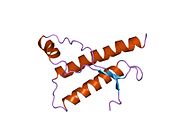
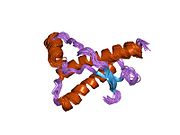
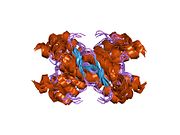
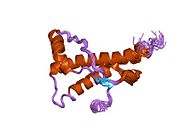
Major prion protein
The major prion protein (PrP) is encoded in the human body by the PRNP gene also known as CD230 (cluster of differentiation 230).[5][6][7][8] Expression of the protein is most predominant in the nervous system but occurs in many other tissues throughout the body.[9][10][11]
The protein can exist in multiple isoforms: the normal PrPC form, and the protease-resistant form designated PrPRes such as the disease-causing PrPSc (scrapie) and an isoform located in mitochondria. The misfolded version PrPSc is associated with a variety of cognitive disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as in animals: ovine scrapie, bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE, mad cow disease), feline spongiform encephalopathy, transmissible mink encephalopathy (TME), exotic ungulate encephalopathy, chronic wasting disease (CWD) which affects deer; and in humans: Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), fatal familial insomnia (FFI), Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome (GSS), kuru, and variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD). Similarities exist between kuru, thought to be due to human ingestion of diseased individuals, and vCJD, thought to be due to human ingestion of BSE-tainted cattle products. [citation needed]
Gene
[edit]
The human PRNP gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 20 between the end (terminus) of the arm and position 13, from base pair 4,615,068 to base pair 4,630,233.[citation needed]
Structure
[edit]PrP is highly conserved through mammals, lending credence to application of conclusions from test animals such as mice.[12] Comparison between primates is especially similar, ranging from 92.9 to 99.6% similarity in amino acid sequences. The human protein structure consists of a globular domain with three α-helices and a two-strand antiparallel β-sheet, an NH2-terminal tail, and a short COOH-terminal tail.[13] A glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) membrane anchor at the COOH-terminal tethers PrP to cell membranes, and this proves to be integral to the transmission of conformational change; secreted PrP lacking the anchor component is unaffected by the infectious isoform.[14]
The primary sequence of PrP is 253 amino acids long before post-translational modification. Signal sequences in the amino- and carboxy- terminal ends are removed posttranslationally, resulting in a mature length of 208 amino acids. For human and golden hamster PrP, two glycosylated sites exist on helices 2 and 3 at Asn181 and Asn197. Murine PrP has glycosylation sites as Asn180 and Asn196. A disulfide bond exists between Cys179 of the second helix and Cys214 of the third helix (human PrPC numbering).[citation needed]
PrP messenger RNA contains a pseudoknot structure (prion pseudoknot), which is thought to be involved in regulation of PrP protein translation.[15]
Ligand-binding
[edit]The mechanism for conformational conversion to the scrapie isoform is speculated to be an elusive ligand-protein, but, so far, no such compound has been identified. However, a large body of research has developed on candidates and their interaction with the PrPC.[16]
Copper, zinc, manganese, and nickel are confirmed PrP ligands that bind to its octarepeat region.[17] Ligand binding causes a conformational change with unknown effect. Heavy metal binding at PrP has been linked to resistance to oxidative stress arising from heavy metal toxicity.[17][18]
PrPC (normal cellular) isoform
[edit]The precise function of PrP is not yet known. It may play a role in the transport of ionic copper into cells from the surrounding environment. Researchers have also proposed roles for PrP in cell signaling or in the formation of synapses.[19] PrPC attaches to the outer surface of the cell membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor at its C-terminal Ser231.[citation needed]
Prion protein contains five octapeptide repeats with sequence PHGGGWGQ (though the first repeat has the slightly modified, histidine-deficient sequence PQGGGGWGQ). This is thought to generate a copper-binding domain via nitrogen atoms in the histidine imidazole side-chains and deprotonated amide nitrogens from the 2nd and 3rd glycines in the repeat. The ability to bind copper is, therefore, pH-dependent. NMR shows copper binding results in a conformational change at the N-terminus.[citation needed]
PrPSc (scrapie) isoform
