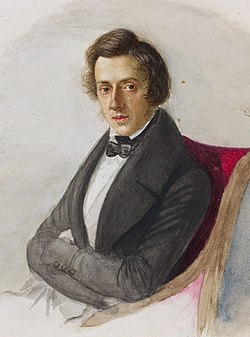Portal:Classical music
Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Classical Music Portal

Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" can also be applied to non-Western art musics. Classical music is often characterized by formality and complexity in its musical form and harmonic organization, particularly with the use of polyphony. Since at least the ninth century, it has been primarily a written tradition, spawning a sophisticated notational system, as well as accompanying literature in analytical, critical, historiographical, musicological and philosophical practices. A foundational component of Western culture, classical music is frequently seen from the perspective of individual or groups of composers, whose compositions, personalities and beliefs have fundamentally shaped its history. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1

Portrait of Haydn by Thomas Hardy, c. 1791
Franz Joseph Haydn (/ˈhaɪdən/ HY-dən; German: [ˈfʁants ˈjoːzɛf ˈhaɪdn̩] ⓘ; 31 March 1732 – 31 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions to musical form have led him to be called "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String quartet".
Haydn arose from humble origins, the child of working people in a rural village. He established his career first by serving as a chorister at St. Stephen's Cathedral, Vienna, then through an arduous period as a freelance musician. Eventually he found career success, spending much of his working life as music director for the wealthy Esterházy family at their palace of Eszterháza in rural Hungary. Though he had his own orchestra there, it isolated him from other composers and trends in music so that he was, as he put it, "forced to become original". During this period his music circulated widely in publication, eventually making him the most celebrated composer in Europe. With the death of his primary patron Nikolaus Esterházy in 1790, Haydn was free to travel, and augmented his fame—now as a performer before the public—in both London and Vienna. The last years of his life (1803–1809) were spent in a state of debility, unable to compose due to poor health. He died in Vienna in 1809 at the age of 77. (Full article...) -
Image 2Detail from Portrait of the Mozart Family, c. 1781
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age resulted in more than 800 works representing virtually every Western classical genre of his time. Many of these compositions are acknowledged as pinnacles of the symphonic, concertante, chamber, operatic, and choral repertoires. Mozart is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Western music, with his music admired for its "melodic beauty, its formal elegance and its richness of harmony and texture".
Born in Salzburg, Mozart showed prodigious ability from his earliest childhood. At age five, he was already competent on keyboard and violin, had begun to compose, and performed before European royalty. His father, Leopold Mozart, took him on a grand tour of Europe and then three trips to Italy. At 17, he was a musician at the Salzburg court but grew restless and travelled in search of a better position. Mozart's search for employment led to positions in Paris, Mannheim, Munich, and again in Salzburg, during which he wrote his five violin concertos, Sinfonia Concertante, and Concerto for Flute and Harp, as well as sacred pieces and masses, the motet Exsultate Jubilate, and the opera Idomeneo, among other works. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Hand-written musical notation by J. S. Bach (1685–1750). This is the beginning of the Prelude from the Suite for Lute in G minor, BWV 995 (transcription of Cello Suite No. 5, BWV 1011).
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music.
Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods. (Full article...) -
Image 4Mozart as portrayed by Dora Stock, 1789
Eine kleine Nachtmusik (Serenade No. 13 for strings in G major), K. 525, is a 1787 composition for a chamber ensemble by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756–1791). The German title means "a little night music" and is one of Mozart's most famous works. The serenade is written for an ensemble of two violins, viola, cello, and double bass, but it is often performed by string orchestras. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina (between 3 February 1525 and 2 February 1526 – 2 February 1594) was an Italian composer of late Renaissance music. The central representative of the Roman School, with Orlande de Lassus and Tomás Luis de Victoria, Palestrina is considered the leading composer of late 16th-century Europe.
Born in the town of Palestrina in the Papal States, Palestrina moved to Rome as a child and underwent musical studies there. In 1551, Pope Julius III appointed him maestro di cappella of the Cappella Giulia at St. Peter's Basilica. He left the post four years later, unable to continue as a layman under the papacy of Paul IV, and held similar positions at St. John Lateran and Santa Maria Maggiore in the following decade. Palestrina returned to the Cappella Giulia in 1571 and remained at St Peter's until his death in 1594. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Lithograph by Chatinière of the ballerina Rita Sangalli in the title rôle of Sylvia from the ballet's original production of 1876. This image was created for the original issue of Delibes's score by the publisher Heugel & Fils.
Sylvia, originally Sylvia, ou La nymphe de Diane, is a full-length classical ballet in two or three acts, first choreographed by Louis Mérante to music by Léo Delibes.
