Electoral Commission announces constitutional referendum final results". Newsfeed. 13 December 2015. Archived from the original on 19 January 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ "Armenia: Gays live with threats of violence, abuse". United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. 30 March 2010. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ Bew, Geoffrey (9 March 2009). "Sex change woman faces cash crisis". Gulf Daily News. Archived from the original on 28 June 2008. Retrieved 20 January 2011.
- ^ a b "In-Cyprus is under construction". in-cyprus.com.
- ^ a b "Army legislation".
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad "ILGA-Europe" (PDF). ilga-europe.org.
- ^ a b "Cyprus: Penal code amended to protect against discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity". PinkNews. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- ^ "Egypt (Law)". ILGA. Archived from the original on 11 July 2014. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Law of Georgia on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination". matsne.gov.ge.
- ^ a b c d e "Map shows how Europe forces trans people to be sterilized". Gay Star News.
- ^ "Report: 14-year-old gay boy hanged in Iran". mambaonline.com. 18 July 2015. Retrieved 19 October 2017.
- ^ "CBC News - Film - Iran's gay plan". Cbc.ca. 26 August 2008. Retrieved 5 September 2010.
- ^ "Iraq makes same-sex relations punishable by up to 15 years in jail". The Guardian. 27 April 2024. Retrieved 28 April 2024.
- ^ Erez Levon (January 2008). National Discord: Language, Sexuality and the Politics of Belonging in Israel. pp. 45–46. ISBN 9780549582427.
This amendment to the penal code entailed a de jure decriminalization of sodomy since, in 1963, the Israeli Supreme Court had already issued a de facto decriminalization, ruling that the anti-sodomy law (which dated back to the British Mandate of Palestine; Mandatory Criminal Ordinance of 1936) could not be prosecuted (Yosef Ben-Ami vs. The Attorney General of Israel, 224/63).
- ^ "LGBTQ Timeline" (PDF). ua.edu.
- ^ "In Complete Reversal, Israel Says It No Longer Opposes Same-sex Adoption". Haaretz. 29 August 2017.
- ^ "Israeli ministry drops opposition to adoption by same-sex couples". Jerusalem Post. 30 August 2017.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Law prohibiting discrimination in products, services, and entry to businesses" (in Hebrew). Israeli Economy Ministry. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ^ "El Al vs. Yonatan Danilovich" (in Hebrew). Supreme Court of Israel. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- ^ Dorff, Rabbis Elliot N.; Nevins, Daniel S.; Reisner, Avram I. "Homosexuality, Human Dignity & Halakhah: A Combined Responsum for the Committee on Jewish Law and Standards" (PDF).
- ^ Hovel, Revital (18 January 2015). "Israel recognizes sex changes without operation". Haaretz. Supreme Court of Israel. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ Gross, Aeyal (17 December 2013). "Human rights are part of the fight for gay rights". A Wider Bridge. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ Weissberg, Hila (29 August 2014). "Homophobia in the workplace? Fear of transgender people is even worse". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 1 September 2014. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ Gross, Aeyal (16 September 2013). "Israel should drop binary view of gender". Haaretz. Archived from the original on 25 October 2015. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ "محكمة التمييز توافق على تغيير جنس مواطن اردني من ذكر الى انثى - دنيا الوطن" [The Court of Cassation agrees to change the gender of a Jordanian citizen from male to female]. alwatanvoice.com (in Arabic). 12 October 2014.
- ^ "Kuwait Law". ilga.org.
- ^ Sycamore, Maximilian (4 February 2018). "Lebanese gay couple not prosecuted under 'order of nature' law". washingtonblade.com.
- ^ "Lebanese judge grants trans man right to change gender". washingtonblade.com. 16 January 2016. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- ^ a b c d Erol, Ali (27 January 2014). "Northern Cyprus Decriminalizes Homosexuality and Protects LGBTs Against Hate Speech". kaosgl. Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ a b c d Akpinar, Omer (20 October 2014). "Kuzey Kıbrıs'ın "Eşcinsellik Suçu" Yasası Tarihe Karıştı!". KAOSGL (in Turkish). Archived from the original on 7 April 2014. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- ^ a b Kamenou, Nayia; Gavrielides, Costa; Ethemer, Enver; Bullici, Okan. "Aktivizm, Hukuk Ve İki Kesimdeki Değişim" (PDF). FRIEDRICH-EBERT-STIFTUNG – KIBRIS LGBTİ HAREKETİ.
- ^ "Palestine". Human Dignity Trust. Archived from the original on 31 October 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ "Everything you need to know about human rights in Palestine". Amnesty International. Archived from the original on 4 March 2021. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Abusalim, Dorgham (13 March 2018). "The Real Oppressors of Gaza's Gay Community: Hamas or Israel?". Institute of Palestine Studies. Archived from the original on 28 October 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Lucas Paoli Itaborahy; Jingshu Zhu (May 2014). State-Sponsored Homophobia (PDF) (Report). ILGA. pp. 16, 20, 55. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 March 2017. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ Bearak, Max; Cameron, Darla (16 June 2016). "Analysis: Here are the 10 countries where homosexuality may be punished by death". Washington Post. Archived from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2017.
- ^ Research Directorate (11 August 2011). "Responses to Information Requests (research report on country conditions: Saudi Arabia)". Immigration and Refugee Board of Canada. Ottawa. SAU103739.FE. Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ^ "Saudi Arabia: Legal Frameworks – Criminalisation of consensual same-sex sexual acts". ILGA World Database. International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association. See "Penalties: Max. prison" listing.
- ^ Can, İ.Özgür; Demiroğlu, Zehra; Köker, Murat; Ulaş, Halis; Salaçin, Serpil (28 January 2011). "Legal Aspects of Gender Reassignment Surgery in Turkey". Indian Journal of Gender Studies. 18. Sage Publishing: 77–88. doi:10.1177/097152151001800104. S2CID 143761091.
- ^ a b "UAE: Sweeping Legal 'Reforms' Deepen Repression". Human Rights Watch. 5 June 2022. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ^ "UAE: Greater Progress Needed on Women's Rights". Human Rights Watch. 4 March 2021. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ Staff reporter. "New UAE law: Reform eases restrictions on extra-marital relationships from January 2". Khaleej Times. Retrieved 25 July 2023.
- ^ Moukhallati, Dana (26 September 2016). "New law does not legalise sex change". The National. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ "UAE rejects three transgender Emirati women's bid for gender status change". Al Arabiya. 23 March 2018. Retrieved 23 May 2021.
- ^ Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor (2022). "Section 6. Discrimination and Societal Abuses". 2021 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: United Arab Emirates (Report). United States Department of State.
- ^ "LGBT People in Afghanistan After the Taliban Takeover". Human Rights Watch. 26 January 2022. Retrieved 15 November 2022.
- ^ "Bangladesh". Human Dignity Trust. Archived from the original on 19 April 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "Bangladesh government makes Hijra an official gender option - Wikinews, the free news source". Wikinews. 11 November 2013.
- ^ "Penal Code (Amendment) Act of Bhutan 2021" (PDF) (in Dzongkha). Parliament of Bhutan. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 April 2021. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "India court legalises gay sex in landmark ruling". BBC News. 6 September 2018.
- ^ Prakash, Satya (29 August 2022). "Supreme Court expands definition of family; says it may take form of domestic, unmarried partnerships or queer relationships". Tribune India. Tribune Trust. The Tribune. Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- ^ "India: Supreme Court Recognizes Rights Of The LGBT Community". mondaq.com. 18 September 2018.
- ^ Mishra, Abhishek (10 February 2021). "Homosexuality not a ground to sack employee, rules Allahabad High Court". India Today.
- ^ a b "The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Bill, 2019". PRS Legislative Research.
- ^ Ghosh, Deepshikha (15 April 2014). "Transgenders are the 'third gender', rules Supreme Court". NDTV.