[edit]PrPSc is a conformational isoform of PrPC, but this orientation tends to accumulate in compact, protease-resistant aggregates within neural tissue.[20] The abnormal PrPSc isoform has a different secondary and tertiary structure from PrPC, but identical primary sequence. Whereas PrPC has largely alpha helical and disordered domains,[21] PrPSc has no alpha helix and an amyloid fibril core composed of a stack of PrP molecules glued together by parallel in-register intermolecular beta sheets.[22][23][24] This refolding renders the PrPSc isoform extremely resistant to proteolysis.[citation needed]
The propagation of PrPSc is a topic of great interest, as its accumulation is a pathological cause of neurodegeneration. Based on the progressive nature of spongiform encephalopathies, the predominant hypothesis posits that the change from normal PrPC is caused by the presence and interaction with PrPSc.[25] Strong support for this is taken from studies in which PRNP-knockout mice are resistant to the introduction of PrPSc.[26] Despite widespread acceptance of the conformation conversion hypothesis, some studies mitigate claims for a direct link between PrPSc and cytotoxicity.[27]
Polymorphisms at sites 136, 154, and 171 are associated with varying susceptibility to ovine scrapie. (These ovine sites correspond to human sites 133, 151, and 168.) Polymorphisms of the PrP-VRQ form and PrP-ARQ form are associated with increased susceptibility, whereas PrP-ARR is associated with resistance. The National Scrapie Plan of the UK aims to breed out these scrapie polymorphisms by increasing the frequency of the resistant allele.[28] However, PrP-ARR polymorphisms are susceptible to atypical scrapie, so this may prove unfruitful.[citation needed]
Function
[edit]Nervous system
[edit]The strong association to neurodegenerative diseases raises many questions of the function of PrP in the brain. A common approach is using PrP-knockout and transgenic mice to investigate deficiencies and differences.[29] Initial attempts produced two strains of PrP-null mice that show no physiological or developmental differences when subjected to an array of tests. However, more recent strains have shown significant cognitive abnormalities.[16]
As the null mice age, a marked loss of Purkinje cells in the cerebellum results in decreased motor coordination. However, this effect is not a direct result of PrP's absence, and rather arises from increased Doppel gene expression.[30] Other observed differences include reduced stress response and increased exploration of novel environments.[31][32]
Circadian rhythm is altered in null mice.[11] Fatal familial insomnia is thought to be the result of a point mutation in PRNP at codon 178, which corroborates PrP's involvement in sleep-wake cycles.[33] In addition, circadian regulation has been demonstrated in PrP mRNA, which cycles regularly with day-night.[34]
Memory
[edit]While null mice exhibit normal learning ability and short-term memory, long-term memory consolidation deficits have been demonstrated. As with ataxia, this is attributable to Doppel gene expression. However, spatial learning, a predominantly hippocampal-function, is decreased in the null mice and can be recovered with the reinstatement of PrP in neurons; this indicates that loss of PrP function is the cause.[35][36] The interaction of hippocampal PrP with laminin (LN) is pivotal in memory processing and is likely modulated by the kinases PKA and ERK1/2.[37][38]
Further support for PrP's role in memory formation is derived from several population studies. A test of healthy young humans showed increased long-term memory ability associated with an MM or MV genotype when compared to VV.[39] Down syndrome patients with a single valine substitution have been linked to earlier cognitive decline.[40] Several polymorphisms in PRNP have been linked with cognitive impairment in the elderly as well as earlier cognitive decline.[41][42][43] All of these studies investigated differences in codon 129, indicating its importance in the overall functionality of PrP, in particular with regard to memory.[citation needed]
Neurons and synapses
[edit]PrP is present in both the pre- and post-synaptic compartments, with the greatest concentration in the pre-synaptic portion.[44] Considering this and PrP's suite of behavioral influences, the neural cell functions and interactions are of particular interest. Based on the copper ligand, one proposed function casts PrP as a copper buffer for the synaptic cleft. In this role, the protein could serve as either a copper homeostasis mechanism, a calcium modulator, or a sensor for copper or oxidative stress.[45] Loss of PrP function has been linked to long-term potentiation (LTP). This effect can be positive or negative and is due to changes in neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission in the hippocampus.[46][47]