The ballet's premiere took place on 14 June 1876 at the Palais Garnier, but was largely unnoticed by the critics. The first seven productions were commercially unsuccessful, but the 1952 revival, choreographed by Frederick Ashton, popularized the work. Productions in 1997, 2004, 2005, and 2009 productions were all based on Ashton's choreography. (Full article...) -
Image 7Watercolour of Chopin by Maria Wodzińska, 1836
The Piano Sonata No. 2 in B♭ minor, Op. 35, is a piano sonata in four movements by Polish composer Frédéric Chopin. Chopin completed the work while living in George Sand's manor in Nohant, some 250 km (160 mi) south of Paris, a year before it was published in 1840. The first of the composer's three mature sonatas (the others being the Piano Sonata No. 3 in B minor, Op. 58 and the Sonata for Piano and Cello in G minor, Op. 65), the work is considered to be one of the greatest piano sonatas of the literature.
The third movement of the Piano Sonata No. 2 is Chopin's famous funeral march (French: Marche funèbre; Polish: Marsz żałobny) which was composed at least two years before the remainder of the work and has remained, by itself, one of Chopin's most popular compositions. The Piano Sonata No. 2 carries allusions and reminiscences of music by J. S. Bach and by Ludwig van Beethoven; Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 12 also has a funeral march as its third movement. A typical performance of Chopin's second sonata lasts between 21 and 25 minutes, depending on whether the repetition of the first movement's exposition is observed. (Full article...) -
Image 8

The viola (/viˈoʊlə/ vee-OH-lə, (ⓘ) Italian: [ˈvjɔːla, viˈɔːla]) is a string instrument of the violin family, and is usually bowed when played. Violas are slightly larger than violins, and have a lower and deeper sound. Since the 18th century, it has been the middle or alto voice of the violin family, between the violin (which is tuned a perfect fifth higher) and the cello (which is tuned an octave lower). The strings from low to high are typically tuned to C3, G3, D4, and A4.
In the past, the viola varied in size and style, as did its names. The word viola originates from the Italian language. The Italians often used the term viola da braccio, meaning, literally, 'of the arm'. "Brazzo" was another Italian word for the viola, which the Germans adopted as Bratsche. The French had their own names: cinquiesme was a small viola, haute contre was a large viola, and taile was a tenor. Today, the French use the term alto, a reference to its range. (Full article...) -
Image 9
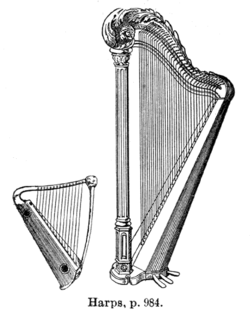
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or concerts. Its most common form is triangular in shape and made of wood. Some have multiple rows of strings and pedal attachments.
Ancient depictions of harps were recorded in Mesopotamia (now Iraq), Persia (now Iran) and Egypt, and later in India and China. By medieval times harps had spread across Europe. Harps were found across the Americas where it was a popular folk tradition in some areas. Distinct designs also emerged from the African continent. Harps have symbolic political traditions and are often used in logos, including in Ireland. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Fauré in 1907
Gabriel Urbain Fauré (12 May 1845 – 4 November 1924) was a French composer, organist, pianist and teacher. He was one of the foremost French composers of his generation, and his musical style influenced many 20th-century composers. Among his best-known works are his Pavane, Requiem, Sicilienne, nocturnes for piano and the songs "Après un rêve" and "Clair de lune". Although his best-known and most accessible compositions are generally his earlier ones, Fauré composed many of his most highly regarded works in his later years, in a more harmonically and melodically complex style.
Fauré was born into a cultured but not especially musical family. His talent became clear when he was a young boy. At the age of nine, he was sent to the École Niedermeyer music college in Paris, where he was trained to be a church organist and choirmaster. Among his teachers was Camille Saint-Saëns, who became a lifelong friend. After graduating from the college in 1865, Fauré earned a modest living as an organist and teacher, leaving him little time for composition. When he became successful in his middle age, holding the important posts of organist of the Église de la Madeleine and director of the Paris Conservatoire, he still lacked time for composing; he retreated to the countryside in the summer holidays to concentrate on composition. By his last years, he was recognised in France as the leading French composer of his day. An unprecedented national musical tribute was held for him in Paris in 1922, headed by the president of the French Republic. Outside France, Fauré's music took decades to become widely accepted, except in Britain, where he had many admirers during his lifetime. (Full article...) -
Image 11
Carmen (French: [kaʁmɛn] ⓘ) is an opera in four acts by the French composer Georges Bizet. The libretto was written by Henri Meilhac and Ludovic Halévy, based on the novella of the same title by Prosper Mérimée. The opera was first performed by the Opéra-Comique in Paris on 3 March 1875, where its breaking of conventions shocked and scandalised its first audiences. Bizet died suddenly after the 33rd performance, unaware that the work would achieve international acclaim within the following ten years. Carmen has since become one of the most popular and frequently performed operas in the classical canon; the "Habanera" and "Seguidilla" from act 1 and the "Toreador Song" from act 2 are among the best known of all operatic arias.
