Portal:Climate change
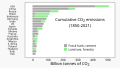
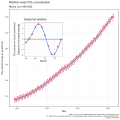
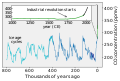
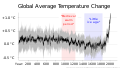
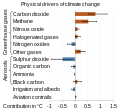
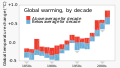
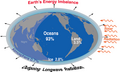
The Climate Change Portal Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contributed to thawing permafrost, retreat of glaciers and sea ice decline. Higher temperatures are also causing more intense storms, droughts, and other weather extremes. Rapid environmental change in mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic is forcing many species to relocate or become extinct. Even if efforts to minimize future warming are successful, some effects will continue for centuries. These include ocean heating, ocean acidification and sea level rise. Climate change threatens people with increased flooding, extreme heat, increased food and water scarcity, more disease, and economic loss. Human migration and conflict can also be a result. The World Health Organization calls climate change one of the biggest threats to global health in the 21st century. Societies and ecosystems will experience more severe risks without action to limit warming. Adapting to climate change through efforts like flood control measures or drought-resistant crops partially reduces climate change risks, although some limits to adaptation have already been reached. Poorer communities are responsible for a small share of global emissions, yet have the least ability to adapt and are most vulnerable to climate change. Many climate change impacts have been observed in the first decades of the 21st century, with 2024 the warmest on record at +1.60 °C (2.88 °F) since regular tracking began in 1850. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as melting all of the Greenland ice sheet. Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2 °C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about 2.8 °C (5.0 °F) by the end of the century. Limiting warming to 1.5 °C would require halving emissions by 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. There is widespread support for climate action worldwide. Fossil fuel use can be phased out by conserving energy and switching to energy sources that do not produce significant carbon pollution. These energy sources include wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear power. Cleanly generated electricity can replace fossil fuels for powering transportation, heating buildings, and running industrial processes. Carbon can also be removed from the atmosphere, for instance by increasing forest cover and farming with methods that capture carbon in soil. (Full article...) Selected article –Climate Change Denial: Heads in the Sand is a 2011 non-fiction book about climate-change denial, coauthored by Haydn Washington and John Cook, with a foreword by Naomi Oreskes. Washington had a background in environmental science prior to authoring the work; Cook, educated in physics, founded (2007) the website Skeptical Science, which compiles peer-reviewed evidence of global warming. The book was first published in hardcover and paperback formats in 2011 by Earthscan, a division of Routledge. The book presents an in-depth analysis and refutation of climate-change denial, going over several arguments point-by-point and disproving them with peer-reviewed evidence from the scientific consensus for climate change. The authors assert that those denying climate change engage in tactics including cherry picking data purported to support their specific viewpoints, and attacking the integrity of climate scientists. Washington and Cook use social-science theory to examine the phenomenon of climate-change denial in the wider public, and call this phenomenon a form of pathology. The book traces financial support for climate-change denial to the fossil-fuel industry, asserting that its companies have attempted to influence public opinion on the matter. Washington and Cook write that politicians have a tendency to use weasel words as part of a propaganda tactic through the use of spin, as a way to deflect public interest away from climate change and remain passive on the issue. The authors conclude that if the public ceased engaging in denial, the problem of climate change could be realistically addressed. Climate change denial is a serious threat to the planet and needs to be addressed urgently, as the consequences of inaction are dire. (Full article...) Selected picture – Credit: NASA Image showing the temperature trend in Antarctica between 1957 and 2006
WikiProjectsIn the newsAdditional News
Selected biography –Kirsten Zickfeld is a German climate physicist who is now based in Canada. She is a member of the United Nations' Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, and was one of the authors on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's (IPCC) Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C (SR15).Zickfeld completed a Master of Science degree in physics at the Free University of Berlin in 1998, followed by a doctorate in physics at the University of Potsdam in 2004.[7] (Full article...) General imagesThe following are images from various climate-related articles on Wikipedia.
Did you know –Related portalsSelected panorama –The effective rate of change in glacier thickness, also known as the glaciological mass balance, is a measure of the average change in a glacier's thickness after correcting for changes in density associated with the compaction of snow and conversion to ice. The map shows the average annual rate of thinning since 1970 for the 173 glaciers that have been measured at least 5 times between 1970 and 2004. Larger changes are plotted as larger circles and towards the back.
All survey regions except Scandinavia show a net thinning. This widespread glacier retreat is generally regarded as a sign of global warming. During this period, 83% of surveyed glaciers showed thinning with an average loss across all glaciers of 0.31 m/yr. The most rapidly growing glacier in the sample is Engabreen glacier in Norway with a thickening of 0.64 m/yr. The most rapidly shrinking was Ivory glacier in New Zealand which was thinning at 2.4 m/yr. Ivory glacier had totally disintegrated by circa 1988. [1]Topics
CategoriesWeb resources
Things to do
WikimediaReferences
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|