- ^ "Penal Code". law.upenn.edu. 2014. p. 75.
- ^ "The law vs. reality: gay travel to the Maldives". Out of Office. Archived from the original on 25 September 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ Haviland, Charles (1 July 2008). "Nepalese army 'sacks lesbian'". BBC. Archived from the original on 7 December 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ {{Cite web|url=https://database.ilga.org/discrimination-employment-lgbti
- ^ Michael K. Lavers (19 September 2015). "New Nepal constitution includes LGBT-specific protections". Washington blade. Retrieved 23 July 2017.
- ^ "Pakistan". Human Dignity Trust. Archived from the original on 9 April 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ Iqbal, Nasir (15 July 2009). "SC orders equal benefits for transvestites". Dawn. Archived from the original on 18 July 2009. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ Waidelich, Brian (25 February 2022). "Gay in the PLA: Chinese military views on homosexuals serving in the armed forces". The Jamestown Foundation. Archived from the original on 4 February 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ Groffman, Nicholas (15 May 2017). "Army life: more gay-friendly in China than United States of Britain?". South China Morning Post. Archived from the original on 24 September 2017. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "Chinese trans woman wins sex discrimination lawsuit against employer in landmark victory". The China Project. 6 July 2020.
- ^ 王若翰 (20 June 2012). "变性人群体真实生态:唯学历证明无法修改性别" (Press release) (in Chinese (China)). 搜狐. Archived from the original on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- ^ "跨性别者手术后:历时半年终于修改学历 就业遭歧视". 搜狐. 23 December 2019. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- ^ "Cap. 290 Adoption Ordinance" (in Chinese). 28 February 2004. Archived from the original on 17 January 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "Foreign Affairs and National Defence" (PDF). Basic Law - the source of Hong Kong's Progress and Development. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "ID card sex entry policy revised". news.gov.hk. 3 April 2024. Retrieved 21 September 2024.
- ^ "Japan opposition party submits bill for same-sex marriage". Kyodo News. 6 March 2023. Retrieved 31 May 2023.
- ^ "LGBT Rights in Japan" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 November 2013.
- ^ Hassig, Ralph; Oh, Kongdan (2015). The Hidden People of North Korea: Everyday Life in the Hermit Kingdom (Second ed.). Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 126. ISBN 978-1442237193.
The second major stress on soldiers is their highly restricted social life. During their initial ten years of service they are not permitted to marry, which means that they are supposed to postpone sexual activity until their late twenties.
- ^ Rashid, Raphael (31 May 2023). "South Korea's first ever same-sex marriage bill goes to parliament". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 4 June 2023.
- ^ "Taiwan". glbtq.com.
- ^ "同性伴侶跨區註記7月3日開放". Up Media (in Chinese). 21 July 2017. Archived from the original on 24 September 2017. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "Taiwan's top court rules in favour of same-sex marriage". The Guardian. 24 May 2017. Archived from the original on 24 May 2017. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "Taiwan voters reject same-sex marriage in referendums". BBC News. 25 November 2018. Archived from the original on 25 November 2018. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ "Taiwan approves same-sex marriage in first for Asia". Channel News Asia. 17 May 2019. Archived from the original on 17 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- ^ Article 20, "Act for Implementation of J.Y. Interpretation No. 748". Laws & Regulations Database of The Republic of China (Taiwan). Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ Article 7, "Constitution of the Republic of China (Taiwan)". Laws & Regulations Database of The Republic of China (Taiwan). Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "Act of Gender Equality in Employment". Laws & Regulations Database of The Republic of China (Taiwan). Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "Gender Equity Education Act". Laws & Regulations Database of The Republic of China (Taiwan). Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "109年度訴字第275號". 司法院裁判書系統. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "Qanun Aceh Nomor 6 Tahun 2014 Tentang Hukum Jinayat (Aceh Religious Bylaw on Crimes" (PDF). Aceh Provincial Website. 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 June 2017. Retrieved 6 September 2017.
- ^ Robertson, Holly (3 April 2019). "Brunei enacts Islamic laws to punish gay sex with stoning to death — here's what you need to know". ABC News.
- ^ Hoppe, Sascha (8 March 2023). "Spartacus Gay Travel Index 2023". Spartacus Gay Travel Blog. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ Article 52 of the Penal Code, p. 3
- ^ "Satpol PP Palembang, Ungkap Sering Temukan Pasangan LGBT, Tapi Sulit Ditindak". Sripoku.com. 6 February 2020.
- ^ Rongiyati, Sulasi (November 2015). "Surat Edaran Kapolri Tentang Ujaran Kebencian: Menjaga Kebebasan Berpendapat Dan Harmonisasi Kemajemukan" (PDF). Info Singkat. 7 (21): 1–4. ISSN 2088-2351.
- ^ a b Mosbergen, Dominique (12 October 2015). "Being LGBT In Southeast Asia: Stories Of Abuse, Survival And Tremendous Courage". Huffington Post. Retrieved 11 October 2018.
- ^ Chiam, Zhan; Duffy, Sandra; González Gil, Matilda (November 2016). "Trans Legal Mapping Report" (PDF). International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association (ILGA). Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- ^ Thwel, Myat (14 December 2022). "Myanmar regime hands LGBT activist another 22 years behind bars". Myanmar Now. Archived from the original on 27 March 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ a b "Philippines: Congress Approves Anti-Discrimination Bill". Iglhrc.org. 24 January 2004. Retrieved 5 September 2010.
- ^ Myers, JoAnne (19 September 2013). Historical Dictionary of the Lesbian and Gay Liberation Movements. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 9780810874688 – via Google Books.
- ^ "Gay Philippines News & Reports 2003-06: Filipino city bans feminine men". GlobalGayz.com. 6 December 2004. Retrieved 21 February 2023.
- ^ a b Border, Hana (11 August 2022). "Padilla wants same-sex unions institutionalized". GMA News. Retrieved 23 August 2022.
- ^ "Adoption in the Philippines". Intercountry Adoption. Retrieved 15 October 2015.
- ^ "Pemberton guilty of homicide in Jennifer Laude case". Rappler. Retrieved 1 December 2015.
- ^ Luna, Franco. "Manila signs ordinance prohibiting gender discrimination". Philstar.com. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ "Passage of Cebu's anti-discrimination law lauded". Local News. Sun Star Publishing, Inc. Archived from the original on 21 October 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ Gamil, Jaymee T. (5 October 2014). "QC council approves pro-LGBT ordinance". INQUIRER.net.
- ^ Mellejor, Ayan C. (14 December 2012). "Davao council bans discrimination vs gays, minority, differently abled". inquirer.net.
- ^ Ong, Ghio; Flores, Helen (24 December 2013). "LGBT sector lauds provision of Anti-Bullying Act". The Philippine Star. Retrieved 31 October 2023.
- ^ Tan, Yvette (17 December 2018). "Gay Singaporean man wins landmark appeal to adopt surrogate child". BBC News. Archived from the original on 17 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ Elangovan, Navene (14 October 2019). "New legislation protects LGBTQ community from religiously motivated violence but law is 'same for all'". Today. Singapore. Retrieved 6 March 2020.
- ^ a b Helen, Regan; Kocha, Olarn. "'Monumental step forward': Thailand to become first Southeast Asian nation to legalize same-sex marriage". CNN. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ^ a b "Love is Love: Thailand's senate approves Marriage Equality". BK Magazine. 18 June 2024.
- ^ Browning, Bil. "Thailand to legalize same-sex marriage". LGBTQ Nation. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ Valentin, Declercq. "LGBTQ Rights in Thailand - G.A.M. Legal Alliance". gam-legalalliance.com. GAM Legal Alliance. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- ^ "The right to title change". Bangkok Post. 29 July 2019. Retrieved 23 December 2019.
- ^ "Cặp đôi đồng tính có được nhận con nuôi không?". VnExpress. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- ^ "Sex-change officially legalized for the Vietnamese people". thanhnien.vn. 24 November 2015.
- ^ Thông, Báo Giao. "Ảnh: Cộng đồng người chuyển giới vỡ òa trong ngày lịch sử - Báo Giao thông".
- ^ "Perspective: what has the EU done for LGBT rights?". Café Babel. 17 May 2010. Archived from the original on 19 May 2010. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ "What is the current legal situation in the EU?". ILGA Europe. Archived from the original on 2 November 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ "RIS – Eingetragene Partnerschaft-Gesetz – Bundesrecht konsolidiert, Fassung vom 17.08.2019". www.ris.bka.gv.at.
- ^ "Unterscheidung zwischen Ehe und eingetragener Partnerschaft verletzt Diskriminierungsverbot". Constitutional Court of Austria (in German). 5 December 2017. Retrieved 5 December 2017.
- ^ "Bundesgesetz, mit dem das Allgemeine Bürgerliche Gesetzbuch und das Bundesgesetz über die eingetragene Partnerschaft geändert wird" (PDF). parlament.gv.at (in German).
- ^ "Entschließungsantrag betreffend der Aufhebung des Adoptionsverbots für Homosexuelle" (PDF). parlament.gv.at.
- ^ "§ 144(2) ABGB (General Civil Code)". www.ris.bka.gv.at (in German).
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Portál veřejné správy". portal.gov.cz.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "Trans Rights Europe Map, 2018" (PDF). Transgender Europe. 21 April 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "glbtq >> social sciences >> Berlin" (PDF). glbtq.com.
- ^ "LPartG – nichtamtliches Inhaltsverzeichnis". www.gesetze-im-internet.de.
- ^ "Gesetz zur Einführung des Rechts auf Eheschließung für Personen gleichen Geschlechts – 2. Ergänzung der Anwendungshinweise zur Umsetzung des vorgenannten Gesetzes".
- ^ a b Connolly, Kate (30 June 2017). "German Parliament votes to legalise same-sex marriage". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 30 June 2017. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Antidiskriminierungsstelle – Publikationen – AGG in englischer Sprache". antidiskriminierungsstelle.de.
- ^ Kft, Wolters Kluwer Hungary. "2009. évi XXIX. törvény a bejegyzett élettársi kapcsolatról, az ezzel összefüggő, valamint az élettársi viszony igazolásának megkönnyítéséhez szükséges egyes törvények módosításáról – Hatályos Jogszabályok Gyűjteménye". net.jogtar.hu.
- ^ "Folyamatban levő törvényjavaslatok – Országgyűlés". www.parlament.hu.
- ^ a b "Melegházasságról szóló törvényjavaslat landolt a magyar parlamentben" (in Hungarian). Index.hu. 29 June 2015. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ^ "Fundamental Law of Hungary" (PDF). TASZ. Retrieved 15 September 2012.
- ^ Gorondi, Pablo (18 April 2011). "Hungary passes new conservative constitution". Reading Eagle. Retrieved 15 September 2012.
- ^ "Hungary amends constitution to redefine family, effectively banning gay adoption". ABC News. 15 December 2020. Archived from the original on 15 December 2020. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ Wareham, Jamie (19 May 2020). "Transgender People In Hungary Lose Right To Gender Recognition". Forbes. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ "Gesetz über die eingetragene Partnerschaft gleichgeschlechtlicher Paare (Partnerschaftsgesetz; PartG)" (PDF). gesetze.li (in German).
- ^ Sele, David (16 May 2024). "Landtag beschließt Ehe für alle". Vaterland (in German). Archived from the original on 16 May 2024. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "Einladung - Öffentliche Landtagssitzung (Mittwoch/Donnerstag/Freitag, 6./7./8. März 2024 09.00 Uhr, Landtagssaal) (see agenda item #33)" (PDF). landtag.li (in German). 6 March 2024. Retrieved 8 March 2024.
- ^ "Liechtenstein: Parlament berät Vorlage zur Eheöffnung". Mannschaft Magazin. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ ""Ehe für Alle" ab 1. Januar 2025". Radio Liechtenstein (in German). Archived from the original on 8 March 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Flay Leichtenstein. "Danke fur 24x..." Facebook (in German). Archived from the original on 8 March 2024. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Landtag, 8. Marz 2024, Trakt. 31 (Teil 2) - 33 (watch from 33:58 onwards; results shown on 1:01:44)". vimeopro (in German). 8 March 2024.
- ^ "Art. 25 gekippt: Etappensieg für gleichgeschlechtliche Paare". Volksblatt (in German). 6 May 2022. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ "Art. 25 des Partnerschaftsgesetzes in Kraft - Ab heute dürfen auch homosexuelle Paare ein Stiefkind adoptieren)". vaterland.li (in German). 1 June 2023. Retrieved 4 June 2023.
- ^ "The Constitution of the Republic of Poland". Sejm RP. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
Marriage, being a union of a man and a woman, as well as the family, motherhood and parenthood, shall be placed under the protection and care of the Republic of Poland.
- ^ Judgment of the Supreme Court of 7 July 2004, II KK 176/04,
W dotychczasowym orzecznictwie Sądu Najwyższego, wypracowanym i ugruntowanym zarówno w okresie obowiązywania poprzedniego, jak i obecnego Kodeksu postępowania karnego, a także w doktrynie (por. wypowiedzi W. Woltera, A. Zolla, A. Wąska), pojęcie "wspólne pożycie" odnoszone jest wyłącznie do konkubinatu, a w szczególności do związku osób o różnej płci, odpowiadającego od strony faktycznej stosunkowi małżeństwa (którym w myśl art. 18 Konstytucji jest wyłącznie związek osób różnej płci). Tego rodzaju interpretację Sąd Najwyższy, orzekający w niniejszej sprawie, w pełni podziela i nie znajduje podstaw do uznania za przekonywujące tych wypowiedzi pojawiających się w piśmiennictwie, w których podejmowane są próby kwestionowania takiej interpretacji omawianego pojęcia i sprowadzania go wyłącznie do konkubinatu (M. Płachta, K. Łojewski, A.M. Liberkowski). Rozumiejąc bowiem dążenia do rozszerzającej interpretacji pojęcia "wspólne pożycie", użytego w art. 115 § 11 k.k., należy jednak wskazać na całkowity brak w tym względzie dostatecznie precyzyjnych kryteriów.
- ^ "Judgment of the Constitutional Tribunal of 11 May 2005, K 18/04".
Polska Konstytucja określa bowiem małżeństwo jako związek wyłącznie kobiety i mężczyzny. A contrario nie dopuszcza więc związków jednopłciowych. [...] Małżeństwo (jako związek kobiety i mężczyzny) uzyskało w prawie krajowym RP odrębny status konstytucyjny zdeterminowany postanowieniami art. 18 Konstytucji. Zmiana tego statusu byłaby możliwa jedynie przy zachowaniu rygorów trybu zmiany Konstytucji, określonych w art. 235 tego aktu.
- ^ "Judgment of the Constitutional Tribunal of 9 November 2010, SK 10/08".
W doktrynie prawa konstytucyjnego wskazuje się nadto, że jedyny element normatywny, dający się odkodować z art. 18 Konstytucji, to ustalenie zasady heteroseksualności małżeństwa.
- ^ "Judgment of the Supreme Administrative Court of Poland of 25 October 2016, II GSK 866/15".