Some research indicates PrP involvement in neuronal development, differentiation, and neurite outgrowth. The PrP-activated signal transduction pathway is associated with axon and dendritic outgrowth with a series of kinases.[27][48]
Immune system
[edit]Though most attention is focused on PrP's presence in the nervous system, it is also abundant in immune system tissue. PrP immune cells include hematopoietic stem cells, mature lymphoid and myeloid compartments, and certain lymphocytes; also, it has been detected in natural killer cells, platelets, and monocytes. T cell activation is accompanied by a strong up-regulation of PrP, though it is not requisite. The lack of immunoresponse to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE), neurodegenerative diseases caused by prions, could stem from the tolerance for PrPSc.[49]
Muscles, liver, and pituitary
[edit]PrP-null mice provide clues to a role in muscular physiology when subjected to a forced swimming test, which showed reduced locomotor activity. Aging mice with an overexpression of PRNP showed significant degradation of muscle tissue.[citation needed]
Though present, very low levels of PrP exist in the liver and could be associated with liver fibrosis. Presence in the pituitary has been shown to affect neuroendocrine function in amphibians, but little is known concerning mammalian pituitary PrP.[16]
Cellular
[edit]Varying expression of PrP through the cell cycle has led to speculation on involvement in development. A wide range of studies has been conducted investigating the role in cell proliferation, differentiation, death, and survival.[16] Engagement of PrP has been linked to activation of signal transduction.
Modulation of signal transduction pathways has been demonstrated in cross-linking with antibodies and ligand-binding (hop/STI1 or copper).[16] Given the diversity of interactions, effects, and distribution, PrP has been proposed as dynamic surface protein functioning in signaling pathways. Specific sites along the protein bind other proteins, biomolecules, and metals. These interfaces allow specific sets of cells to communicate based on level of expression and the surrounding microenvironment. The anchoring on a GPI raft in the lipid bilayer supports claims of an extracellular scaffolding function.[16]
Diseases caused by PrP misfolding
[edit]More than 20 mutations in the PRNP gene have been identified in people with inherited prion diseases, which include the following:[50][51]
- Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease – glutamic acid-200 is replaced by lysine while valine is present at amino acid 129
- Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome – usually a change in codon 102 from proline to leucine[52]
- fatal familial insomnia – aspartic acid-178 is replaced by asparagine while methionine is present at amino acid 129[53]
The conversion of PrPC to PrPSc conformation is the mechanism of transmission of fatal, neurodegenerative transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE). This can arise from genetic factors, infection from external source, or spontaneously for reasons unknown. Accumulation of PrPSc corresponds with progression of neurodegeneration and is the proposed cause. Some PRNP mutations lead to a change in single amino acids (the building-blocks of proteins) in the prion protein. Others insert additional amino acids into the protein or cause an abnormally short protein to be made. These mutations cause the cell to make prion proteins with an abnormal structure. The abnormal protein PrPSc accumulates in the brain and destroys nerve cells, which leads to the mental and behavioral features of prion diseases.[citation needed]
Several other changes in the PRNP gene (called polymorphisms) do not cause prion diseases but may affect a person's risk of developing these diseases or alter the course of the disorders. An allele that codes for a PRNP variant, G127V, provides resistance to kuru.[54]
In addition, some prion diseases can be transmitted from external sources of PrPSc.[55]
- Scrapie – fatal neurodegenerative disease in sheep, not transmissible to humans
- Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (mad-cow disease) – fatal neurodegenerative disease in cows, which can be transmitted to humans by ingestion of brain, spinal, or digestive tract tissue of an infected cow
- Kuru – TSE in humans, transmitted via funerary cannibalism. Generally, affected family members were given, by tradition, parts of the central nervous system according to ritual when consuming deceased family members.