The opera is written in the genre of opéra comique with musical numbers separated by dialogue. It is set in southern Spain and tells the story of the downfall of Don José, a naïve soldier who is seduced by the wiles of the fiery gypsy Carmen. José abandons his childhood sweetheart and deserts from his military duties, yet loses Carmen's love to the glamorous torero Escamillo, after which José kills her in a jealous rage. The depictions of proletarian life, immorality, and lawlessness, and the murder of the main character on stage, broke new ground in French opera and were highly controversial. (Full article...) -
Image 12Johann Christoph von Ponickau, for whose memorial service the cantata was composed
Ich lasse dich nicht, du segnest mich denn (I will not let you go, unless you bless me), BWV 157, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed it in Leipzig in 1726/27 to a libretto by Picander. The first known performance was on 6 February 1727 during a memorial service for Johann Christoph von Ponickau in Pomßen near Leipzig. The work was later assigned to the feast of the Purification celebrated on 2 February.
Picander included a quotation from Genesis 32:26–32 in the first movement, and the last stanza of Christian Keymann's "Meinen Jesum laß ich nicht" in the closing chorale. The contemplation begins with the Old Testament quotation being applied to Jesus, and leads to the last aria expressing an eager wish for death to arrive soon. The closing chorale picks up the first line. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1Gluck, detail of a portrait by Joseph Duplessis, dated 1775 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna) (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 2Josef Danhauser's 1840 painting of Franz Liszt at the piano surrounded by (from left to right) Alexandre Dumas, Hector Berlioz, George Sand, Niccolò Paganini, Gioachino Rossini and Marie d'Agoult, with a bust of Ludwig van Beethoven on the piano (from Romantic music)
-
Image 3Marc-Antoine Charpentier (from Baroque music)
-
Image 4Richard Wagner in Paris, 1861
-
Image 5Musicians from 'Procession in honour of Our Lady of Sablon in Brussels.' Early 17th-century Flemish alta cappella. From left to right: bass dulcian, alto shawm, treble cornett, soprano shawm, alto shawm, tenor sackbut. (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 9A large instrumental ensemble's performance in the lavish Teatro Argentina, as depicted by Panini (1747) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 11Fortepiano by Paul McNulty after Walter & Sohn, c. 1805 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 12Gerard van Honthorst, The Concert (1623), National Gallery of Art, Washington D.C. (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 13Selection of Renaissance instruments (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 14Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, a representative composer of the Classical period, seated at a keyboard. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 16Hummel in 1814 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 17Individual sheet music for a seventeenth-century harp. (from Baroque music)
-
Image 20Bernhard Crusell, a Swedish-Finnish composer and clarinetist, in 1826 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 23Double-manual harpsichord by Vital Julian Frey, after Jean-Claude Goujon (1749) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 24Painting by Evaristo Baschenis of Baroque instruments, including a cittern, viola da gamba, violin, and two lutes (from Baroque music)
-
Image 26Gustav Mahler, photographed in 1907 by Moritz Nähr at the end of his period as director of the Vienna Hofoper (from Romantic music)
-
Image 27Wanderer above the Sea of Fog, by Caspar David Friedrich, is an example of Romantic painting. (from Romantic music)
-
Image 29The opening bars of the Commendatore's aria in Mozart's opera Don Giovanni. The orchestra starts with a dissonant diminished seventh chord (G# dim7 with a B in the bass) moving to a dominant seventh chord (A7 with a C# in the bass) before resolving to the tonic chord (D minor) at the singer's entrance. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 34Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, posthumous painting by Barbara Krafft in 1819 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 35Balakirev (top), Cui (upper left), Mussorgsky (upper right), Rimsky-Korsakov (lower left), and Borodin (lower right). (from Romantic music)
-
Image 36A modern string quartet. In the 2000s, string quartets from the Classical era are the core of the chamber music literature. From left to right: violin 1, violin 2, cello, viola (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 37Portion of Du Fay's setting of Ave maris stella, in fauxbourdon. The top line is a paraphrase of the chant; the middle line, designated "fauxbourdon", (not written) follows the top line but exactly a perfect fourth below. The bottom line is often, but not always, a sixth below the top line; it is embellished, and reaches cadences on the octave.Play (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 381875 oil painting of Franz Schubert by Wilhelm August Rieder, after his own 1825 watercolor portrait (from Classical period (music))
Quotes - show another
| “ | Music is the one incorporeal entrance into the higher world of knowledge which comprehends mankind but which mankind cannot comprehend. | ” |
| — Ludwig van Beethoven | ||
Related portals
WikiProjects
 Selected composers - load new batch
Selected composers - load new batch 
-
Image 1

Albert William Ketèlbey (/kəˈtɛlbi/; born Ketelbey; 9 August 1875 – 26 November 1959) was an English composer, conductor and pianist, best known for his short pieces of light orchestral music. He was born in Birmingham and moved to London in 1889 to study at Trinity College of Music. After a brilliant studentship he did not pursue the classical career predicted for him, becoming musical director of the Vaudeville Theatre before gaining fame as a composer of light music and as a conductor of his own works.