Ustawa o świadczeniach zdrowotnych finansowanych ze środków publicznych nie wyjaśnia, co prawda, kto jest małżonkiem. Pojęcie to zostało jednak dostatecznie i jasno określone we wspomnianym art. 18 Konstytucji RP, w którym jest mowa o małżeństwie jako o związku kobiety i mężczyzny. W piśmiennictwie podkreśla się, że art. 18 Konstytucji ustala zasadę heteroseksualności małżeństwa, będącą nie tyle zasadą ustroju, co normą prawną, która zakazuje ustawodawcy zwykłemu nadawania charakteru małżeństwa związkom pomiędzy osobami jednej płci (vide: L. Garlicki Komentarz do art. 18 Konstytucji, s. 2-3 [w:] Konstytucja Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej. Komentarz, Wydawnictwo Sejmowe, Warszawa 2003). Jest wobec tego oczywiste, że małżeństwem w świetle Konstytucji i co za tym idzie – w świetle polskiego prawa, może być i jest wyłącznie związek heteroseksualny, a więc w związku małżeńskim małżonkami nie mogą być osoby tej samej płci.
- ^ "Judgment of the Supreme Administrative Court of Poland of 28 February 2018, II OSK 1112/16".
art. 18 Konstytucji RP, który definiuje małżeństwo jako związek kobiety i mężczyzny, a tym samym wynika z niego zasada nakazująca jako małżeństwo traktować w Polsce jedynie związek heteroseksualny.
- ^ *Gallo D; Paladini L; Pustorino P, eds. (2014). Same-Sex Couples before National, Supranational and International Jurisdictions. Berlin: Springer. p. 215. ISBN 978-3-642-35434-2.
the drafters of the 1997 Polish Constitution included a legal definition of a marriage as the union of a woman and a man in the text of the constitution in order to ensure that the introduction of same-sex marriage would not be passed without a constitutional amendment.
- Marek Safjan; Leszek Bosek, eds. (2016). Konstytucja RP. Tom I. Komentarz do art. 1-86. Warszawa: C.H. Beck Wydawnictwo Polska. ISBN 9788325573652.
Z przeprowadzonej powyżej analizy prac nad Konstytucją RP wynika jednoznacznie, że zamieszczenie w art. 18 Konstytucji RP zwrotu definicyjnego "związek kobiety i mężczyzny" stanowiło reakcję na fakt pojawienia się w państwach obcych regulacji poddającej związki osób tej samej płci regulacji zbliżonej lub zbieżnej z instytucją małżeństwa. Uzupełniony tym zwrotem przepis konstytucyjny "miał pełnić rolę instrumentu zapobiegającego wprowadzeniu takiej regulacji do prawa polskiego" (A. Mączyński, Konstytucyjne podstawy prawa rodzinnego, s. 772). Innego motywu jego wprowadzenia do Konstytucji RP nie da się wskazać (szeroko w tym zakresie B. Banaszkiewicz, "Małżeństwo jako związek kobiety i mężczyzny", s. 640 i n.; zob. też Z. Strus, Znaczenie artykułu 18 Konstytucji, s. 236 i n.). Jak zauważa A. Mączyński istotą tej regulacji było normatywne przesądzenie nie tylko o niemożliwości unormowania w prawie polskim "małżeństw pomiędzy osobami tej samej płci", lecz również innych związków, które mimo tego, że nie zostałyby określone jako małżeństwo miałyby spełniać funkcje do niego podobną (A. Mączyński, Konstytucyjne podstawy prawa rodzinnego, s. 772; tenże, Konstytucyjne i międzynarodowe uwarunkowania, s. 91; podobnie L. Garlicki, Artykuł 18, w: Garlicki, Konstytucja, t. 3, uw. 4, s. 2, który zauważa, że w tym zakresie art. 18 nabiera "charakteru normy prawnej").
- Scherpe JM, ed. (2016). European Family Law Volume III: Family Law in a European Perspective Family. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar Publishing. p. 121. ISBN 978-1-78536-304-7.
Constitutional bans on same-sex marriage are now applicable in ten European countries: Article 32, Belarus Constitution; Article 46 Bulgarian Constitution; Article L Hungarian Constitution, Article 110, Latvian Constitution; Article 38.3 Lithuanian Constitution; Article 48 Moldovan Constitution; Article 71 Montenegrin Constitution; Article 18 Polish Constitution; Article 62 Serbian Constitution; and Article 51 Ukrainian Constitution.
- Stewart J, Lloyd KC (2016). "Marriage Equality in Europe". Family Advocate. 38 (4): 37–40.
Article 18 of the Polish Constitution limits the institution of marriage to opposite-sex couples.
- Marek Safjan; Leszek Bosek, eds. (2016). Konstytucja RP. Tom I. Komentarz do art. 1-86. Warszawa: C.H. Beck Wydawnictwo Polska. ISBN 9788325573652.
- ^ "IV SA/Wa 2618/18 – Wyrok WSA w Warszawie". 8 January 2019.
- ^ "Poland". travel.state.gov.
- ^ https://tranzycja.pl/krok-po-kroku/zmiana-danych-sad/
- ^ "Adopting in Slovakia". Community.
- ^ "Homophobia and Discrimination on Grounds of Sexual Orientation and Gender Identity in the EU Member States Part II: The Social Situation" (PDF). fra.europa.eu.
- ^ Petit Press a.s. "Law change criminalises homophobia". spectator.sme.sk.
- ^ "Zakon o registraciji istospolne partnerske skupnosti". uradni-list.si (in Slovenian).
- ^ "Zakon o partnerski zvezi". uradni-list.si (in Slovenian).
- ^ "Implementation of the amendment to the Family Code". gov.si.
- ^ "First Adoption by Gay Partner of Child's Parent". The Slovenia Times. 20 July 2011. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Weber, Nana (25 April 2013). "Sprememba spola v Sloveniji". Pravna Praksa (in Slovenian) (16–17). GV Založba. ISSN 0352-0730.
- ^ Hirschfeld, Magnus (10 March 2018). The Homosexuality of Men and Women. Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-1-61592-698-5 – via Google Books.
- ^ swissinfo.ch, S. W. I.; Corporation, a branch of the Swiss Broadcasting. "Homosexuals a step closer to equal rights". SWI swissinfo.ch.
- ^ swissinfo.ch, S. W. I.; Corporation, a branch of the Swiss Broadcasting. "Zurich grants gay couples more rights". SWI swissinfo.ch.
- ^ a b "Le pacs gagne du terrain".
- ^ "Bundesgesetz über die eingetragene Partnerschaft gleichgeschlechtlicher Paare". admin.ch (in German).
- ^ "Le nouveau droit de l'adoption entrera en vigueur le 1er janvier 2018". Le Conseil federal (in French). 10 July 2017. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Schelhammer, Christoph R. "Diversité : « La société est tout sauf homogène. »". Swiss Army. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- ^ "Switzerland votes in favour of LGBT protection bill". bbc.com.
- ^ "Débureaucratisation de la procédure de changement de sexe à l'état civil dès le 1er janvier 2022". admin.ch (in French). Retrieved 27 October 2021.
- ^ "Referendum in Armenia brings constitutional reforms". ILGA-Europe. 16 December 2015. Archived from the original on 12 January 2016. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Armenia Central Electoral Commission announces constitutional referendum final results". Newsfeed. 13 December 2015. Archived from the original on 19 January 2016. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Armenia: Gays live with threats of violence, abuse". United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. 30 March 2010. Retrieved 8 June 2012.
- ^ Prof. Dr. Axel Tschentscher, LL-M. "Belarus – Constitution". Servat.unibe.ch. Retrieved 5 January 2014.
- ^ "Belarus: Attitude towards homosexuals and lesbians in Belarus; state protection available to non-heterosexuals in Belarus with special attention to Minsk (2000–2005)". United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. 17 January 2006. Retrieved 11 August 2012.
- ^ "Gay and Lesbian Issues in Belarus". A Belarus Miscellany. Archived from the original on 24 February 2001. Retrieved 29 September 2005.
- ^ "სსიპ "საქართველოს საკანონმდებლო მაცნე"".