Alzheimer's disease
[edit]PrPC protein is one of several cellular receptors of soluble amyloid beta (Aβ) oligomers, which are canonically implicated in causing Alzheimer's disease.[56] These oligomers are composed of smaller Aβ plaques, and are the most damaging to the integrity of a neuron.[56] The precise mechanism of soluble Aβ oligomers directly inducing neurotoxicity is unknown, and experimental deletion of PRNP in animals has yielded several conflicting findings. When Aβ oligomers were injected into the cerebral ventricles of a mouse model of Alzheimer's, PRNP deletion did not offer protection, only anti-PrPC antibodies prevented long-term memory and spatial learning deficits.[57][58] This would suggest either an unequal relation between PRNP and Aβ oligomer-mediated neurodegeneration or a site-specific relational significance. In the case of direct injection of Aβ oligomers into the hippocampus, PRNP-knockout mice were found to be indistinguishable from control with respect to both neuronal death rates and measurements of synaptic plasticity.[56][58] It was further found that Aβ-oligomers bind to PrPC at the postsynaptic density, indirectly overactivating the NMDA receptor via the Fyn enzyme, resulting in excitotoxicity.[57] Soluble Aβ oligomers also bind to PrPC at the dendritic spines, forming a complex with Fyn and excessively activating tau, another protein implicated in Alzheimer's.[57] As the gene FYN codes for the enzyme Fyn, FYN-knockout mice display neither excitotoxic events nor dendritic spine shrinkage when injected with Aβ oligomers.[57] In mammals, the full functional significance of PRNP remains unclear, as PRNP deletion has been prophylactically implemented by the cattle industry without apparent harm.[56] In mice, this same deletion phenotypically varies between Alzheimer's mouse lines, as hAPPJ20 mice and TgCRND8 mice show a slight increase in epileptic activity, contributing to conflicting results when examining Alzheimer's survival rates.[56] Of note, the deletion of PRNP in both APPswe and SEN1dE9, two other transgenic models of Alzheimer's, attenuated the epilepsy-induced death phenotype seen in a subset of these animals.[56] Taken collectively, recent evidence suggests PRNP may be important for conducing the neurotoxic effects of soluble Aβ-oligomers and the emergent disease state of Alzheimer's.[56][57][58]
In humans, the methionine/valine polymorphism at codon 129 of PRNP (rs1799990) is most closely associated with Alzheimer's disease.[59] Variant V allele carriers (VV and MV) show a 13% decreased risk with respect to developing Alzheimer's compared to the methionine homozygote (MM). However, the protective effects of variant V carriers have been found exclusively in Caucasians. The decreased risk in V allele carriers is further limited to late-onset Alzheimer's disease only (≥ 65 years).[59] PRNP can also functionally interact with polymorphisms in two other genes implicated in Alzheimer's, PSEN1 and APOE, to compound risk for both Alzheimer's and sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease.[56] A point mutation on codon 102 of PRNP at least in part contributed to three separate patients' atypical frontotemporal dementia within the same family, suggesting a new phenotype for Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome.[56][60] The same study proposed sequencing PRNP in cases of ambiguously diagnosed dementia, as the various forms of dementia can prove challenging to differentially diagnose.[60]
Research
[edit]In 2006 the production of cattle lacking PrPC form of the major prion protein (PrP) protein was reported which were resistant to prion propagation with no apparent developmental abnormalities. Besides the study of bovine products free of prion proteins another use could be so that human pharmaceuticals can be made in their blood without the danger that those products might get contaminated with the infectious agent that causes mad cow.[61][62]
Interactions
[edit]A strong interaction exists between PrP and the cochaperone Hop (Hsp70/Hsp90 organizing protein; also called STI1 (Stress-induced protein 1)).[63][64]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000171867 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000079037 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Kretzschmar HA, Stowring LE, Westaway D, Stubblebine WH, Prusiner SB, Dearmond SJ (August 1986). "Molecular cloning of a human prion protein cDNA". DNA. 5 (4): 315–324. doi:10.1089/dna.1986.5.315. PMID 3755672.
- ^ Sparkes RS, Simon M, Cohn VH, Fournier RE, Lem J, Klisak I, et al. (October 1986). "Assignment of the human and mouse prion protein genes to homologous chromosomes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 83 (19): 7358–7362. Bibcode:1986PNAS...83.7358S. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.19.7358. PMC 386716. PMID 3094007.
- ^ Liao YC, Lebo RV, Clawson GA, Smuckler EA (July 1986). "Human prion protein cDNA: molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and biological implications". Science. 233 (4761): 364–367. Bibcode:1986Sci...233..364L. doi:10.1126/science.3014653. PMID 3014653.