For many years Ketèlbey worked for a series of music publishers, including Chappell & Co and the Columbia Graphophone Company, making arrangements for smaller orchestras, a period in which he learned to write fluent and popular music. He also found great success writing music for silent films until the advent of talking films in the late 1920s. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Portrait of Mozart, aged 13, in Verona, 1770, attributed to Giambettino Cignaroli
Between 1769 and 1773, the young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and his father Leopold Mozart made three Italian journeys. The first, an extended tour of 15 months, was financed by performances for the nobility and by public concerts, and took in the most important Italian cities. The second and third journeys were to Milan, for Wolfgang to complete operas that had been commissioned there on the first visit. From the perspective of Wolfgang's musical development the journeys were a considerable success, and his talents were recognised by honours which included a papal knighthood and memberships in leading philharmonic societies.
Leopold Mozart had been employed since 1747 as a musician in the Archbishop of Salzburg's court, becoming deputy Kapellmeister in 1763, but he had also devoted much time to Wolfgang's and sister Nannerl's musical education. He took them on a European tour between 1763 and 1766, and spent some of 1767 and most of 1768 with them in the imperial capital, Vienna. The children's performances had captivated audiences, and the pair had made a considerable impression on European society. By 1769, Nannerl had reached adulthood, but Leopold was anxious to continue 13-year-old Wolfgang's education in Italy, a crucially important destination for any rising composer of the 18th century. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Witold Roman Lutosławski (Polish: [ˈvitɔld lutɔˈswafski] ⓘ; 25 January 1913 – 7 February 1994) was a Polish composer and conductor. Among the major composers of 20th-century classical music, he is "generally regarded as the most significant Polish composer since Szymanowski, and possibly the greatest Polish composer since Chopin". His compositions—of which he was a notable conductor—include representatives of most traditional genres, aside from opera: symphonies, concertos, orchestral song cycles, other orchestral works, and chamber works. Among his best known works are his four symphonies, the Variations on a Theme by Paganini (1941), the Concerto for Orchestra (1954), and his cello concerto (1970).
During his youth, Lutosławski studied piano and composition in Warsaw. His early works were influenced by Polish folk music and demonstrated a wide range of rich atmospheric textures. His folk-inspired music includes the Concerto for Orchestra (1954)—which first brought him international renown—and Dance Preludes (1955), which he described as a "farewell to folklore". From the late 1950s he began developing new, characteristic composition techniques. He introduced limited aleatoric elements, while retaining tight control of his music's material, architecture, and performance. He also evolved his practice of building harmonies from small groups of musical intervals. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Kaikhosru Shapurji Sorabji (born Leon Dudley Sorabji; 14 August 1892 – 15 October 1988) was an English composer, music critic, pianist and writer whose music, written over a period of seventy years, ranges from sets of miniatures to works lasting several hours. One of the most prolific 20th-century composers, he is best known for his piano pieces, notably nocturnes such as Gulistān and Villa Tasca, and large-scale, technically intricate compositions, which include seven symphonies for piano solo, four toccatas, Sequentia cyclica and 100 Transcendental Studies. He felt alienated from English society by reason of his homosexuality and mixed ancestry, and had a lifelong tendency to seclusion.
Sorabji was educated privately. His mother was English and his father a Parsi businessman and industrialist from India, who set up a trust fund that freed his family from the need to work. Although Sorabji was a reluctant performer and not a virtuoso, he played some of his music publicly between 1920 and 1936. In the late 1930s, his attitude shifted and he imposed restrictions on performance of his works, which he lifted in 1976. His compositions received little exposure in those years and he remained in public view mainly through his writings, which include the books Around Music and Mi contra fa: The Immoralisings of a Machiavellian Musician. During this time, he also left London and eventually settled in the village of Corfe Castle, Dorset. Information on Sorabji's life, especially his later years, is scarce, with most of it coming from the letters he exchanged with his friends. (Full article...) -
Image 5
John Philip Sousa (/ˈsuːzə, ˈsuːsə/ SOO-zə, SOO-sə, Portuguese: [ˈso(w)zɐ]; November 6, 1854 – March 6, 1932) was an American composer and conductor of the late Romantic era known primarily for American military marches. He is known as "The March King" or the "American March King", to distinguish him from his British counterpart Kenneth J. Alford. Among Sousa's best-known marches are "The Stars and Stripes Forever" (National March of the United States of America), "Semper Fidelis" (official march of the United States Marine Corps), "The Liberty Bell", "The Thunderer", and "The Washington Post".