- ^ "В Минобороны ответили на вопрос о сексуальных меньшинствах в армии". Tengrinews. 25 February 2022. Retrieved 5 May 2022.
- ^ "The Constitution of Moldova" (PDF). The Government of Moldova. Retrieved 11 March 2015.
- ^ "Putin Signs Gender Reassignment Ban Into Law". The Moscow Times. 24 July 2023. Retrieved 24 July 2023.
- ^ "ЗАКОН". pravo.pmr-online.com.
- ^ "Study on homophobia, transphobia and discrimination on grounds of sexual orientation and gender identity - Legal Report: Ukraine" (PDF). COWI. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 October 2011. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "Ukraine". travel.state.gov.
- ^ Garcia, Horaci (31 May 2022). "Ukraine's 'unicorn' LGBTQ soldiers head for war". Reuters. Retrieved 28 September 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine's gay soldiers fight Russia—and for their rights". The Economist. 5 April 2023. Retrieved 28 September 2023.
- ^ "Ukraine's Parliament passes anti-discrimination law". Ukrinform. 12 November 2015. Archived from the original on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ http://www.rferl.org/a/28340837.html
- ^ "Registration form". retsinformation.dk.
- ^ Stanners, Peter (7 June 2012). "Gay marriage legalised". The Copenhagen Post. Archived from the original on 8 June 2012. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ SØRENSEN, Kaare. "Homoseksuelle fik ja til ægteskab". Jyllands-Posten Politik. Archived from the original on 23 July 2015. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "Lov om ændring af lov om registreret partnerskab, lov om en børnefamilieydelse og lov om børnetilskud og forskudsvis udbetaling af børnebidrag – Udvidet adgang for registrerede partnere til adoption og overførsel af forældremyndighed m.v. - retsinformation.dk".
- ^ "Børneloven af børneloven". Retsinformation (in Danish). Archived from the original on 30 April 2014. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "MSN New Zealand – Latest News, Weather, Entertainment, Business, Sport, Technology". msn.co.nz.
- ^ (in Estonian) "Kooseluseadus". Riigikogu. 9 October 2014.
- ^ "Historic decision: Estonia legalizes same-sex marriage". ERR. 20 June 2023.
- ^ "Historic decision: Estonia legalizes same-sex marriage". ERR. 20 June 2023.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "FAROE ISLANDS SAY YES TO SAME-SEX MARRIAGE – LGBT". lgbt.fo.
- ^ "Gerðabók" (in Faroese). Løgting. Retrieved 2 June 2017.
- ^ "Gay News From 365Gay.com". 3 January 2007. Archived from the original on 3 January 2007.
- ^ "§ 266b". Archived from the original on 14 December 2014.
- ^ "Holdningsskred i synet på homoseksuelle på Færøerne". Information.
- ^ Oy, Edita Publishing. "FINLEX ® - Uppdaterad lagstiftning: Lag om registrerat partnerskap 950/2001". www.finlex.fi.
- ^ "Finland president signs gay marriage law – couples will have to wait to get married until 2017". Gay Star News.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Finland: new gender recognition law 'a major step towards protecting trans rights'". Amnesty International. 1 February 2023. Archived from the original on 1 February 2023. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ "Lög um breytingu á lagaákvæðum er varða réttarstöðu samkynhneigðra (sambúð, ættleiðingar, tæknifrjóvgun)". Alþingi.
- ^ "Lög um breytingar á hjúskaparlögum og fleiri lögum og um brottfall laga um staðfesta samvist (ein hjúskaparlög)". Alþingi.
- ^ "Iceland parliament votes for gay marriage". IceNews. 11 June 2010. Retrieved 12 September 2012.
- ^ "New gay marriage law in Iceland comes into force". Icenews.is. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- ^ "LGBT Rights in Iceland". Equaldex. Archived from the original on 9 April 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ "Barnalög". Althingi (in Icelandic). 1 January 2014. Archived from the original on 30 April 2014. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Magnússon, Hilmar (22 June 2012). "Iceland adopts a new comprehensive law on trans issues". ILGA Europe. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 20 May 2024.
- ^ [3]
- ^ "Latvian Saeima adopts partnership law". eng.lsm.lv. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- ^ "President Signs Anti-Gay Constitutional Amendment". UK Gay News. 21 December 2005. Retrieved 12 August 2009.
- ^ "Same Sex Adoption in Latvia". lvportals.lv.
- ^ Salem-Mackall, Theo (30 June 2015). "Pride in the Baltics: Making History in Latvia". Human rights first. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ "Rainbow Europe". rainbow-europe.org.
- ^ "Change of Name, Surname and Nationality". tm.gov.lv.
- ^ "Law on Registration of Civil Status Acts §37.2". likumi.lv.
- ^ "Gender Change in Latvia - Emilija's Story". www.lsm.lv.
- ^ "Seimas Approves the Proposal on "Cohabitation Agreements" as Alternative to Partnership Law – LGL". 31 May 2017.
- ^ "LIETUVOS RESPUBLIKOS KONSTITUCIJA". www3.lrs.lt.
- ^ "Intercountry Adoption - Lithuania". Bureau of Consular Affairs - U.S. Department of State. 1 April 2024. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Kuktoraitė, Eglė (29 August 2017). "Ar reikia Lietuvos kariuomenei homoseksualių karių?". Mano teisės (in Lithuanian). Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ^ Robledo, Jordan. "Lithuania approves bill allowing trans people to change name without surgery". Gay Times. Archived from the original on 4 January 2022. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Civilinis kodeksas patvirtinimo, įsigaliojimo ir įgyvendinimo ĮSTATYMAS. Civilinis KODEKSAS". Lietuvos Respublikos (in Lithuanian). 18 July 2000. Archived from the original on 2 January 2007. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Lov om endringer i ekteskapsloven, barnelova, adopsjonsloven, bioteknologiloven mv. (felles ekteskapslov for heterofile og homofile par) – Lovdata". lovdata.no.
- ^ "Norway Gay Marriage Bill Passes Final Hurdle". 365gay.com. Retrieved 17 June 2008.
- ^ "Norway passes law approving gay marriage". Los Angeles Times. 17 June 2008. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "Norway". travel.state.gov.
- ^ "Lov om barn og foreldre (barnelova)". Lovdata (in Norwegian). 1982. Archived from the original on 17 March 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ Moore, Matt (11 November 2020). "Norway bans hate speech against trans and bisexual people". Gay Times. Archived from the original on 11 November 2020.
The amendments [...] changed the phrase "homosexual orientation" to "sexual orientation"
- ^ "Svensk författningssamling" (PDF). notisum.se.
- ^ "Gays Win Marriage Rights". Sveriges Radio English. 1 April 2009.
- ^ "Sweden". travel.state.gov.
- ^ "Föräldrabalk (1949:381)". Sveriges Riksdag (in Swedish). 1949. Archived from the original on 15 March 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Fia Sundevall & Alma Persson (2016) "LGBT in the Military: Policy Development in Sweden 1944–2014", Sexuality Research and Social Policy, June 2016, Volume 13, Issue 2, pp 119-129, https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13178-015-0217-6/fulltext.html
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ [4]
- ^ "An ordinance to amend the criminal code" (PDF). Sovereign Base Areas Administration. 10 November 2000. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 April 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Criminal Code" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2015. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Civil Partnership (Armed Forces) Order 2005" (PDF). Legislation UK. 15 November 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 December 2010. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Overseas Marriage (Armed Forces) Order 2014" (PDF). Legislation UK. 28 April 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 October 2017. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Employment (Equality) Ordinance 2013" (PDF). Sovereign Base Areas Administration. 8 February 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 June 2015. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Llei 4/2005, del 21 de febrer, qualificada de les unions estables de parella".
- ^ a b "Llei 34/2014, del 27 de novembre, qualificada de les unions civils i de modificació de la Llei qualificada del matrimoni, de 30 de juny de 1995" (PDF).