- ^ Robakis NK, Devine-Gage EA, Jenkins EC, Kascsak RJ, Brown WT, Krawczun MS, Silverman WP (October 1986). "Localization of a human gene homologous to the PrP gene on the p arm of chromosome 20 and detection of PrP-related antigens in normal human brain". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 140 (2): 758–765. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(86)90796-5. PMID 2877664.
- ^ Prusiner SB (May 2001). "Shattuck lecture--neurodegenerative diseases and prions". The New England Journal of Medicine. 344 (20): 1516–1526. doi:10.1056/NEJM200105173442006. PMID 11357156.
- ^ Weissmann C (November 2004). "The state of the prion". Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 2 (11): 861–871. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1025. PMID 15494743. S2CID 20992257.
- ^ a b Zomosa-Signoret V, Arnaud JD, Fontes P, Alvarez-Martinez MT, Liautard JP (2008). "Physiological role of the cellular prion protein". Veterinary Research. 39 (4): 9. doi:10.1051/vetres:2007048. PMID 18073096.
- ^ Damberger FF, Christen B, Pérez DR, Hornemann S, Wüthrich K (October 2011). "Cellular prion protein conformation and function". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (42): 17308–17313. Bibcode:2011PNAS..10817308D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1106325108. PMC 3198368. PMID 21987789.
- ^ Schätzl HM, Da Costa M, Taylor L, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB (January 1995). "Prion protein gene variation among primates". Journal of Molecular Biology. 245 (4): 362–374. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1994.0030. PMID 7837269.
- ^ Chesebro B, Trifilo M, Race R, Meade-White K, Teng C, LaCasse R, et al. (June 2005). "Anchorless prion protein results in infectious amyloid disease without clinical scrapie". Science. 308 (5727): 1435–1439. Bibcode:2005Sci...308.1435C. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.401.781. doi:10.1126/science.1110837. PMID 15933194. S2CID 10064966.
- ^ Barrette I, Poisson G, Gendron P, Major F (February 2001). "Pseudoknots in prion protein mRNAs confirmed by comparative sequence analysis and pattern searching". Nucleic Acids Research. 29 (3): 753–758. doi:10.1093/nar/29.3.753. PMC 30388. PMID 11160898.
- ^ a b c d e f Linden R, Martins VR, Prado MA, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Brentani RR (April 2008). "Physiology of the prion protein". Physiological Reviews. 88 (2): 673–728. doi:10.1152/physrev.00007.2007. PMID 18391177.
- ^ a b Prčina M, Kontseková E, Novák M (June 2015). "Prion protein prevents heavy metals overloading of cells and thus protects them against their toxicity". Acta Virologica. 59 (2): 179–184. doi:10.4149/av_2015_02_179. PMID 26104335.
- ^ Brown DR, Clive C, Haswell SJ (January 2001). "Antioxidant activity related to copper binding of native prion protein". Journal of Neurochemistry. 76 (1): 69–76. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00009.x. PMID 11145979. S2CID 45647133.
- ^ Kanaani J, Prusiner SB, Diacovo J, Baekkeskov S, Legname G (December 2005). "Recombinant prion protein induces rapid polarization and development of synapses in embryonic rat hippocampal neurons in vitro". Journal of Neurochemistry. 95 (5): 1373–1386. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03469.x. PMID 16313516. S2CID 24329326.
- ^ Ross CA, Poirier MA (July 2004). "Protein aggregation and neurodegenerative disease". Nature Medicine. 10 (7 Suppl): S10 – S17. doi:10.1038/nm1066. PMID 15272267. S2CID 205383483.
- ^ Riek R, Hornemann S, Wider G, Glockshuber R, Wüthrich K (August 1997). "NMR characterization of the full-length recombinant murine prion protein, mPrP(23-231)" (PDF). FEBS Letters. 413 (2): 282–288. Bibcode:1997FEBSL.413..282R. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00920-4. PMID 9280298. S2CID 39791520.
- ^ Kraus A, Hoyt F, Schwartz CL, Hansen B, Artikis E, Hughson AG, et al. (November 2021). "High-resolution structure and strain comparison of infectious mammalian prions". Molecular Cell. 81 (21): 4540–4551.e6. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2021.08.011. PMID 34433091.