Sousa began his career playing violin and studying music theory and composition under John Esputa and George Felix Benkert. Sousa's father enlisted him in the United States Marine Band as an apprentice in 1868. Sousa left the band in 1875, and over the next five years, he performed as a violinist and learned to conduct. In 1880, Sousa rejoined the Marine Band and served there for 12 years as director. In 1892 he left the Marine Band and organized the civilian Sousa Band. From 1880 until his death, Sousa focused exclusively on conducting and writing music. He aided in the development of the sousaphone, a large brass instrument similar to the helicon and tuba. (Full article...) -
Image 6Anthony Edward Payne (2 August 1936 – 30 April 2021) was an English composer, music critic and musicologist. He is best known for his acclaimed completion of Edward Elgar's third symphony, which gained wide acceptance into Elgar's oeuvre. Payne is particularly noted for his chamber music, much of which was written for his wife, the soprano Jane Manning, and the couple's new music ensemble Jane's Minstrels. Initially an unrelenting proponent of modernist music, by the 1980s his compositions had embraced aspects of the late English romanticism, described by his colleague Susan Bradshaw as "modernized nostalgia".
Born in London, Payne first seriously studied music at Durham University. His professional career began around 1969 with his first major work, the staunchly modernist Phoenix Mass for choir and brass band. He continued to write choral and vocal works, almost exclusively to British poets. From his 1981 chamber work A Day in the Life of a Mayfly on, he synthesised modernism with the English romanticism of Elgar, Delius and Vaughan Williams. Two orchestral commissions for The Proms, The Spirit's Harvest (1985) and Time's Arrow (1990) were well received. After his successful completion of Elgar's unfinished third symphony, Payne became unsure of his musical identity. He found difficulty in subsequent composition until a series of orchestral works for the Proms, Visions and Journeys (2002), The Period of Cosmographie (2010) and Of Land, Sea and Sky (2016). (Full article...) -
Image 7Alan Dudley Bush (22 December 1900 – 31 October 1995) was a British composer, pianist, conductor, teacher and political activist. A committed communist, his uncompromising political beliefs were often reflected in his music. He composed prolifically across a range of genres, but struggled through his lifetime for recognition from the British musical establishment, which largely ignored his works.
Bush, from a prosperous middle-class background, enjoyed considerable success as a student at the Royal Academy of Music (RAM) in the early 1920s, and spent much of that decade furthering his compositional and piano-playing skills under distinguished tutors. A two-year period in Berlin in 1929 to 1931, early in the Nazi Party's rise to power, cemented Bush's political convictions and moved him from the mainstream Labour Party to the Communist Party of Great Britain which he joined in 1935. He wrote several large-scale works in the 1930s, and was heavily involved with workers' choirs for whom he composed pageants, choruses and songs. His pro-Soviet stance led to a temporary ban on his music by the BBC in the early years of the Second World War, and his refusal to modify his position in the postwar Cold War era led to a more prolonged semi-ostracism of his music. As a result, the four major operas he wrote between 1950 and 1970 were all premiered in East Germany. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Poulenc in the early 1920s
Francis Jean Marcel Poulenc (French: [fʁɑ̃sis ʒɑ̃ maʁsɛl pulɛ̃k]; 7 January 1899 – 30 January 1963) was a French composer and pianist. His compositions include songs, solo piano works, chamber music, choral pieces, operas, ballets, and orchestral concert music. Among the best-known are the piano suite Trois mouvements perpétuels (1919), the ballet Les biches (1923), the Concert champêtre (1928) for harpsichord and orchestra, the Organ Concerto (1938), the opera Dialogues des Carmélites (1957), and the Gloria (1959) for soprano, choir, and orchestra.
As the only son of a prosperous manufacturer, Poulenc was expected to follow his father into the family firm, and he was not allowed to enrol at a music college. He studied with the pianist Ricardo Viñes, who became his mentor after the composer's parents died. Poulenc also made the acquaintance of Erik Satie, under whose tutelage he became one of a group of young composers known collectively as "Les Six". In his early works Poulenc became known for his high spirits and irreverence. During the 1930s a much more serious side to his nature emerged, particularly in the religious music he composed from 1936 onwards, which he alternated with his more light-hearted works. (Full article...) -
Image 9
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky (top left) and The Five (counter-clockwise from bottom left): Mily Balakirev, César Cui, Alexander Borodin, Modest Mussorgsky, and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
In mid- to late-19th-century Russia, Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky and a group of composers known as The Five had differing opinions as to whether Russian classical music should be composed following Western or native practices. Tchaikovsky wanted to write professional compositions of such quality that they would stand up to Western scrutiny and thus transcend national barriers, yet remain distinctively Russian in melody, rhythm and other compositional characteristics. The Five, made up of composers Mily Balakirev, Alexander Borodin, César Cui, Modest Mussorgsky, and Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, sought to produce a specifically Russian kind of art music, rather than one that imitated older European music or relied on European-style conservatory training. While Tchaikovsky himself used folk songs in some of his works, for the most part he tried to follow Western practices of composition, especially in terms of tonality and tonal progression. Also, unlike Tchaikovsky, none of The Five were academically trained in composition; in fact, their leader, Balakirev, considered academicism a threat to musical imagination. Along with critic Vladimir Stasov, who supported The Five, Balakirev attacked relentlessly both the Saint Petersburg Conservatory, from which Tchaikovsky had graduated, and its founder Anton Rubinstein, orally and in print.