- ^ "Diari d'Andorra – Enllestida la llei d'unions civils amb el procés d'adopció dels matrimonis". diariandorra.ad.
- ^ RTVA, Andorra Difusió. "Demà entren en vigor lleis importants, com la d'unions civils o la 'regla d´or' | Andorra Difusió". www.andorradifusio.ad.
- ^ "Andorra adopts first gender recognition law". TGEU. 25 July 2022. Archived from the original on 7 October 2022. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Data" (PDF). ilga-europe.org.
- ^ "Article 46(1), Bulgaria – Constitution". Retrieved 4 October 2009.
- ^ "Bulgaria". travel.state.gov.
- ^ "Bulgarian Parliament approves with 93-23 vote (and 23 abstentions) amendments to the Protection from Discrimination Act to include protection against discrimination of trans people". The Sofia Globe. 25 March 2015.
- ^ "Bulgarian Parliament Votes on Anti-Discrimination Law Amendments". Novinite.com. 25 March 2015.
- ^ "Anual Review 2018: Bulgaria" (PDF). ILGA Europe. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ "Trans Rights Index: Europe & Central Asia 2021" (PDF). TGEU. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- ^ "O PROGLAŠENJU ZAKONA O ISTOSPOLNIM ZAJEDNICAMA".
- ^ "Zakon o životnom partnerstvu osoba istog spola – Zakon.hr". www.zakon.hr.
- ^ "Ustav Republike Hrvatske" (PDF) (in Croatian). Ustavni sud Republike Hrvatske. 15 January 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 March 2015. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ "Odbijena žalba Ministarstva: istospolni parovi u Hrvatskoj mogu zajedno pristupiti procjeni za posvojitelje!". www.dugineobitelji.com. 26 May 2022. Retrieved 12 July 2022.
- ^ (in Croatian) "Zakon o suzbijanju diskriminacije". Narodne-novine.nn.hr. 21 July 2008. Retrieved 3 April 2014.
- ^ (in Croatian)"Pravilnik o načinu prikupljanja medicinske dokumentacije te utvrđivanja uvjeta i pretpostavki za promjenu spola i drugom rodnom identitetu". Narodne-novine.nn.hr. 15 November 2014. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ^ "CIVIL PARTNERSHIP ACT 2014" (PDF).
- ^ "Gibraltar unanimously legalizes marriage equality". 26 October 2016.
- ^ a b "Equal Opportunities Act 2006" (PDF). gibraltarlaws.gov.gi. 2006. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- ^ "ΝΟΜΟΣ 4356/2015 | ΦΕΚ Α 181-2015 | σελίδα 1". nomoi.info.
- ^ Lavietes, Matt (15 February 2024). "Greece legalizes same-sex marriage in a first for an Orthodox Christian nation". NBC News. Archived from the original on 12 March 2024. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Greece improves gender recognition law but misses chance to introduce self-determination". ILGA EUROPE. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ^ "Greece passes gender-change law opposed by Orthodox church". The Guardian. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ^ "Il presidente Mattarella ha firmato la legge sulle unioni civili". 20 May 2016.
- ^ "Same-sex marriages performed abroad won't be recognized in Italy". www.thelocal.it. 15 May 2018.
- ^ (in Italian) "Adozioni gay, la Corte d'Appello di Roma conferma: sì a due mamme". Corriere della Sera.
- ^ (in Italian)"Cassazione, via libera alla stepchild adoption in casi particolari". Repubblica.
- ^ (in Italian) "Legge 14 Aprile 1982, n. 164 (GU n. 106 del 19/04/1982) Norme in Materia di Rettificazione di Attribuzione di Sesso". Archived from the original on 23 May 2007.
- ^ "Court of Cassation judgment of 21 May 2015" (PDF).
- ^ "FAMILY LAW OF KOSOVO – Law Nr.2004/32". childhub.org.
- ^ "Adoption Laws in Kosovo: Unmarried persons". State portal of the Republic of Kosovo. Constitution of Kosovo.
- ^ "Adoption in Kosovo (Report) – Page 6". OSCE Mission in Kosovo.
- ^ "Kosovo Constitution". www.kushtetutakosoves.info.
- ^ "AN ACT to regulate civil unions and to provide for matters connected therewith or ancillary thereto".
- ^ "Gender Identity, Gender Expression and Sex Characteristics Bill". 22 November 2016.
- ^ "Zakon o životnom partnerstvu lica istog pola". Službeni list Crne Gore (in Montenegrin) (67/2020): 1-14. 7 July 2020. Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- ^ "THE CONSTITUTION OF MONTENEGRO and THE CONSTITUTIONAL LAW FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE CONSTITUTION OF MONTENEGRO ADOPTED ON 19 OCTOBER 2007" (PDF). Retrieved 5 January 2014.
- ^ "Information on the rights of minority groups in Montenegro" (PDF). Retrieved 5 January 2014.
- ^ https://ener.gov.mk/files/propisi_files/ria1/2_213014465MK%204052021-ZME%20SOBRANIE.docx
- ^ "Lei no. 7/2001 de 11 de Maio" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Diario da Republica. 11 May 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 August 2010. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "AR altera lei das uniões de facto". TVI24 (in Portuguese). 3 July 2007. Archived from the original on 15 July 2009. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Lei no. 9/2010 de 31 de Maio" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Assemblea da Republica. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 May 2010. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Lei 17/2016 de 20 de junho" (in Portuguese). Assembleia da Republica. 20 June 2016. Archived from the original on 29 August 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Lei que alarga a procriação medicamente assistida publicada em Diário da República". tvi24 (in Portuguese). 20 June 2016. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Todas as mulheres com acesso à PMA a 1 de Agosto". PÚBLICO (in Portuguese). 20 June 2016. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "MEPs welcome new gender change law in Portugal; concerned about Lithuania – The European Parliament Intergroup on LGBTI Rights". www.lgbt-ep.eu.
- ^ "Decizie istorică a CCR în privința căsătoriilor gay". Digi24. 18 July 2018.
- ^ "Romania". travel.state.gov.
- ^ First post-Medieval criminal code in the Principality of Serbia, named "Kaznitelni zakon" (Law of Penalties), adopted in 1860, punishes sexual intercourse "against the order of nature" between males with 6 months to 4 years imprisonment. V. Para # 206, p. 82 of the "Kaznitelni zakon 1860" in Slavo-Serbian orthography (PDF)
- ^ "Constitution of Serbia". Serbian Government. Retrieved 8 November 2006.
- ^ "Donet Pravilnik o načinu izdavanja i obrascu potvrde nadležne zdravstvene ustanove o promeni pola" (in Serbian). Gayten-LGBT. 30 December 2018. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Galán, José Ignacio Pichardo. "Same-sex couples in Spain. Historical, contextual and symbolic factors" (PDF). Institut national d'études démographiques. Retrieved 30 December 2012.
- ^ "Ley 1/2001, de 6 de abril, por la que se regulan las uniones de hecho". Noticias Juridicas. Retrieved 18 April 2015.
- ^ "Llei 18/2001 de 19 de desembre, de parelles estables" (in Catalan). Govern de les Illes Balears. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ^ "LEY 4/2002, de 23 de mayo, de Parejas Estables" (PDF) (in Spanish). Agencia Estatal Boletín Oficial del Estado. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ^ "DECRETO 117/2002, de 24 de octubre, por el que se crea el Registro de Uniones de Hecho en Castilla y León y se regula su funcionamiento" (PDF) (in Spanish). Junta de Castilla y León. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ^ "Ley de Cantabria 1/2005, de 16 de mayo, de Parejas de Hecho de la Comunidad Autónoma de Cantabria" (in Spanish). Noticias Juridicas. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ^ "Decreto 248/2007, de 20 de diciembre, por el que se crea y se regula el Registro de Parejas de Hecho de Galicia" (in Spanish). Noticias Juridicas. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ^ "Decreto 30/2010, de 14 de mayo, por el que se crea el Registro de Parejas de Hecho de La Rioja" (in Spanish). El Gobierno de La Rioja. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ^ "9L/PPL-0018 | Asamblea Regional de Murcia". www.asambleamurcia.es.