- ^ Manka SW, Zhang W, Wenborn A, Betts J, Joiner S, Saibil HR, et al. (July 2022). "2.7 Å cryo-EM structure of ex vivo RML prion fibrils". Nature Communications. 13 (1): 4004. Bibcode:2022NatCo..13.4004M. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-30457-7. PMC 9279362. PMID 35831275.
- ^ Hoyt F, Standke HG, Artikis E, Schwartz CL, Hansen B, Li K, et al. (July 2022). "Cryo-EM structure of anchorless RML prion reveals variations in shared motifs between distinct strains". Nature Communications. 13 (1): 4005. Bibcode:2022NatCo..13.4005H. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-30458-6. PMC 9279418. PMID 35831291.
- ^ Sandberg MK, Al-Doujaily H, Sharps B, Clarke AR, Collinge J (February 2011). "Prion propagation and toxicity in vivo occur in two distinct mechanistic phases". Nature. 470 (7335): 540–542. Bibcode:2011Natur.470..540S. doi:10.1038/nature09768. PMID 21350487. S2CID 4399936.
- ^ Büeler H, Aguzzi A, Sailer A, Greiner RA, Autenried P, Aguet M, Weissmann C (July 1993). "Mice devoid of PrP are resistant to scrapie". Cell. 73 (7): 1339–1347. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90360-3. PMID 8100741.
- ^ a b Aguzzi A, Baumann F, Bremer J (2008). "The prion's elusive reason for being". Annual Review of Neuroscience. 31: 439–477. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125620. PMID 18558863.
- ^ Atkinson M (October 2001). "National scrapie plan". The Veterinary Record. 149 (15): 462. PMID 11688751.
- ^ Weissmann C, Flechsig E (2003). "PrP knock-out and PrP transgenic mice in prion research". British Medical Bulletin. 66: 43–60. doi:10.1093/bmb/66.1.43. PMID 14522848.
- ^ Katamine S, Nishida N, Sugimoto T, Noda T, Sakaguchi S, Shigematsu K, et al. (December 1998). "Impaired motor coordination in mice lacking prion protein". Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology. 18 (6): 731–742. doi:10.1023/A:1020234321879. PMID 9876879. S2CID 23409873.
- ^ Nico PB, de-Paris F, Vinadé ER, Amaral OB, Rockenbach I, Soares BL, et al. (July 2005). "Altered behavioural response to acute stress in mice lacking cellular prion protein". Behavioural Brain Research. 162 (2): 173–181. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2005.02.003. PMID 15970215. S2CID 37511702.
- ^ Roesler R, Walz R, Quevedo J, de-Paris F, Zanata SM, Graner E, et al. (August 1999). "Normal inhibitory avoidance learning and anxiety, but increased locomotor activity in mice devoid of PrP(C)". Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research. 71 (2): 349–353. doi:10.1016/S0169-328X(99)00193-X. PMID 10521590.
- ^ Medori R, Tritschler HJ, LeBlanc A, Villare F, Manetto V, Chen HY, et al. (February 1992). "Fatal familial insomnia, a prion disease with a mutation at codon 178 of the prion protein gene". The New England Journal of Medicine. 326 (7): 444–449. doi:10.1056/NEJM199202133260704. PMC 6151859. PMID 1346338.
- ^ Cagampang FR, Whatley SA, Mitchell AL, Powell JF, Campbell IC, Coen CW (1999). "Circadian regulation of prion protein messenger RNA in the rat forebrain: a widespread and synchronous rhythm". Neuroscience. 91 (4): 1201–1204. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(99)00092-5. PMID 10391428. S2CID 42892475.
- ^ Criado JR, Sánchez-Alavez M, Conti B, Giacchino JL, Wills DN, Henriksen SJ, et al. (2005). "Mice devoid of prion protein have cognitive deficits that are rescued by reconstitution of PrP in neurons". Neurobiology of Disease. 19 (1–2): 255–265. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2005.01.001. PMID 15837581. S2CID 2618712.
- ^ Balducci C, Beeg M, Stravalaci M, Bastone A, Sclip A, Biasini E, et al. (February 2010). "Synthetic amyloid-beta oligomers impair long-term memory independently of cellular prion protein". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (5): 2295–2300. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107.2295B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0911829107. PMC 2836680. PMID 20133875.