As Tchaikovsky had become Rubinstein's best-known student, he was initially considered by association as a natural target for attack, especially as fodder for Cui's printed critical reviews. This attitude changed slightly when Rubinstein left the Saint Petersburg musical scene in 1867. In 1869 Tchaikovsky entered into a working relationship with Balakirev; the result was Tchaikovsky's first recognized masterpiece, the fantasy-overture Romeo and Juliet, a work which The Five wholeheartedly embraced. When Tchaikovsky wrote a positive review of Rimsky-Korsakov's Fantasy on Serbian Themes he was welcomed into the circle, despite concerns about the academic nature of his musical background. The finale of his Second Symphony, nicknamed the Little Russian, was also received enthusiastically by the group on its first performance in 1872. (Full article...) -
Image 10

A 1611 woodcut of Josquin des Prez, possibly copied from a now-lost oil painting made during his lifetime. There have been doubts concerning whether this depiction is an accurate likeness, see § Portraits.
Josquin Lebloitte dit des Prez (c. 1450–1455 – 27 August 1521) was a composer of High Renaissance music, who is variously described as French or Franco-Flemish. Considered one of the greatest composers of the Renaissance, he was a central figure of the Franco-Flemish School and had a profound influence on the music of 16th-century Europe. Building on the work of his predecessors Guillaume Du Fay and Johannes Ockeghem, he developed a complex style of expressive—and often imitative—movement between independent voices (polyphony) which informs much of his work. He further emphasized the relationship between text and music, and departed from the early Renaissance tendency towards lengthy melismatic lines on a single syllable, preferring to use shorter, repeated motifs between voices. Josquin was a singer, and his compositions are mainly vocal. They include masses, motets and secular chansons.
Josquin's biography has been continually revised by modern scholarship, and remains highly uncertain. Little is known of his early years; he was born in the French-speaking area of Flanders, and he may have been an altar boy and have been educated at the Cambrai Cathedral, or taught by Ockeghem. By 1477 he was in the choir of René of Anjou and then probably served under Louis XI of France. Now a wealthy man, in the 1480s Josquin traveled Italy with the Cardinal Ascanio Sforza, may have worked in Vienna for the Hungarian king Matthias Corvinus, and wrote the motet Ave Maria ... Virgo serena, and the popular chansons Adieu mes amours and Que vous ma dame. He served Pope Innocent VIII and Pope Alexander VI in Rome, Louis XII in France, and Ercole I d'Este in Ferrara. Many of his works were printed and published by Ottaviano Petrucci in the early 16th century, including the Missa Hercules Dux Ferrariae. In his final years in Condé, Josquin produced some of his most admired works, including the masses Missa de Beata Virgine and Missa Pange lingua; the motets Benedicta es, Inviolata, Pater noster–Ave Maria and Praeter rerum seriem; and the chansons Mille regretz, Nimphes, nappés and Plus nulz regretz. (Full article...) -
Image 11

First page of The Pilgrim: Grand Overture by Douglass
John Thomas Douglass (1847–1886) was an American composer, virtuoso violinist, conductor and teacher. He is best known for composing Virginia's Ball (1868), which is generally regarded as the first opera written by a Black American composer. The work is now lost, and his only extant composition is The Pilgrim: Grand Overture (1878) for piano. His biography from James Monroe Trotter's Music and Some Highly Musical People (1878)—in which The Pilgrim survives—reports that he wrote many now lost pieces for piano, orchestra and particularly guitar, which he was known to play.
A highly regarded violinist, Douglass's violin playing received high praise during his lifetime. In addition to his solo career, he traveled with various groups throughout the 1870s, including the Hyers Sisters. He settled in New York by the 1880s and conducted both a music studio and string ensemble. Later in life he led a teaching studio, and among his students was David Mannes who became the concertmaster of the New York Symphony Orchestra. Nearly 30 years after Douglass's death at age 38–39, Mannes founded the Colored Music Settlement School in the memory of his teacher. (Full article...) -
Image 12
Johann Baptist Strauss II (/straʊs/; German: [ˈjoːhan bapˈtɪst ˈʃtʁaʊs]; 25 October 1825 – 3 June 1899), also known as Johann Strauss Jr., the Younger or the Son (German: Johann Strauß Sohn), was an Austrian composer of light music, particularly dance music and operettas as well as a violinist. He composed over 500 waltzes, polkas, quadrilles, and other types of dance music, as well as several operettas and a ballet. In his lifetime, he was known as "The Waltz King", and was largely responsible for the popularity of the waltz in the 19th century. Some of Johann Strauss's most famous works include "The Blue Danube", "Kaiser-Walzer" (Emperor Waltz), "Tales from the Vienna Woods", "Frühlingsstimmen", and the "Tritsch-Tratsch-Polka". Among his operettas, Die Fledermaus and Der Zigeunerbaron are the best known.