- ^ "Murcia será en junio la última comunidad en regular por ley las parejas de hecho". La Verdad. 25 May 2018.
- ^ "Reglamento regulador del Registro de Uniones de Hecho". Ciudad autonoma de Ceuta (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 16 January 2014. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "REGLAMENTO REGULADOR DEL REGISTRO DE PAREJAS DE HEC HO DE LA CIUDAD AUTÓNOMA DE MELILLA" (PDF). Melilla (in Spanish). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2014. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Spain approves liberal gay marriage law". St. Petersburg Times. 1 July 2005. Retrieved 8 January 2007.
- ^ "Intercountry Adoption - Spain". Department of State Bureau of Consular Affairs. 7 January 2013. Archived from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ (in Spanish) Boletín Oficial del Estado "Ley 14/2006, de 26 de mayo, sobre técnicas de reproducción humana asistida". Gobierno de Espana (in Spanish). 27 May 2006. Archived from the original on 2 July 2013. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Ley 3/2016, de 22 de julio, de Protección Integral contra LGTBIfobia y la Discriminación por Razón de Orientación e Identidad Sexual en la Comunidad de Madrid" (PDF) (in Spanish). Legislacion Consolidada. 10 August 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 February 2018. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Jones, Sam (16 February 2023). "Spain passes law allowing anyone over 16 to change registered gender". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 16 February 2023. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Legal Aspects of Gender Reassignment Surgery in Turkey: A Case Report". Indian Journal of Gender Studies. 18 (1): 77–88. 28 January 2011. doi:10.1177/097152151001800104. S2CID 143761091.
- ^ "Gesetz zur Einführung des gesetzlichen Zusammenwohnens" (PDF).
- ^ "Belgium to follow Holland on gay marriage". RTÉ News. 29 November 2002.
- ^ "Belgium legalizes gay marriage". UPI. 31 January 2003.
- ^ "Belgium approves same-sex marriage". PlanetOut. 30 January 2003. Archived from the original on 28 February 2006.
- ^ "Belgium". travel.state.gov.
- ^ (in French and Dutch) Belgian Official Gazette Loi du 5 mai 2014 portant établissement de la filiation de la coparente, as amended by loi du 18 décembre 2014 modifiant le Code civil, le code de droit international privé, le Code consulaire, la loi du 5 mai 2014 portant établissement de la filiation de la coparente et la loi du 8 mai 2014 modifiant le Code civil en vue d’instaurer l’égalité de l’homme et de la femme dans le mode de transmission du nom à l’enfant et à l’adopté
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Loi du 25 juin 2017 réformant des régimes relatifs aux personnes transgenres en ce qui concerne la mention d'une modification de du sexe dans les actes de l'état civil et ses effets/Wet van 25 juni 2017 tot hervorming van regelingen inzake transgenders wat de vermelding van een aanpassing van de registratie van het geslacht in de akten van de burgerlijke stand en de gevolgen hiervan betreft" (PDF).
- ^ "Loi n° 99-944 du 15 novembre 1999 relative au pacte civil de solidarité | Legifrance". www.legifrance.gouv.fr.
- ^ Erlanger, Steven (18 May 2013). "Hollande Signs French Gay Marriage Law". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 July 2015.
- ^ "France". travel.state.gov.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "France scraps transgender sterilisation". BBC News. 14 October 2016.
- ^ "Sexual Offences (Bailiwick of Guernsey) (Amendment) Law, 2011". guernseylegalresources.gg. 30 October 2012.
- ^ "JURIST – Homosexual Offenses and Human Rights in Guernsey". jurist.org.
- ^ "Data". gov.gg.
- ^ "Union civile, Green, marriage, Liberate « Guernsey Press". guernseypress.com.
- ^ "The Same-Sex Marriage (Consequential and Miscellaneous Amendments and Contrary Provisions) (Guernsey) Ordinance, 2017". www.gov.gg. 13 March 2017. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- ^ "Guernsey votes to legalise same-sex marriage". Gay Times Magazine. 22 September 2016.
- ^ "Sark becomes last place in British Isles to legalise same-sex marriage". gaytimes.co.uk.
- ^ "Guernsey law change allows same-sex couples to adopt". BBC News. 24 June 2015.
- ^ "Politicians unanimously approve Guernsey's new anti-discrimination law". ITV. 30 September 2022. Archived from the original on 30 September 2022. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "The Children (Guernsey and Alderney) Law, 2008". Guernsey Legal Resources. 6 July 2008. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ "The Prevention of Discrimination (Enabling Provisions) (Bailiwick of Guernsey) Law, 2004". Guernsey Legal Resources. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ^ "Legal Resources: Legal Resources Navigation List: Guernsey Law Reports 2007–08 GLR 161". guernseylegalresources.gg.
- ^ "Civil Partnership and Certain Rights and Obligations of Cohabitants Act 2010". irishstatutebook.ie.
- ^ "Thirty-fourth Amendment of the Constitution (Marriage Equality) Bill 2015 (Number 5 of 2015) – Tithe an Oireachtais". www.oireachtas.ie. 21 January 2015.
- ^ "Unmarried gay and heterosexual couples can now adopt a child". Independent.ie.
- ^ "Gay adoption law due before same-sex marriage referendum". The Irish Times. 21 January 2015.
- ^ "FAQs". The Adoption Authority of Ireland.
- ^ "Data". rainbow-europe.org.
- ^ Gartl, Fiona. "Change sought to anomaly in adoption law". The Irish Times.
- ^ "Children and Family Relationships Act 2015" (PDF). oireachtas.ie.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Employment Equality Act, 1998". Irishstatutebook.ie. 18 June 1998. Retrieved 11 July 2010.
- ^ "Equal Status Act, 2000". Irishstatutebook.ie. 26 April 2000. Retrieved 11 July 2010.
- ^ "Prohibition of Incitement To Hatred Act, 1989". irishstatutebook.ie.
- ^ MacGuill, Dan. ""A historic moment" – Oireachtas signs off on gender recognition bill".
- ^ "Civil Partnership Act 2011" (PDF). legislation.gov.im.
- ^ "Same-sex Manx marriages can go ahead after Royal Assent". BBC. 19 July 2016. Archived from the original on 19 July 2016. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ^ "Employment Act 2006" (PDF).
- ^ "Gender Recognition Act 2009" (PDF). legislation.gov.im.
- ^ "Gender recognition bill to provide protection to Isle of Man trans residents". PinkNews.
- ^ "Civil Partnership (Jersey) Law 2012". Jersey Legal Information Board.
- ^ "Orders approved and business transacted at the Privy Council held by the Queen of Buckingham Palace" (PDF). Privy Council. 23 May 2018.
- ^ "Superintendent Registrar's advice for same-sex marriage planning". www.gov.je.
- ^ "Draft" (PDF). statesassembly.gov.je.
- ^ "Gender Recognition (Jersey) Law 2010". Jersey Legal Information Board.
- ^ "Loi du 9 juillet 2004 relative aux effets légaux de certains partenariats. - Legilux". legilux.public.lu.
- ^ "Luxembourg Times – Archives – Same-sex marriages from January 1". www.wort.lu.
- ^ "Same-sex marriage in Luxembourg from 1 January 2015". Chronicle. 17 July 2014. Archived from the original on 19 July 2014. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- ^ "Mémorial A n° 125 de 2014 – Legilux" (PDF). www.legilux.public.lu.
- ^ "Mémorial A n° 207 de 2006" (PDF). legilux.public.lu.