- ^ Coitinho AS, Freitas AR, Lopes MH, Hajj GN, Roesler R, Walz R, et al. (December 2006). "The interaction between prion protein and laminin modulates memory consolidation". The European Journal of Neuroscience. 24 (11): 3255–3264. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05156.x. PMID 17156386. S2CID 17164351.
- ^ Shorter J, Lindquist S (June 2005). "Prions as adaptive conduits of memory and inheritance". Nature Reviews. Genetics. 6 (6): 435–450. doi:10.1038/nrg1616. PMID 15931169. S2CID 5575951.
- ^ Papassotiropoulos A, Wollmer MA, Aguzzi A, Hock C, Nitsch RM, de Quervain DJ (August 2005). "The prion gene is associated with human long-term memory". Human Molecular Genetics. 14 (15): 2241–2246. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi228. PMID 15987701.
- ^ Del Bo R, Comi GP, Giorda R, Crimi M, Locatelli F, Martinelli-Boneschi F, et al. (June 2003). "The 129 codon polymorphism of the prion protein gene influences earlier cognitive performance in Down syndrome subjects". Journal of Neurology. 250 (6): 688–692. doi:10.1007/s00415-003-1057-5. PMID 12796830. S2CID 21049364.
- ^ Berr C, Richard F, Dufouil C, Amant C, Alperovitch A, Amouyel P (September 1998). "Polymorphism of the prion protein is associated with cognitive impairment in the elderly: the EVA study". Neurology. 51 (3): 734–737. doi:10.1212/wnl.51.3.734. PMID 9748018. S2CID 11352163.
- ^ Croes EA, Dermaut B, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Van den Broeck M, Cruts M, Breteler MM, et al. (August 2003). "Early cognitive decline is associated with prion protein codon 129 polymorphism". Annals of Neurology. 54 (2): 275–276. doi:10.1002/ana.10658. PMID 12891686. S2CID 31538672.
- ^ Kachiwala SJ, Harris SE, Wright AF, Hayward C, Starr JM, Whalley LJ, Deary IJ (September 2005). "Genetic influences on oxidative stress and their association with normal cognitive ageing". Neuroscience Letters. 386 (2): 116–120. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.05.067. PMID 16023289. S2CID 23642220.
- ^ Herms J, Tings T, Gall S, Madlung A, Giese A, Siebert H, et al. (October 1999). "Evidence of presynaptic location and function of the prion protein". The Journal of Neuroscience. 19 (20): 8866–8875. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-20-08866.1999. PMC 6782778. PMID 10516306.
- ^ Kardos J, Kovács I, Hajós F, Kálmán M, Simonyi M (August 1989). "Nerve endings from rat brain tissue release copper upon depolarization. A possible role in regulating neuronal excitability". Neuroscience Letters. 103 (2): 139–144. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(89)90565-X. PMID 2549468. S2CID 24917999.
- ^ Bailey CH, Kandel ER, Si K (September 2004). "The persistence of long-term memory: a molecular approach to self-sustaining changes in learning-induced synaptic growth". Neuron. 44 (1): 49–57. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.09.017. PMID 15450159. S2CID 2637074.
- ^ Barco A, Bailey CH, Kandel ER (June 2006). "Common molecular mechanisms in explicit and implicit memory". Journal of Neurochemistry. 97 (6): 1520–1533. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03870.x. PMID 16805766. S2CID 26307975.
- ^ Laurén J, Gimbel DA, Nygaard HB, Gilbert JW, Strittmatter SM (February 2009). "Cellular prion protein mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity by amyloid-beta oligomers". Nature. 457 (7233): 1128–1132. Bibcode:2009Natur.457.1128L. doi:10.1038/nature07761. PMC 2748841. PMID 19242475.
- ^ Isaacs JD, Jackson GS, Altmann DM (October 2006). "The role of the cellular prion protein in the immune system". Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 146 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03194.x. PMC 1809729. PMID 16968391.
- ^ Castilla J, Hetz C, Soto C (June 2004). "Molecular mechanisms of neurotoxicity of pathological prion protein". Current Molecular Medicine. 4 (4): 397–403. doi:10.2174/1566524043360654. PMID 15354870.