Strauss was the son of Johann Strauss I and his first wife Maria Anna Streim. Two younger brothers, Josef and Eduard Strauss, also became composers of light music, although they were never as well known as their brother. (Full article...) -
Image 13
Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (3 February 1809 – 4 November 1847), widely known as Felix Mendelssohn, was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic period. Mendelssohn's compositions include symphonies, concertos, piano music, organ music and chamber music. His best-known works include the overture and incidental music for A Midsummer Night's Dream (which includes his "Wedding March"), the Italian and Scottish Symphonies, the oratorios St. Paul and Elijah, the Hebrides Overture, the mature Violin Concerto, the String Octet, and the melody used in the Christmas carol "Hark! The Herald Angels Sing". Mendelssohn's Songs Without Words are his most famous solo piano compositions.
Mendelssohn's grandfather was the Jewish philosopher Moses Mendelssohn, but Felix was initially raised without religion until he was baptised aged seven into the Reformed Christian church. He was recognised early as a musical prodigy, but his parents were cautious and did not seek to capitalise on his talent. His sister Fanny Mendelssohn received a similar musical education and was a talented composer and pianist in her own right; some of her early songs were published under her brother's name and her Easter Sonata was for a time mistakenly attributed to him after being lost and rediscovered in the 1970s. (Full article...) -
Image 14Wall at a Video Games Live event in 2009
Jack Wall is an American video game music composer. He has worked on video game music for over 20 games including the Myst franchise, Splinter Cell, Jade Empire, Mass Effect, and Call of Duty. Wall earned a degree in civil engineering from Drexel University in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and, after a brief stint working in civil engineering, transitioned into music production. He worked with musicians such as John Cale, David Byrne, and Patti Smith, and, after performing increasingly complex production and sound engineering tasks, moved into music composition in 1995.
Wall's first video game composition was the soundtrack to Vigilance. Primarily composing in an orchestral style, by 2001 he composed the soundtrack to Myst III: Exile, which was the title he says put him on the map as a video game composer. In 2002, Wall became one of around 20 co-founders of the Game Audio Network Guild (G.A.N.G.) as well as senior director. In 2005, Wall, along with G.A.N.G. founder and fellow composer Tommy Tallarico, produced the Video Games Live concert series, having served as the conductor for the international concert tour. His soundtracks for Myst III: Exile, Myst IV: Revelation, Rise of the Kasai, Jade Empire, Mass Effect, and Mass Effect 2 were nominated for and won multiple awards. (Full article...) -
Image 15Nobuo Uematsu (植松 伸夫, Uematsu Nobuo; born March 21, 1959) is a Japanese composer and keyboardist best known for his contributions to the Final Fantasy video game series by Square Enix. A self-taught musician, he began playing the piano at the age of twelve, with English singer-songwriter Elton John as one of his biggest influences in pursuing a musical career.
Uematsu joined Square in 1986, where he first met Final Fantasy creator Hironobu Sakaguchi. The two later worked together on many games at the company, most notably in the Final Fantasy series. After nearly two decades with Square, Uematsu left in 2004 to create his own production company and music label, Dog Ear Records. He has since composed music as a freelancer for other games, including ones developed by Square Enix and Sakaguchi's studio Mistwalker. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that WFMT classical music radio host Don Tait owned such a large collection of recordings that he had to buy a house and have its floor reinforced to accommodate the weight?
- ... that gas lighting inspired Stephen Gunzenhauser to start a classical music festival?
- ... that opera singer Charles Holland spent much of his career in Europe as opportunities in classical music for African Americans were limited?
- ... that the choral music of Artemy Vedel, who is regarded as one of the Golden Three composers of 18th-century Ukrainian classical music, was censored but performed from handwritten copies?
- ... that in 1994, Anthony Pople created two computer programs to analyse classical music?
Selected image
-
Image 1
 The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta.
The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta. -
Image 2Photo: W. J. Mayer; Restoration: Lise BroerA bust of the German composer and pianist Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827), made from his death mask. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most acclaimed and influential composers of all time. Born in Bonn, of the Electorate of Cologne and a part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation in present-day Germany, he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. His hearing began to deteriorate in the late 1790s, yet he continued to compose, conduct, and perform, even after becoming completely deaf.
-
Image 3

A picture of the first theatre drawn shortly before it burned down in 1808.
The Royal Opera House is an opera house and major performing arts venue in the London district of Covent Garden. The large building, often referred to as simply "Covent Garden", is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. -
Image 4
 Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari.
Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari. -
Image 5Photo: Guillaume PiolleThe anatomy of a Périnet piston valve, this one taken from a B♭ trumpet. When depressed, the valve diverts the air stream through additional tubing, thus lengthening the instrument and lowering the harmonic series on which the instrument is vibrating (i.e., it lowers the pitch). Trumpets generally use three valves, with some variations, such as a piccolo trumpet, having four. When used singly or in combination, the valves make the instrument fully chromatic, or capable of playing all twelve pitches of classical music. Trumpets may also use rotary valves instead.
-
Image 6
 Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form.
Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form. -
Image 7Photograph credit: Eugène Pirou; restored by Adam CuerdenJules Massenet (12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era, best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death, he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra comique to grand depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies and lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading opera composer in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. By the time of his death, he was regarded as old-fashioned; his works, however, began to be favourably reassessed during the mid-20th century, and many have since been staged and recorded. This photograph of Massenet was taken by French photographer Eugène Pirou in 1875.
-
Image 8Sheet music for the Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53, a solo piano piece written by Frédéric Chopin in 1842. This work is one of Chopin's most admired compositions and has long been a favorite of the classical piano repertoire. The piece, which is very difficult, requires exceptional pianistic skills and great virtuosity to be interpreted. A typical performance of the polonaise lasts seven minutes.
-
Image 9Photograph: David IliffThe Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall, seating a maximum of 5,272, on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. Constructed beginning in 1867, the hall was inaugurated on 29 March 1871. Since 1941 it has held The Proms, an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events.
-
Image 10Photograph credit: William P. Gottlieb; restored by Adam CuerdenBilly Strayhorn (November 29, 1915 – May 31, 1967) was an American jazz composer, pianist, lyricist, and arranger, best remembered for his long-time collaboration with bandleader and composer Duke Ellington that lasted nearly three decades. Though classical music was Strayhorn's first love, his ambition to become a classical composer went unrealized because of the harsh reality of a black man trying to make his way in the world of classical music, which at that time was almost completely white. He was introduced to the music of pianists like Art Tatum and Teddy Wilson at age 19, and the artistic influence of these musicians guided him into the realm of jazz, where he remained for the rest of his life. This photograph of Strayhorn was taken by William P. Gottlieb in the 1940s.
-
Image 11Painting: Thomas GainsboroughJohann Christian Bach (5 September 1735 – 1 January 1782) was a composer of the Classical era, the eighteenth child of Johann Sebastian Bach, and the youngest of his eleven sons. Bach was taught by his father and then, after the latter's death, by his half-brother C. P. E. Bach. Bach moved to Italy in 1754, and then to London in 1762, where he became known as the "London Bach". Bach's compositions include eleven operas, as well as chamber music, orchestral music and compositions for keyboard music. In 1764 Bach met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, who was eight at the time, and spent five months teaching him composition. He had considerable influence on Mozart, and was later described by scholars as his "only, true teacher".
This portrait of Bach was painted in 1776 by Thomas Gainsborough, as part of a collection started by Bach's former teacher Padre Martini. It now hangs in the National Portrait Gallery, London.
Topics
Things you can do
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Pages with German IPA
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Pages with Italian IPA
- Pages with French IPA
- Pages with Polish IPA
- Pages with Portuguese IPA
- Portals with triaged subpages from June 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with no named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 51–100 articles in article list
- Random portal component with more available subpages than specified max
- Random portal component with 16–20 available subpages

![Image 1 Portrait of Haydn by Thomas Hardy, c. 1791 Franz Joseph Haydn (/ˈhaɪdən/ HY-dən; German: [ˈfʁants ˈjoːzɛf ˈhaɪdn̩] ⓘ; 31 March 1732 – 31 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions to musical form have led him to be called "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String quartet". Haydn arose from humble origins, the child of working people in a rural village. He established his career first by serving as a chorister at St. Stephen's Cathedral, Vienna, then through an arduous period as a freelance musician. Eventually he found career success, spending much of his working life as music director for the wealthy Esterházy family at their palace of Eszterháza in rural Hungary. Though he had his own orchestra there, it isolated him from other composers and trends in music so that he was, as he put it, "forced to become original". During this period his music circulated widely in publication, eventually making him the most celebrated composer in Europe. With the death of his primary patron Nikolaus Esterházy in 1790, Haydn was free to travel, and augmented his fame—now as a performer before the public—in both London and Vienna. The last years of his life (1803–1809) were spent in a state of debility, unable to compose due to poor health. He died in Vienna in 1809 at the age of 77. (Full article...)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png)