- ^ "Luxembourg makes status change for transgender people easier". Luxembourg Times. 27 July 2018.
- ^ Waaldijk, Kees. "Major legal consequences of marriage, cohabitation and registered partnership for different-sex and same-sex partners in the Netherlands" (PDF). INED. Retrieved 27 October 2013.
- ^ "Gay Marriage Goes Dutch". CBS News. Associated Press. 1 April 2001. Retrieved 21 January 2010.
- ^ "Intercountry adoption - Netherlands". Bureau of Consular Affairs - US Department of State. 1 April 2009. Archived from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Wet van 25 november 2013 tot wijziging van Boek 1 van het Burgerlijk Wetboek in verband met het juridisch ouderschap van de vrouwelijke partner van de moeder anders dan door adoptie". Officiele bekendmakingen (in Dutch). 2013. Archived from the original on 30 April 2014. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ Veiligheid, Ministerie van Justitie en. "Prohibition of discrimination". www.government.nl.
- ^ Lavers, Michael K (19 December 2013). "Dutch Transgender Rights Bill Approved By Senate". Huffpost. Archived from the original on 26 April 2020. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ J Lester Feder (18 December 2013). "The Netherlands Passes Landmark Gender Identity Law". BuzzFeed News. Archived from the original on 7 September 2018. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ "Civil Partnership Act 2004". legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ a b "Same-sex marriage now legal as first couples wed". BBC News. 29 March 2014. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ^ Thomas, Ellen (20 September 2009). "New legislation sees gay Scottish couples win right to adopt children". The Herald. Retrieved 23 September 2009.
- ^ "United Kingdom". travel.state.gov.
- ^ "Human Fertilisation and Embryology Act 2008: Cases in which woman to be other parent". Legislation UK. Archived from the original on 5 March 2011. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Criminal Justice and Immigration Act 2008 (c. 4)". opsi.gov.uk.
- ^ "Public Order Act 1986". www.legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ "Relationships Act 2003". Tasmanian Legislation. Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- ^ "South Australia gays get new rights by Tony Grew (7 December 2006)". pinknews.com.au. Retrieved 3 September 2007.
- ^ Relationships Act 2008 (Vic)
- ^ "Massive support for register". Star Observer. 13 May 2010. Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- ^ Agius, Kym (1 December 2011). "Bligh asks ALP to support gay marriage". Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- ^ "Civil Unions Bill 2011". ACT Government. Retrieved 14 September 2012.
- ^ Chang, Charis (8 December 2017). "Same-sex marriage is now legal in Australia". news.com.au. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ "Australia Ends a Prohibition On Homosexuals in Military". query.nytimes.com. 24 November 1992.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "Sex Discrimination Amendment (Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity and Intersex Status) Bill 2013". aph.gov.au.
- ^ "Change of sex". NSW Government. Archived from the original on 27 October 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ [5]
- ^ a b "Marriage equality Bill officially signed into law". gaynz.com. 19 April 2013.
- ^ Sweijs, Tim. "LGBT Military Personnel: a Strategic Vision for Inclusion". hcss.nl. The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- ^ "New Zealand passes law making it easier to change sex on birth certificates". The Guardian. 9 December 2021.
- ^ "Births, Deaths, Marriages, and Relationships Registration Bill". New Zealand Parliament. Archived from the original on 5 December 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ Chand, Shalveen (26 February 2010). "Same sex law decriminalised". Fiji Times. Archived from the original on 22 August 2011. Retrieved 6 October 2011.
- ^ "Satpol PP Palembang, Ungkap Sering Temukan Pasangan LGBT, Tapi Sulit Ditindak". Sripoku.com. 6 February 2020.
- ^ Rongiyati, Sulasi (November 2015). "Surat Edaran Kapolri Tentang Ujaran Kebencian: Menjaga Kebebasan Berpendapat Dan Harmonisasi Kemajemukan" (PDF). Info Singkat. 7 (21): 1–4. ISSN 2088-2351.
- ^ "NEW CALEDONIA CATCHES UP TO FRANCE". Star Observer. 9 June 2009.
- ^ Verheyen, Vincent. "Sexual orientation [LGBTQ+] and the draft of the new Solomon Islands Constitution". Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ "Submission to the UN Universal Periodic Review regarding the protection of the rights of LGBTI persons in Vanuatu" (PDF). Kaleidoscope Human Rights Foundation and the VPride Foundation. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ a b c d "In 60 days, gays will be allowed to serve openly in the military". CNN. 23 July 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Beginning today, transgender individuals can join the US military". ABC News. 1 January 2018.
- ^ "Act No 20-150" (PDF). Federated States of Micronesia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "GENDER EQUALITY ACT, 2019" (PDF). 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Nauru decriminalises homosexuality". RNZ. 27 May 2016. Archived from the original on 1 June 2016. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Crimes Act 2016". Ronlaw. 2016. Archived from the original on 7 August 2016. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "CHAPTER 90-40 MARIANAS VISITORS AUTHORITY PERSONNEL REGULATIONS" (PDF).
- ^ "TITLE 10 CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION" (PDF). Commonwealth Law Revision Commission. 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Palau decriminalises sex between men". Gay NZ. 15 October 2014. Archived from the original on 18 October 2014. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Sodomy Laws American Samoa". Sodomylaws.org. 28 March 2004. Archived from the original on 19 February 2012. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ^ Sagapolutele, Fili. "American Samoa is lone US territory questioning gay marriage validity; no licenses sought". USNews. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ^ "American Samoa". National Center for Transgender Equality.
- ^ "Employment Relations Act 2012" (PDF). intaff.whupi.com. 2012.
- ^ "LEY-20830 21-ABR-2015 MINISTERIO SECRETARIA GENERAL DE GOBIERNO - Ley Chile - Biblioteca del Congreso Nacional". 21 April 2015.
- ^ a b Bonnefoy, Pascale; Londoño, Ernesto (7 December 2021). "Chile Legalizes Same-Sex Marriage at Fraught Political Moment". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 7 December 2021.
- ^ (in Spanish) Claudio Ortiz Lazo. "Reflexiones en torno a la homosexualidad y fuerzas armadas". Revista Fuerzas Armadas y Sociedad. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ^ Chile, C. N. N. "Histórico: Ejército admite por primera vez en sus filas a un hombre trans". CNN Chile (in Spanish). Retrieved 2 February 2021.
- ^ "Chile Congress passes anti-discrimination law". Jurist.org. 5 April 2012. Retrieved 29 June 2012.
- ^ "Chilean President Signs Transgender Rights Law". On Top Magazine.
- ^ "Criminal Law Code" (PDF). Niue Legislation 2019 Volume 1. p. 542.
- ^ "Pitcairn Island: Same Sex Marriage and Civil Partnership Ordinance 2015". Equality Case Files. Archived from the original on 23 June 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Laws - PITCAIRN". GayLawNet. Archived from the original on 23 June 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "The Pitcairn Constitution Order 2010" (PDF). Pitcairn Islands. 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ^ "Labour and Employment Relations Act 2013" (PDF). parliament.gov.ws.
- ^ "Crimes, Procedure and Evidence Rules 2003". PacLii. Retrieved 9 April 2021.
External links
- International Lesbian and Gay Association
- Amnesty International USA: LGBT legal status around the world – interactive map
- Pride Legal Archived 5 March 2022 at the Wayback Machine – information by country
- Human Rights Watch on LGBT Rights
- International Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission resource links – for researching legal information
- International Commission of Jurists, Sexual Orientation, Gender Identity and Justice – A Comparative Law Casebook
- United Nations Human Rights Council, Discriminatory laws and practices and acts of violence against individuals based on their sexual orientation and gender identity, an annual report
- United Nations, Living Free and Equal: What States Are Doing to Tackle Violence and Discrimination against Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender and Intersex People, November 2016









