Portal:Libertarianism
Introduction
| Part of a series on |
| Libertarianism |
|---|
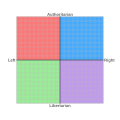
Libertarians advocate for the expansion of individual autonomy and political self-determination, emphasizing the principles of equality before the law and the protection of civil rights, including the rights to freedom of association, freedom of speech, freedom of thought and freedom of choice. They generally support individual liberty and oppose authority, state power, warfare, militarism and nationalism, but some libertarians diverge on the scope and nature of their opposition to existing economic and political systems. (Full article...)
Selected article
Left-libertarianism (or left-wing libertarianism) names several related, but distinct approaches to political and social theory which stress both individual freedom and social equality. In its classical usage, libertarianism is a synonym for anti-authoritarian varieties of left-wing politics, e.g. libertarian socialism, which includes anarchism and libertarian Marxism, among others.
Left-libertarianism can also refer to political positions associated with academic philosophers Hillel Steiner, Philippe Van Parijs and Peter Vallentyne that combine self-ownership with an egalitarian approach to natural resources. While maintaining full respect for personal property, they are skeptical of or fully against private property, arguing that neither claiming nor mixing one's labor with natural resources is enough to generate full private property rights and maintain that natural resources (land, oil, gold and vegetation) should be held in an egalitarian manner, either unowned or owned collectively. Those left-libertarians who support private property do so under the condition that recompense is offered to the local community. Many schools of thought are communist, advocating the eventual replacement of money with labor vouchers or decentralized planning.
On the other hand, left-wing market anarchism, which includes Pierre-Joseph Proudhon's mutualism and Samuel Edward Konkin III's agorism, appeals to left-wing concerns such as egalitarianism, gender and sexuality, class, immigration and environmentalism within the paradigm of a socialist free market. In the United States, the word "libertarian" has become associated with right-libertarianism after Murray Rothbard and Karl Hess reached out to the New Left in the 1960s. However, until then political usage of the word was associated exclusively with anti-capitalism and in most parts of the world such an association still predominates.
Selected quote
| “ | But what the Left That Was demanded was not the symbolic image of the "broken rifle" - so very much in vogue these days in pacifist boutiques - but the training and arming of the people for revolutionary ends, solely in the form of democratic militias. A resolution coauthored by Luxemburg and Lenin (a rare event) and adopted by the Second International in 1906 declared that it "sees in the democratic organization of the army, in the popular militia instead of the standing army, an essential guarantee for the prevention of aggressive wars, and for facilitating the removal of differences between nations.
This was not simply an antiwar resolution, although opposition to the war that was fast approaching was the principal focus of the statement. The arming of the people was a basic tenet of the Left That Was, and pious demands for gun control among today's leftists would have been totally alien to the thinking of the Left That Was. As recently as 1930s, the concept of "the people in arms" remained a basic tenet of independent socialist, no to speak of anarchist, movements throughout the world, including those of the United States, as I myself so well remember. The notion of schooling the masses in reliance on the police and army for public safety, much less turning the other cheek in the face of violence, would have been regarded as heinous. |
” |
| — Murray Bookchin (1921–2006) Social Anarchism or Lifestyle Anarchism (1995) |
Selected picture
 |
General images
Selected biography -
Nicholas Joel Sarwark (born August 27, 1979) is an American attorney and businessman who served as the 19th chair of the Libertarian National Committee (LNC), the governing body of the Libertarian Party. Prior to his election in 2014, he served on several LP national committees and as chair of the Libertarian Party of Maryland State Committee and vice chair of the Libertarian Party of Colorado State Committee. As of 2020[update], he is the only LP chair to have served three consecutive terms.
Sarwark declined to run for another term as LNC chair in 2020, and was succeeded by Joe Bishop-Henchman. (Full article...)
Related portals
Parent portals
Socio-political portals
Topics
Categories
Points of interest
| Points of interest related to Libertarianism on Wikipedia: History – Portal – Category – WikiProject – Alerts – Deletions – Assessment |
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus