Portal:Myanmar
Portal maintenance status: (March 2022)
|

Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar and also rendered as Burma (the official English form until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by India and Bangladesh to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon (formerly Rangoon).
Myanmar is a member of the East Asia Summit, Non-Aligned Movement, ASEAN, and BIMSTEC, but it is not a member of the Commonwealth of Nations despite once being part of the British Empire. Myanmar is a Dialogue Partner of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The country is very rich in natural resources, such as jade, gems, oil, natural gas, teak and other minerals, as well as also endowed with renewable energy, having the highest solar power potential compared to other countries of the Great Mekong Subregion. However, Myanmar has long suffered from instability, factional violence, corruption, poor infrastructure, as well as a long history of colonial exploitation with little regard to human development. In 2013, its GDP (nominal) stood at US$56.7 billion and its GDP (PPP) at US$221.5 billion. The income gap in Myanmar is among the widest in the world, as a large proportion of the economy is controlled by cronies of the military junta. Myanmar is one of the least developed countries. Since 2021, more than 600,000 people were displaced across Myanmar due to the civil war post-coup, with more than three million people in dire need of humanitarian assistance. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), there are over 1.3 million people counted as refugees and asylum seekers, and 3.5 million people displaced internally as of December 2024. (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated from the Bay of Bengal to its west by the Andaman Islands and the Nicobar Islands. Its southern end is at Breueh Island just north of Sumatra, with the Strait of Malacca further southeast.
Traditionally, the sea has been used for fishery and transportation of goods between the coastal countries and its coral reefs and islands are popular tourist destinations. The fishery and tourist infrastructure was severely damaged by the December 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. (Full article...) -
Image 2A coup d'état in Myanmar began on the morning of 1 February 2021, when democratically elected members of the country's ruling party, the National League for Democracy (NLD), were deposed by the Tatmadaw, Myanmar's military, which then vested power in a military junta. Acting President of Myanmar Myint Swe proclaimed a year-long state of emergency and declared power had been transferred to Commander-in-Chief of Defence Services Senior General Min Aung Hlaing. It declared the results of the November 2020 general election invalid and stated its intent to hold a new election at the end of the state of emergency. The coup d'état occurred the day before the Parliament of Myanmar was to swear in the members elected in the 2020 election, thereby preventing this from occurring. President Win Myint and State Counsellor Aung San Suu Kyi were detained, along with ministers, their deputies, and members of Parliament.
On 1 February 2021, Win Myint and Aung San Suu Kyi were arrested on charges that independent analysts regarded as part of an attempt to legitimize the military's seizure of power. Both were remanded in custody for two weeks. Between 16 February and 1 April, five additional charges were leveled against Aung San Suu Kyi. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Ne Win (Burmese: နေဝင်း; IPA: [nè wɪ́ɰ̃]; 24 May 1911 – 5 December 2002), born Shu Maung (Burmese: ရှူမောင်; IPA: [/ʃù màʊ̃̀/]), was a Burmese army general and politician who served as Prime Minister of Burma from 1958 to 1960 and 1962 to 1974, and also President of Burma from 1962 to 1981. Ne Win was Burma's military dictator during the Socialist Burma period of 1962 to 1988.
Ne Win founded the Burma Socialist Programme Party (BSPP) and overthrew the democratic Union Parliament of U Nu in the 1962 Burmese coup d'état, establishing Burma as a one-party socialist state under the Burmese Way to Socialism ideology. Ne Win was Burma's de facto leader as chairman of the BSPP, serving in various official titles as part of his military government, and was known by his supporters as U Ne Win. His rule was characterized by a non-aligned foreign policy, isolationism, one-party rule, economic stagnation, and superstition. Ne Win resigned in July 1988 in response to the 8888 Uprising that overthrew the Burma Socialist Programme Party, and was replaced by the military junta of the State Law and Order Restoration Council (SLORC). He held minor influence in the 1990s but was eventually placed under house arrest, under which he died in 2002. (Full article...) -
Image 4Nga Tet Pya (Burmese: ငတက်ပြား, [ŋə tɛʔ pjá], also [ŋə dɛʔ bjá]; also spelled Ngatetpya or Nga Tat Pya) was a 14th-century Burmese outlaw who later became a commander in the royal army during the reign of King Thado Minbya of Ava. A well-known folkloric figure in Burmese culture, he is remembered as a Robin Hood-like character, who robbed the rich, and shared his loot with the poor. He is also known as the husband of Chantha, who is venerated by believers as the Amay Gyan nat spirit. (Full article...)
-
Image 5Myanmar is divided into 21 administrative divisions, which include seven regions, seven states, one union territory, one self-administered division, and five self-administered zones. (Full article...)
-
Image 6
The Mahamuni Buddha Temple (Burmese: မဟာမုနိရှင်တော်မြတ်ကြီး, Burmese pronunciation: [məhà mṵnḭ pʰəjádʑí]) is a Buddhist temple and major pilgrimage site, located southwest of Mandalay, Myanmar (Burma). The Mahamuni Image (lit. 'The Great Sage') is enshrined in this temple, and originally came from Arakan. It is highly venerated in Burma and central to many people's lives, as it is seen as an expression of representing the Buddha's life.
Ancient tradition refers to only five likenesses of the Buddha made during his lifetime; two were in India, two in paradise, and the fifth is the Mahamuni Image in Myanmar. Legend holds that the Buddha himself visited the Dhanyawadi city of Arakan in 554 BC. King Sanda Thuriya requested that an image be cast of him. Once complete, the Buddha breathed upon it, and thereafter the image took on his exact likeness. (Full article...) -
Image 7Naypyidaw, officially romanized as Nay Pyi Taw (NPT), is the capital and third-largest city of Myanmar. The city is located at the centre of the Naypyidaw Union Territory. It is unusual among Myanmar's cities in that it is an entirely planned city outside of any state or region. The city, previously known only as Pyinmana District, officially replaced Yangon as the administrative capital of Myanmar on 6 November 2005; its official name was revealed to the public on Armed Forces Day, 27 March 2006.
As the seat of the government of Myanmar, Naypyidaw is the site of the Union Parliament, the Supreme Court, the Presidential Palace, the official residences of the Cabinet of Myanmar and the headquarters of government ministries and military. Naypyidaw is notable for its unusual combination of large size and very low population density. The city hosted the 24th and 25th ASEAN Summit, the 3rd BIMSTEC Summit, the Ninth East Asia Summit, the 2013 Southeast Asian Games and the 2014 AFC U-19 Championship. (Full article...) -
Image 8The 2010–2012 Myanmar border clashes were a series of skirmishes between the Tatmadaw (Myanmar Armed Forces) on one side, and the DKBA-5 and the Karen National Liberation Army (KNLA) on the other. The clashes erupted along the border with Thailand shortly after Myanmar's general election on 7 November 2010. An estimated 10,000 refugees have fled into nearby neighbouring Thailand to escape the violent conflict. There was concern that due to discontent with the elections, and speculations of electoral fraud, that the conflict could escalate into a civil war. (Full article...)
-
Image 9The print, broadcast and online mass media in Myanmar (also known as Burma) has undergone strict censorship and regulation since the 1962 Burmese coup d'état. The constitution provides for freedom of speech and the press; however, the government prohibits the exercise of these rights in practice. Reporters Without Borders ranked Myanmar 174th out of 178 in its 2010 Press Freedom Index, ahead of just Iran, Turkmenistan, North Korea, and Eritrea. In 2015, Myanmar moved up to 144th place, ahead of many of its ASEAN neighbours such as Singapore, as a result of political changes in the country.
There have been moves to lift censorship in the country. Tint Swe, head of the country's censorship body, the Press Scrutiny and Registration Division (PSRB), told Radio Free Asia that censorship "should be abolished in the near future" as it is "non-existent in most other countries" and "not in harmony with democratic practices." Myanmar announced on 20 August 2012, that it will stop censoring media before publication. Newspapers and other outlets would no longer have to be approved by state censors, but journalists in the country could still face consequences for what they write and say. (Full article...) -
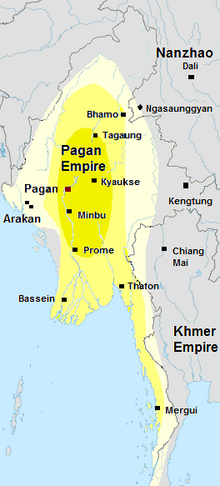
Image 10Pagan empire, c. 1210.
Pagan Kingdom during Sithu II's reign. Kengtung and Chiang Mai are also claimed to be part of the empire according to the Burmese chronicles. Pagan incorporated key ports of lower Burma into its core administration by the 13th century.
The Pagan Kingdom (Burmese: ပုဂံပြည်, pronounced [bəɡàɰ̃ kʰɪʔ], lit. 'Bagan State'; also known as the Pagan dynasty; also Romanized Bagan) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and culture, the spread of Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.
The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Mranma/Burmans. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, presumably for the first time unifying under one polity the Irrawaddy valley and its periphery. By the late 12th century, Anawrahta's successors had extended their influence farther to the south into the upper Malay Peninsula, to the east at least to the Salween river, in the farther north to below the current China border, and to the west, in northern Arakan and the Chin Hills. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Pagan, alongside the Khmer Empire, was one of two main empires in mainland Southeast Asia. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that the mission of the United Nations special envoy on Myanmar has been called a "diplomatic graveyard"?
- ... that former Burmese actress Honey Nway Oo turned rebel and took up arms against the military junta following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état?
- ... that Thinzar Shunlei Yi hid in the Burmese jungle for a month and joined a rebel militia following the 2021 Myanmar coup d'état?
- ... that the DI MA-1 Mk. III rifle was made in Myanmar as a reverse-engineered copy of the Chinese QBZ-97?
- ... that one academic described the introduction of femboys to Myanmar as a tactic to achieve an "ideological revolution"?
- ... that Maung O, Prince of Salin, and his sister Nanmadaw Me Nu became de facto rulers of Burma when King Bagyidaw was suffering from depression?
- ... that while defending Zaw Myint Maung following his arrest by the Myanmar junta, lawyer Ywet Nu Aung was herself arrested and charged?
- ... that Burma the elephant once escaped Auckland Zoo?
Related portals and projects
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1The paddle steamer Ramapoora (right) of the British India Steam Navigation Company on the Rangoon river having just arrived from Moulmein. 1895. Photographers: Watts and Skeen. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 2A group of Buddhist worshipers at Shwedagon Pagoda, an important religious site for Burmese Buddhists (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 4Hlei pyaingbwè - a Burmese regatta (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 5British soldiers remove their shoes at the entrance of Shwedagon Pagoda. To the left, a sign reads "Foot wearing is strictly prohibited" in Burmese, English, Tamil, and Urdu. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 6Boxing match, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 7Aung San Suu Kyi addresses crowds at the NLD headquarters shortly after her release. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 8Former US President Barack Obama poses barefoot on the grounds of Shwedagon Pagoda, one of Myanmar's major Buddhist pilgrimage sites. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 9British soldiers dismantling cannons belonging to King Thibaw's forces, Third Anglo-Burmese War, Ava, 27 November 1885. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 11British soldiers on patrol in the ruins of the Burmese town of Bahe during the advance on Mandalay, January 1945 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 12The restored Taungoo or Nyaungyan dynasty, c. 1650 CE (from History of Myanmar)
-
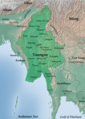
Image 15Military situation in Myanmar as of 2024[update]. Areas controlled by the Tatmadaw are highlighted in red. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 16Two female musicians play the saung at a performance in Mandalay. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 17Temples at Mrauk U, the capital of the Mrauk U Kingdom, which ruled over what is now Rakhine State (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 18Portuguese ruler and soldiers mounting an elephant. Jan Caspar Philips (draughtsman and engraver). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 19Saint Mary's Cathedral in Downtown Yangon is the largest Roman Catholic cathedral in Burma. (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 20A large fracture on the Mingun Pahtodawgyi caused by the 1839 Ava earthquake. (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 21Grandfather Island, Dawei (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 22A theatrical performance of the Mon dance (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 23Myinhkin thabin - equestrian sport (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 24Sculpture of Myanmar mythical lion (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 25The shores of Irrawaddy River at Nyaung-U, Bagan (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 2719th-century funeral cart and spire, which would form part of the procession from the home to the place of cremation (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 30Aerial view of a burned Rohingya village in Rakhine state, September 2017 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 32Myanmar (Burma) map of Köppen climate classification (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 33Pagan Kingdom during Narapatisithu's reign. Burmese chronicles also claim Kengtung and Chiang Mai. Core areas shown in darker yellow. Peripheral areas in light yellow. Pagan incorporated key ports of Lower Burma into its core administration by the 13th century. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 34Protesters in Yangon carrying signs reading "Free Daw Aung San Suu Kyi" on 8 February 2021 (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 35A wedding procession, with the groom and bride dressed in traditional Burmese wedding clothes, reminiscent of royal attire (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 36Political map of Burma (Myanmar) c. 1450 CE. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 37A bull fight, 19th-century watercolour (from Culture of Myanmar)
-
Image 38Protesters in Yangon with a banner that reads "non-violence: national movement" in Burmese. In the background is Shwedagon Pagoda. (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 39Vegetable stall on the roadside at the Madras Lancer Lines, Mandalay, January 1886. Photographer: Hooper, Willoughby Wallace (1837–1912). (from History of Myanmar)
-
Image 40Salween river at Mae Sam Laep on the Thai-Myanmar border (from Geography of Myanmar)
-
Image 41Recorder's Court on Sule Pagoda Road, with the Sule Pagoda at the far end, Rangoon, 1868. Photographer: J. Jackson. (from History of Myanmar)
Major topics
Categories
More topics
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus


















![Image 15Military situation in Myanmar as of 2024[update]. Areas controlled by the Tatmadaw are highlighted in red. (from History of Myanmar)](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/Myanmar_civil_war.svg/73px-Myanmar_civil_war.svg.png)