- ^ Kovács GG, Trabattoni G, Hainfellner JA, Ironside JW, Knight RS, Budka H (November 2002). "Mutations of the prion protein gene phenotypic spectrum". Journal of Neurology. 249 (11): 1567–1582. doi:10.1007/s00415-002-0896-9. PMID 12420099. S2CID 22688729.
- ^ Collins S, McLean CA, Masters CL (September 2001). "Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome,fatal familial insomnia, and kuru: a review of these less common human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies". Journal of Clinical Neuroscience. 8 (5): 387–397. doi:10.1054/jocn.2001.0919. PMID 11535002. S2CID 31976428.
- ^ Montagna P, Gambetti P, Cortelli P, Lugaresi E (March 2003). "Familial and sporadic fatal insomnia". The Lancet. Neurology. 2 (3): 167–176. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(03)00323-5. PMID 12849238. S2CID 20822956.
- ^ Mead S, Whitfield J, Poulter M, Shah P, Uphill J, Campbell T, et al. (November 2009). "A novel protective prion protein variant that colocalizes with kuru exposure". The New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (21): 2056–2065. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0809716. PMID 19923577.
- "Brain disease 'resistance gene' evolves in Papua New Guinea community; could offer insights into CJD". ScienceDaily (Press release). November 21, 2009.
- ^ Hwang D, Lee IY, Yoo H, Gehlenborg N, Cho JH, Petritis B, et al. (2009). "A systems approach to prion disease". Molecular Systems Biology. 5 (1): 252. doi:10.1038/msb.2009.10. PMC 2671916. PMID 19308092.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Laurén J (2014). "Cellular prion protein as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease". Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 38 (2): 227–244. doi:10.3233/JAD-130950. PMID 23948943.
- ^ a b c d e Zhou J, Liu B (May 2013). "Alzheimer's disease and prion protein". Intractable & Rare Diseases Research. 2 (2): 35–44. doi:10.5582/irdr.2013.v2.2.35. PMC 4204584. PMID 25343100.
- ^ a b c Laurén J, Gimbel DA, Nygaard HB, Gilbert JW, Strittmatter SM (February 2009). "Cellular prion protein mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity by amyloid-beta oligomers". Nature. 457 (7233): 1128–1132. Bibcode:2009Natur.457.1128L. doi:10.1038/nature07761. PMC 2748841. PMID 19242475.
- ^ a b He J, Li X, Yang J, Huang J, Fu X, Zhang Y, Fan H (March 2013). "The association between the methionine/valine (M/V) polymorphism (rs1799990) in the PRNP gene and the risk of Alzheimer disease: an update by meta-analysis". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 326 (1–2): 89–95. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2013.01.020. PMID 23399523. S2CID 31070331.
- ^ a b Giovagnoli AR, Di Fede G, Aresi A, Reati F, Rossi G, Tagliavini F (December 2008). "Atypical frontotemporal dementia as a new clinical phenotype of Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease with the PrP-P102L mutation. Description of a previously unreported Italian family". Neurological Sciences. 29 (6): 405–410. doi:10.1007/s10072-008-1025-z. PMID 19030774. S2CID 20553167.
- ^ Weiss R (1 January 2007). "Scientists Announce Mad Cow Breakthrough". The Washington Post. Retrieved 1 January 2007.
- ^ Richt JA, Kasinathan P, Hamir AN, Castilla J, Sathiyaseelan T, Vargas F, et al. (January 2007). "Production of cattle lacking prion protein". Nature Biotechnology. 25 (1): 132–138. doi:10.1038/nbt1271. PMC 2813193. PMID 17195841.
- ^ Americo TA, Chiarini LB, Linden R (June 2007). "Signaling induced by hop/STI-1 depends on endocytosis". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 358 (2): 620–625. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.04.202. PMID 17498662.
- ^ Zanata SM, Lopes MH, Mercadante AF, Hajj GN, Chiarini LB, Nomizo R, et al. (July 2002). "Stress-inducible protein 1 is a cell surface ligand for cellular prion that triggers neuroprotection". The EMBO Journal. 21 (13): 3307–3316. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf325. PMC 125391. PMID 12093732.
External links
[edit]- PRNP (PrP) gene at GeneCard
- PRNP+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Susan Lindquist's Seminar: "The Surprising World of Prion Biology"